Warm-up:
Fred is conducting a laser experiment on a very, very, very fast train. He attaches a mirror to the roof of the train car and shines a quick pulse of laser light directly upward at the mirror. Hank is standing still outside the train. The train car is made of glass, so Hank can see the whole thing.
The pulse of laser light goes up, reflects off of the mirror, and then goes back down to the floor. There's enough dust in the air to make the laser pulse visible.
1) If Fred and Hank were to draw the laser pulse's "flight path" (as each of them sees it), what would each of them draw?
2) Who would see light travel a greater distance?
3) Assuming that the speed of the laser light is the same for both observers, who sees it travel for the longest amount of time?

Today:
- Check/review final exam review packets Answer Key**#16 is wrong. The answer should be I, not C.
- Work on notecards
Homework:
- Prepare for the exam.
- On exam day, bring something to do when you are finished. You will finish early. The test is only 40-50 multiple choice and 5-10 short answer.. You can't leave early, go the the cafeteria, go to the library, etc.
Warm-up: Some more review questions...
1. Which produces clouds and rain -- sinking air or rising air?
2. What causes winds?
3. What type of pressure belts create deserts?
4. Give one reason why the Earth is hot on the inside.
5. At divergent plate boundaries, are there rising mantle currents or sinking mantle currents?
6. What type of lava can be found in a volcano at an ocean/continent convergent plate boundary -- mafic, felsic, or both?
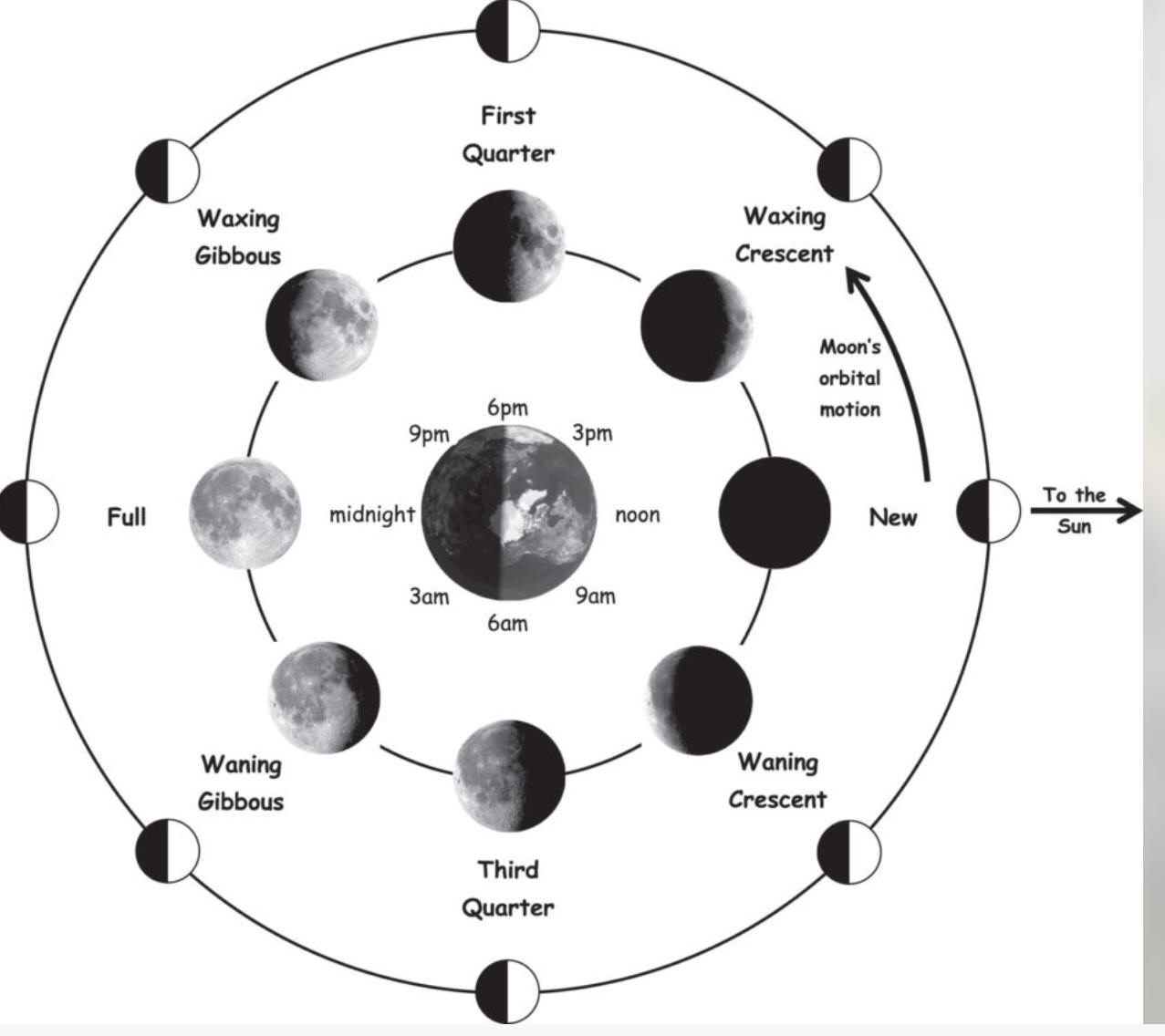
7. How many weeks after a full moon does the next new moon arrive?
8. By looking at the moon, how can you tell if moon is waxing or waning? What do waxing and waning mean?
Today:
- Return Quizzes and other papers
- Final exam review work time
Homework:
- Final exam review packets are due on Thursday.
Warm-up: Some review
1. Where, in the United States, is there a famous transform plate boundary?
2. Which way does a comet's tail point?
3. What is the Sun's primary fuel?
4. What keeps planets from flying away from the Sun, and what keeps them from falling into the Sun?
5. What's the name of the Earth layer between the crust and the outer core?
6. What's the word for "turning from a gas to a liquid?"
7. When we see clouds, which of the following are we not seeing: solid water, liquid water, water vapor (gas).
Today:
- Quiz
- Review for final?
- 5"x8" note card (both sides ) or one side of a sheet ofcopy paper.
- 40-50 Multiple choice
- 5-10 short answer
- +5 points for completing the review -- if completed by the beginning of class on Thursday
- Play games?
Homework:
- Prepare for the final exam
Warm Up:
A positive feedback loop occurs when an effect increases the cause that created the effect. A positive feedback loop causes change and instability.
Negative feedback occurs when an effect decreases the cause that created the effect. Negative feedback results in stability.
1. What type of feedback is microphone feedback? How does it work?
2. Which of these is an example of positive feedback, and which is negative?
A) A room gets hotter. The thermostat senses this and turns off the heater, causing the room to get cooler.
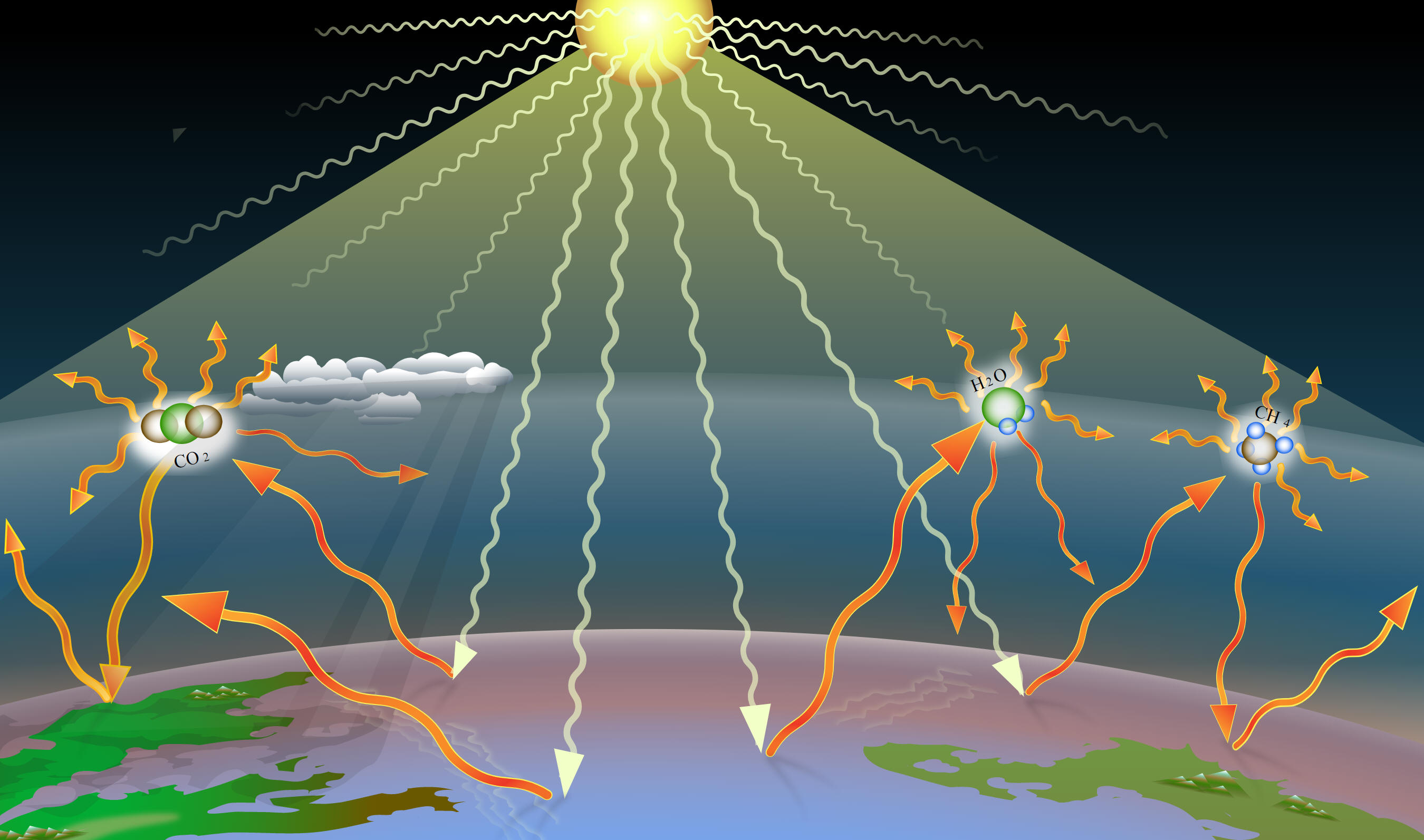
B) The Earth gets hotter. This melts snow. As the snow disappears, the darker ground below is better able to absorb sunlight, causing the Earth to get hotter.
3. Methane is a powerful greenhouse gas, and there is a lot of methane trapped beneath frozen permafrost. How might this cause a positive or negative feedback loop.
Today:
- Discuss Projects
- Return grading sheets
-
What to do -- many have not been submitted. Unless you
have discussed an extension with me, if you haven't submitted
anything, your grade is zero.
- If you haven't turned it in, turn it in.
- If you don't like your grade, fix your project and resubmit it. You may ony do this once.
- Prepare for a Climate Change Quiz
- Together, go throughMr. Stapleton's climate change slides
- As we go, add your answers to this climate change quiz template. I will be adding mine.
- Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class. -- The class 76 video is actually from a few years ago, but it matches up well.
Homework:
- Study -- quiz next class, identical to the climate change quiz template, above.
 Class
75:
Friday,
5/24/24
Class
75:
Friday,
5/24/24Warm Up:
What is the greenhouse effect? How does it work?
Today:
- Last topic -- climate change
- Climate mapping slideshows are due today.
- Google Classroom PhET assignment
Homework:
- None
Warm Up: No warm-up today. Get right to work.
Today:
- Climate project work time
Homework:
- Climate mapping slideshows are due on Friday.
Warm Up:
Sadly, you're going to run out of free Screencastify videos, because the school does not have a Screencastify license. So, we're going to be using the WeVideo app instead, because the school does have a WeVideo license.
The major differences (vs Screencastify): instead of cropping, drag the picture to move and resize; use the EWSD account/license.
Right now, for practice, lets use WeVideo to make and edit a video, at put it in your slideshow. Get out your chromebook...
Today:
- Climate Mapping Project work time.
- If you don't know how to draw climate features, watch class videos on the class Youtube Playlist
- These are the steps...
- Draw your new climate feature.
- Plan what you're going to say.
- Make your video.
- Edit your video.
- Insert your video into the slideshow.
- Move on to the next slide.
- Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
Homework:
- Climate mapping slideshows are due on Friday.
 Class
72:
Thursday,
5/16/24
Class
72:
Thursday,
5/16/24Warm Up:
How can you make and edit a video like this one (and put it in a Google Slideshow) using your chromebook and screencastify?
Today:
- Climate Mapping Project work time
- Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
Homework:
- None
 Class
71:
Tuesday,
5/14/24
Class
71:
Tuesday,
5/14/24Warm Up:
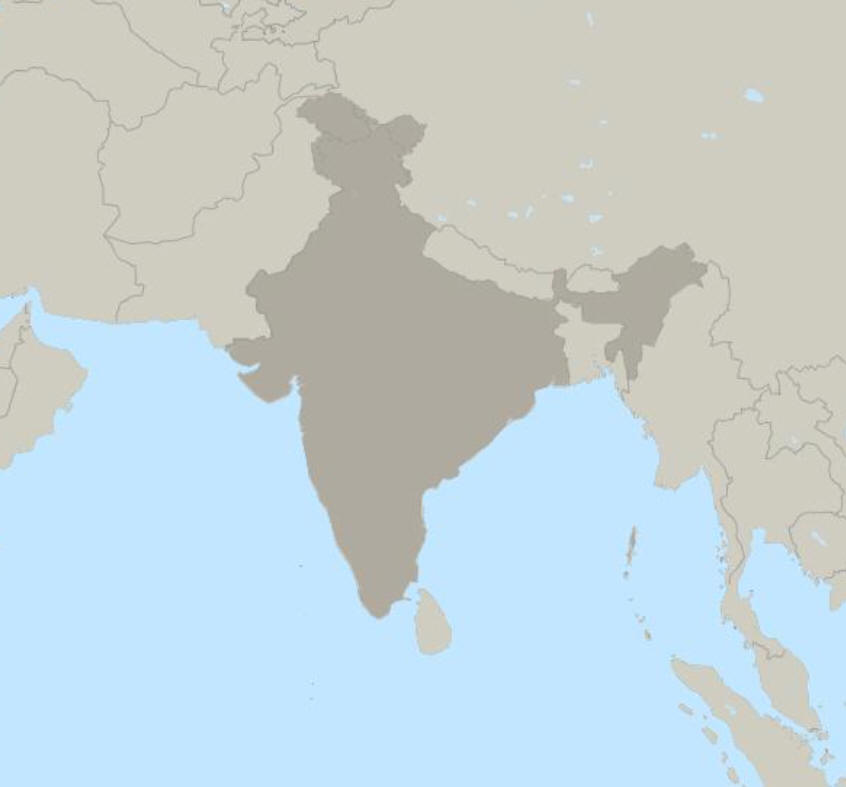
A monsoon is a "seasonally reversing wind" that can cause changes in precipitation and weather in general.
India's monsoon rains are caused by either rising air or sinking air.
1. What causes the air to rise or sink?
2. Why does that cause rain?
Today:
- Climate map drawing quiz #3! After today, if you want to retake the quz, you'll have to do it during FLEX.
- Begin the Climate Mapping Project (instead of a test)
- Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
Homework:
- None
 Class
70:
Friday,
5/10/24
Class
70:
Friday,
5/10/24Warm Up:
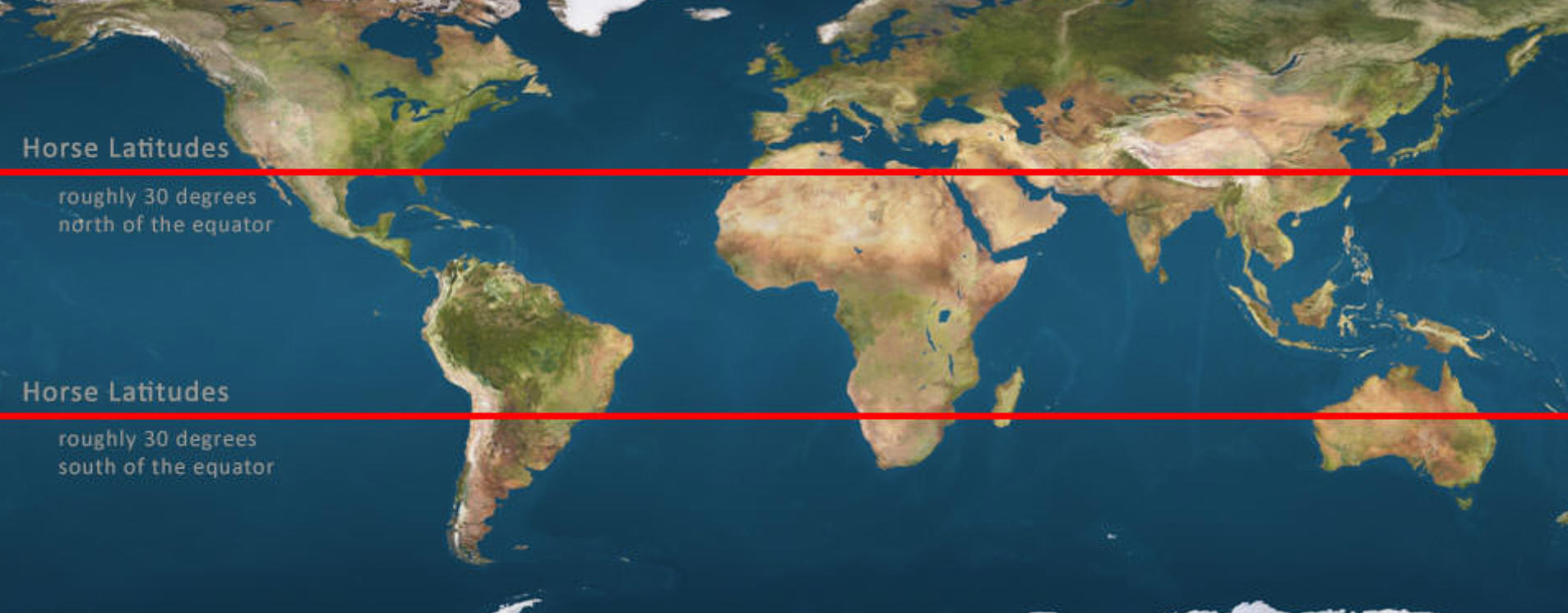
1. What are the Horse Latitudes? How did they get their name?
2. What is(are) The Doldrums? Where did the name come from? What's another name for The Doldrums?
Today:
- Go over practice quiz #2.
- Take the climate map drawing quiz. Get it graded. Go over the answers.
- Finish Meteorology Part 4 Climate Map Drawing PDF -- North America
- Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
Homework:
- Next class you will get a 2nd chance to take the climate map drawing quiz.
 Class
69:
Wednesday,
5/8/24
Class
69:
Wednesday,
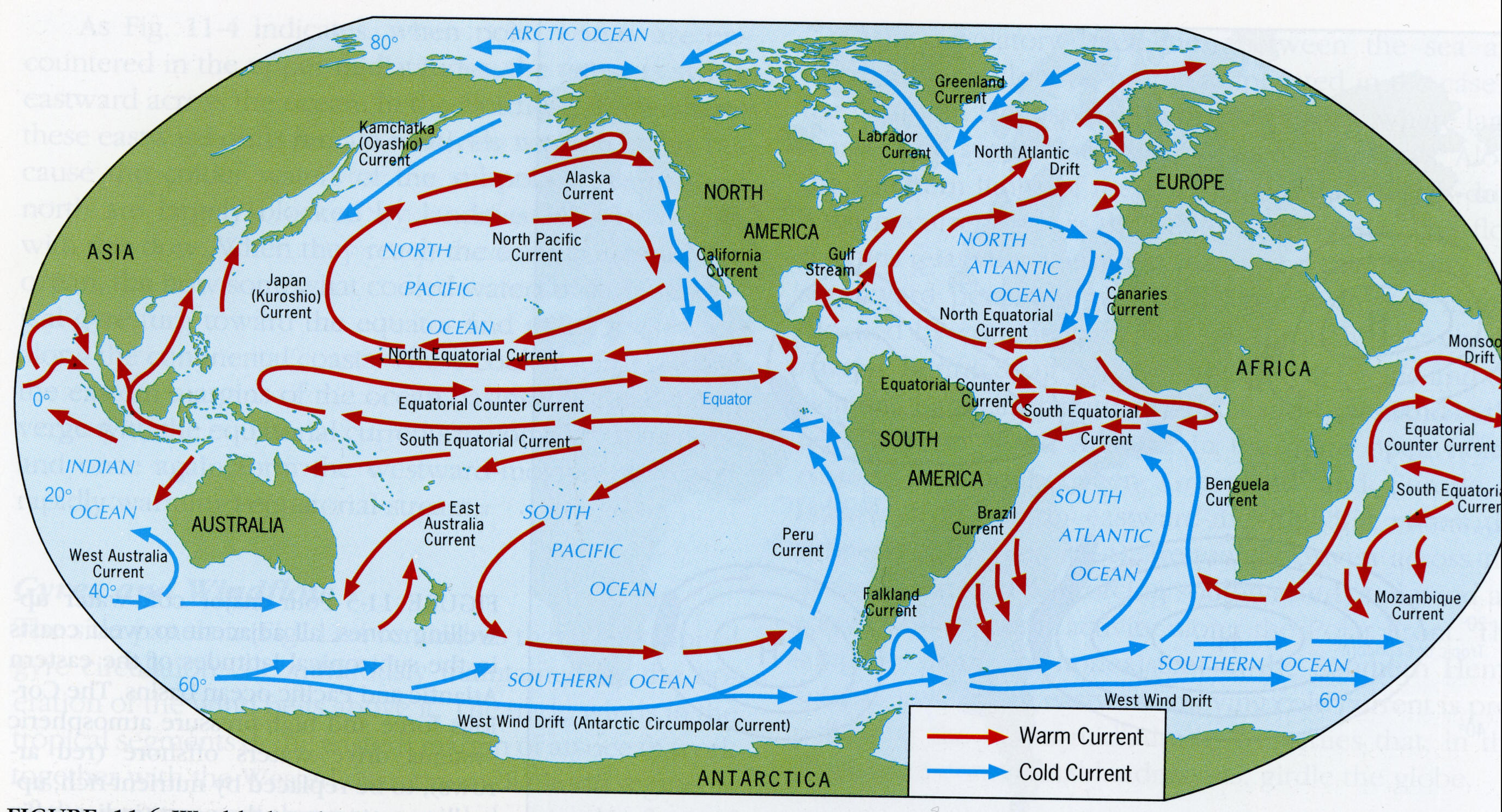
5/8/24Warm Up: What are gyres? What causes them? How can the concept of gyres help you draw ocean currents?
Today:
- Check/review homework -- go over the practice quiz.
- Hand out notes on how to draw climate maps
- Finish Meteorology Part 4 Climate Map Drawing PDF -- North America and Practice Quiz #2.
- Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
Homework:
- Practice for the quiz next class.
 Class
68:
Monday,
5/6/24
Class
68:
Monday,
5/6/24Warm Up: A Canadian company is building a compressed air "battery" to store renewable energy.
1. Why is renewable energy storage important?
2. How does it work?
3. Why is there a "heat storage" unit? -- Does this relate to rising air or sinking air (and its role in weather)?
4. What is the purpose of the water (in the cavern, shaft, and reservoir?)
Today:
- Return quizzes
- Meteorology Part 4 -- the final part: Continue Climate Map Drawing PDF Color Scans of Notes -- Australia, South America, and Africa
- Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
Homework:
- Complete Climate Mapping Practice Quiz -- Complete #1, unless we have already completed it in class. If we've already done #1, complete #2. Here's the link to the handout (you should already have it) -- Climate Map Drawing PDF.
 Class
67:
Tuesday,
5/2/24
Class
67:
Tuesday,
5/2/24Warm Up: 1. When we make a cloud in a bottle, does the cloud appear when we squeeze or when we release? Why?
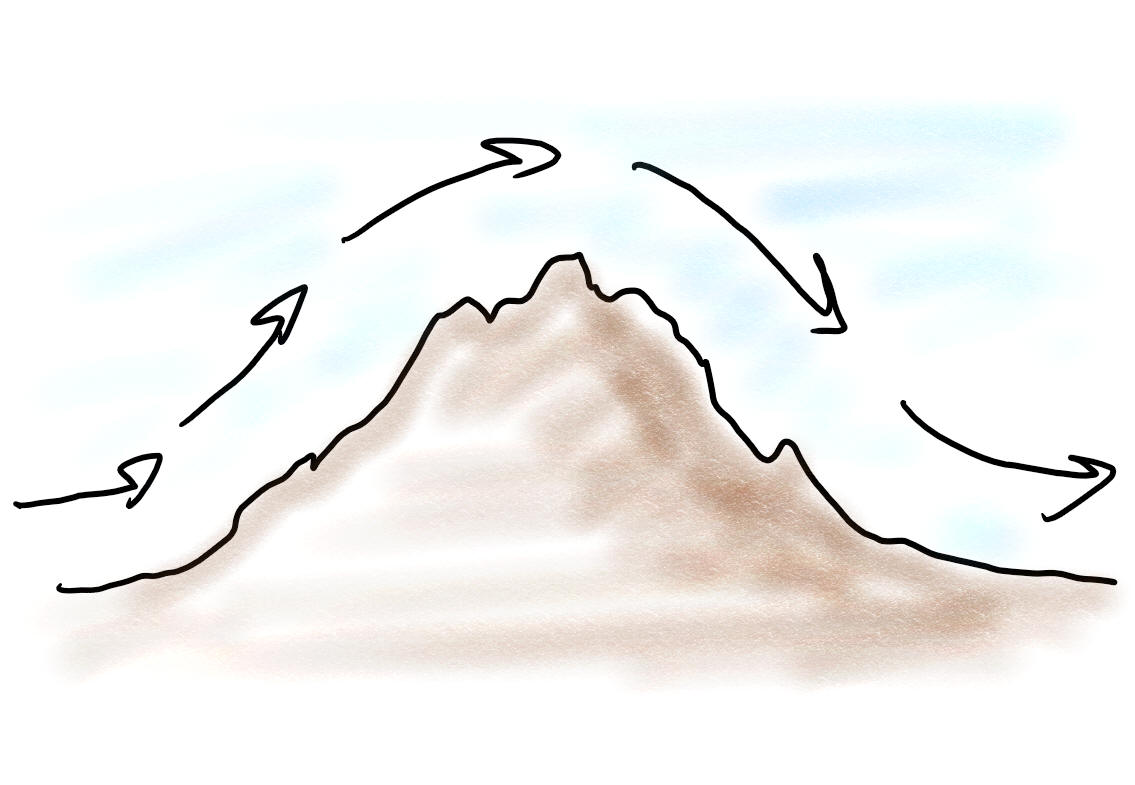
2. When winds pass over mountain ranges, which side of the mountains is wetter, and which is drier?
3. When winds pass over an ocean, which coast is wetter, and which is drier?
Today:
- Return quizzes
- Quiz over rising air, sinking air, and weather.
- Meteorology Part 4 -- the final part: Climate Map Drawing PDF
- Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
Homework:
- None
 Class
66:
Tuesday,
4/30/24
Class
66:
Tuesday,
4/30/24Warm Up: Where did this storm occur?
Today:
- Check homework -- at least one side of the practice quiz sheet.
- Quiz: drawing atmospheric circulation, pressure belts, and prevailing winds. Here's the Quiz.
- Meteorology Part 3 -- Water Cycle and Cloud Formation PDF Answer key Make a video suggesting how to study for next class' quiz.
- If there's time -- start Meteorology Part 4: Climate Map Drawing PDF
- Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
Homework:
- Study for quiz over "rising air, sinking air, and weather," from the notes. Answer key
 Class
65:
Friday,
4/19/24
Class
65:
Friday,
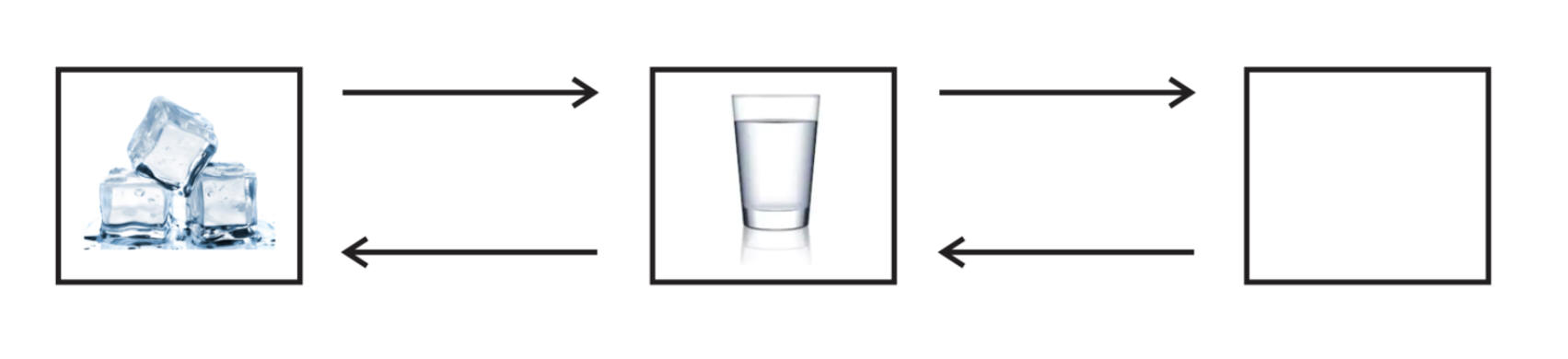
4/19/24Warm Up: The diagram on the right shows water in its three phases.
1. What are the three phases?
2. Which arrows require heat to be added to water? Which require the removal of heat?
Today:
- Return quizzes
- Finish Notes -- Meteorology Handout 2 -- Coriolis Effect and Prevailing Winds PDF
- Meteorology Part 3 -- Water Cycle and Cloud Formation PDF
- Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
Homework:
- Quiz next class (Tuesday after break). It will be exactly like this practice quiz (Meteorology Practice Quiz 2 -- PDF). Complete at least one side and check your answers with my video from class.
 Class
64:
Wednesday,
4/17/24
Class
64:
Wednesday,
4/17/24Warm Up:
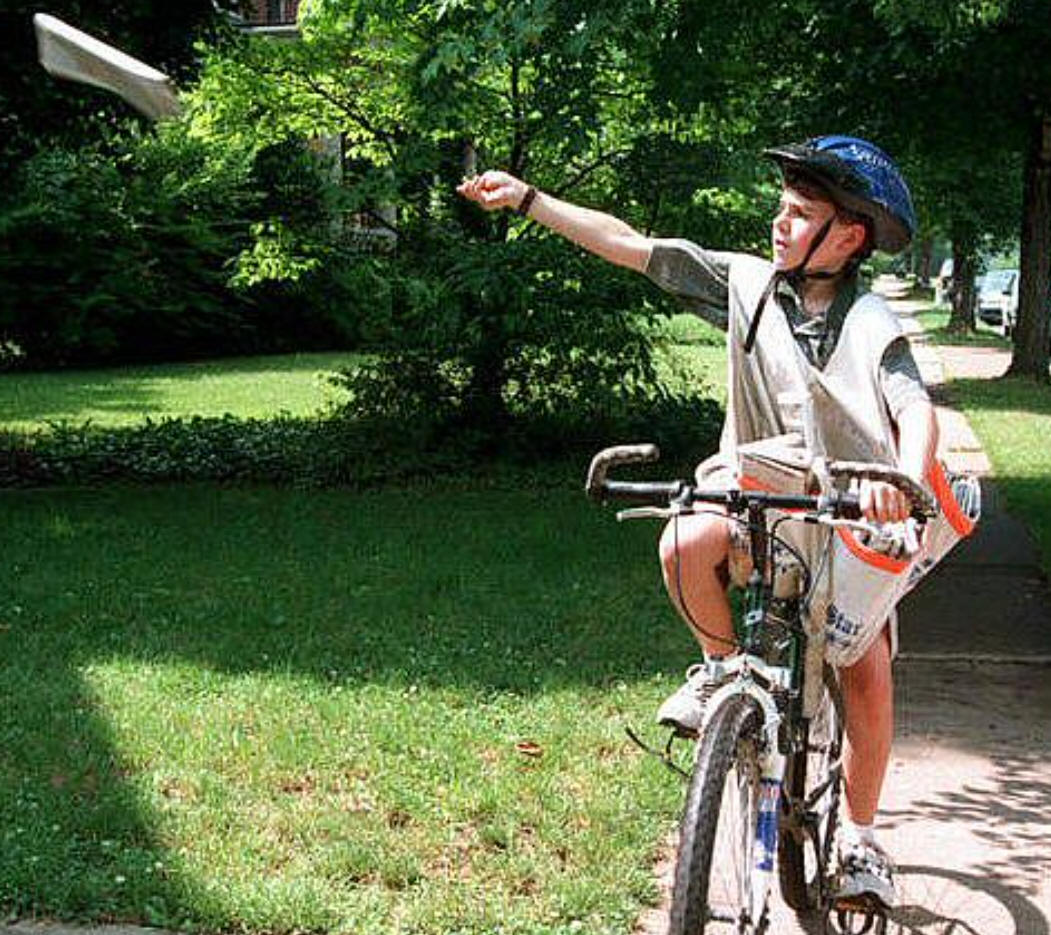
The paper deliverer throws the paper from a moving bicycle. From their point of view, where should they aim if they want the paper to land on the doorstep? Why? How does this relate to the Coriolis Effect?
Today:
- Meteorology Quiz 1: Pressure and Winds
- Finish Notes -- Meteorology Handout 2 -- Coriolis Effect and Prevailing Winds PDF
- Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
Homework:
- None
 Class
63:
Monday,
4/15/24
Class
63:
Monday,
4/15/24Warm Up:
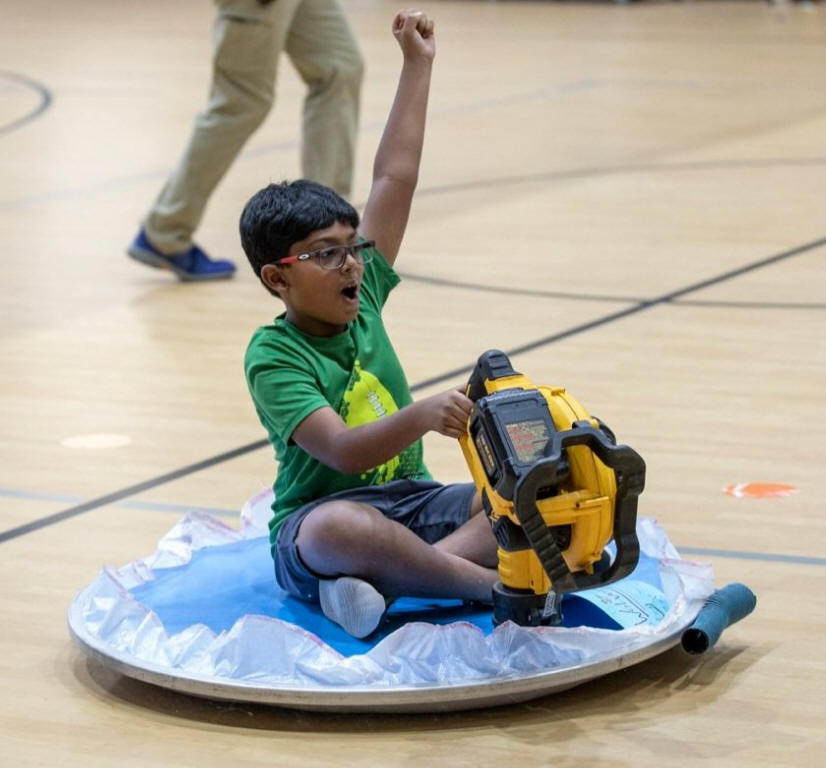
1. How do hovercrafts work?
2. How many psi are necessary to make a high school student to hover?
3. How can we measure the pressure produced by a hovercraft?
4. How high does a hovercraft hover?
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Meteorology Practice Quiz 1 PDF
- Notes -- Meteorolgy Handout 2 -- Coriolis Effect and Prevailing Winds PDF
- Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
Homework:
- Prepare for quiz next class
 Class
62:
Thursday,
4/11/24
Class
62:
Thursday,
4/11/24Warm Up:
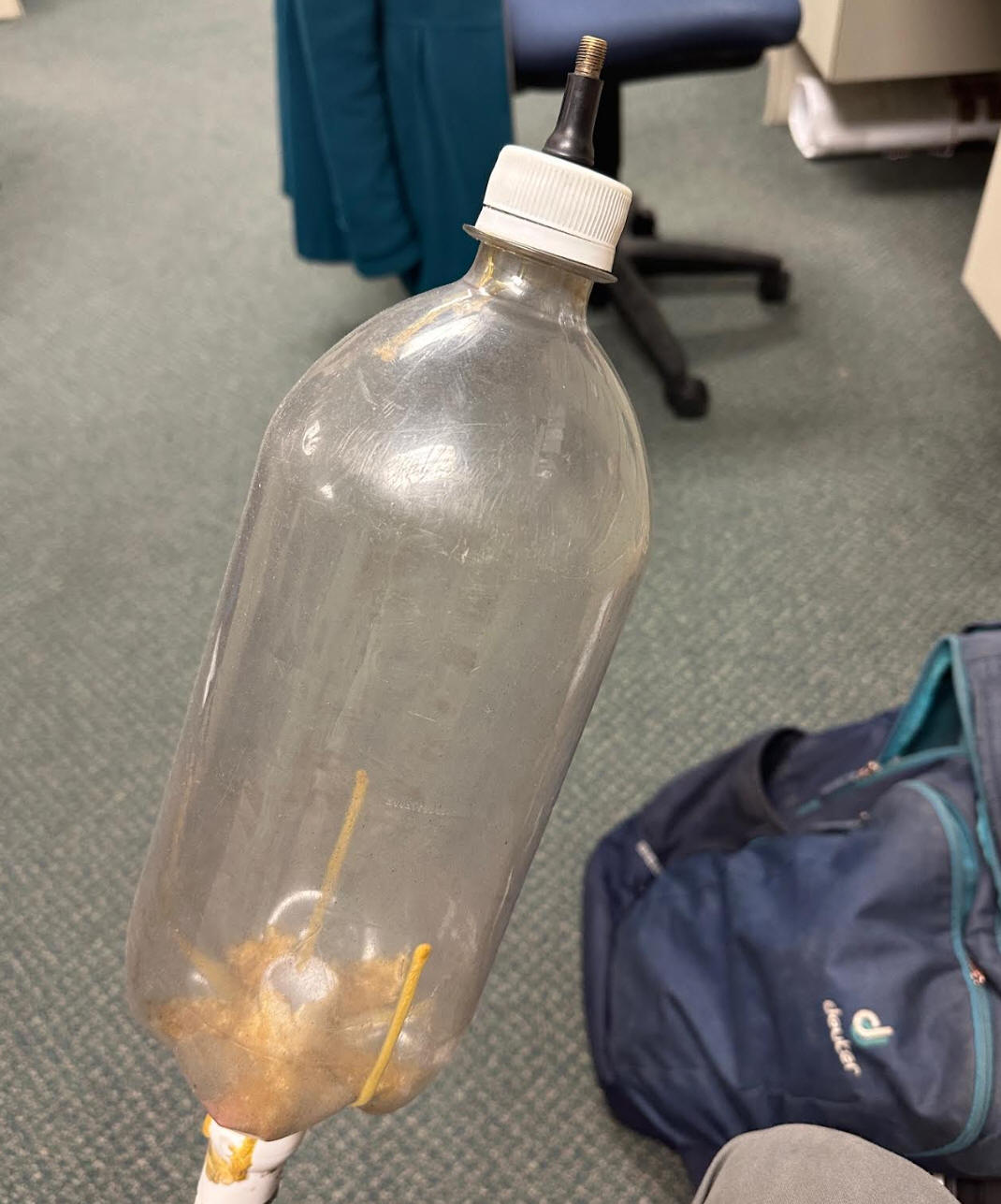
1. How much heavier will this bottle become if we pump air into it?
2. What can we do with that pressurized air?
Today:
- Check your grades in PowerSchool. Several people need to make up the Earth, Moon, Sun test. Flex tomorrow would be a good time for that.
- Finish Notes -- Meteorology Handout 1 -- Winds and Pressure PDF Answer Key
- Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
- Can students do pull-ups with suction cups?
Homework:
- Winds and Pressure Practice Questions (p. 5-6 of the handout) Answer Key (if you want to check your answers)

 Class
61:
Tuesday,
4/9/24
Class
61:
Tuesday,
4/9/24Warm Up:
1. Why is the sky blue?
2. Why are sunsets red?
3. Why didn't the sun turn red when it disappeared during the eclipse? Why did everything just get gray before dark, rather than turning golden like at a regular sunset?
4. Did anyone see anything else interesting during the eclipse?
Today:
-
Discuss the eclipse
-
Return tests
- Continue Notes -- Meteorology Handout 1 -- Winds and Pressure PDF Answer Key
- Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
-
Vacuum
packing a student
- How much pressure can you produce?
- Can you blow up a balloon under water?
Homework:
- None
 Class
60:
Friday,
4/5/24
Class
60:
Friday,
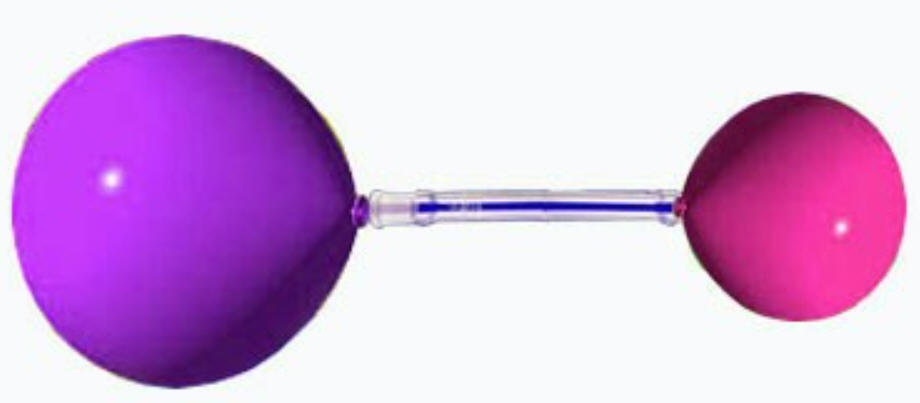
4/5/24Warm Up: If I half inflate one balloon and 1/4 inflate another, what will happen if I connect the two balloons with a straw and let air flow between them?
Today:
-
Test Retake -- you can do retake any or all of the sections (first page, middle section, last page)
- Notes -- Meteorology Handout 1 -- Winds and Pressure PDF Answer Key
- Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
-
Vacuum
packing a student
- How much pressure can you produce?
- Can you blow up a balloon under water?
Homework:
- Watch the eclipse!
 Class
59:
Wednesday,
4/3/24
Class
59:
Wednesday,
4/3/24Warm Up:
1. What causes meteor showers?
2. Why is it best to view meteors between midnight and 4AM?
3. When is the next meteor shower?
4. What's a Nor'easter?
Today:
-
Return tests.
-
More practice/review. This is a very practiceable test. How can you practice on your own?
-
Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
-
New Unit -- Meteorology (Weather and Climate)
- Change of plans -- we're starting
meteorology (weather and climate) instead of properties of
water.
Here's what's next...
- Atmospheric Pressure and Winds
- Cloud formation/Wet & Dry climates
- Coriolis Effect
- Climate Mapping
- Notes -- Meteorology Handout 1 (PDF Version) filled-in version
- Change of plans -- we're starting
meteorology (weather and climate) instead of properties of
water.
Here's what's next...
Homework:
- Prepare for the retake next class. You can retake any or all of the three parts of the test.
- More? TBD
Warm Up: Shadows don't always look like the objects that cast them.
1. How can one solid block cast a shadow with any of the shapes below?
2. What shape can cast a circular shadow, no matter how its is oriented?
3. How did question #2 help people figure out that the Earth is round?

Today:
-
If we're having a solar eclipse in one week, what is today's moon phase? Check the April 8th weather forecast.
-
Check/review homework
-
Test questions -- is there anything you want to practice before the test?
-
Test -- System of the Earth, moon, and sun
-
Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
Homework:
- None
 Class
57:
Thursday,
3/28/24
Class
57:
Thursday,
3/28/24Warm Up:
1. Let's practice identifying moon phases, times of moonrise, time of day, etc.
2. Based on what I have shared with you, you might think you could tell me the time of high tide for any moon phase. How could you do that? In reality, why doesn't it work?
3. What we can figure out is how much the times of high and low tide change every day. For example, if it's high tide right now, when will the same tide occur tomorrow? Approximately when will the other tides (high and low) occur?
Today:
-
Check/review homework -- page 1 of Practice test #1.
-
Finish practice test #1.
-
Callback reminder
-
Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
Homework:
- Finish practice test #2 and check your answers. Answer Key
- We will have the test next class, and it will be the same format as practice test #2. We can do some review before the test, so be ready to ask questions about anything that you didn't understand on the practice test.
- There will be an in-class retake offered for any section (p.1, p.2-3, or p.4) of the test.
Warm Up:
1. Has anyone seen the moon recently? What phase is it? When has it been rising?
2. During what two moon phases can we have an eclipse? How long until we reach the next one?
3. What type of eclipse can occur during each? NASA Eclipse Stuff
4. During those moon phases, why do we usually not have an eclipse?
Today:
-
Finish System of the Earth, Moon and Sun
-
Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
Homework:
- Complete page one of the practice test. Answer Key If you want help and explanations, watch the page 1 video on the class Youtube Playlist.
Warm Up:
Today:
-
Continue Earth Moon and Sun
-
Tides and eclipses
-
-
Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
Homework:
- None
 Class
54:
Tuesday,
3/19/24
Class
54:
Tuesday,
3/19/24Warm Up:
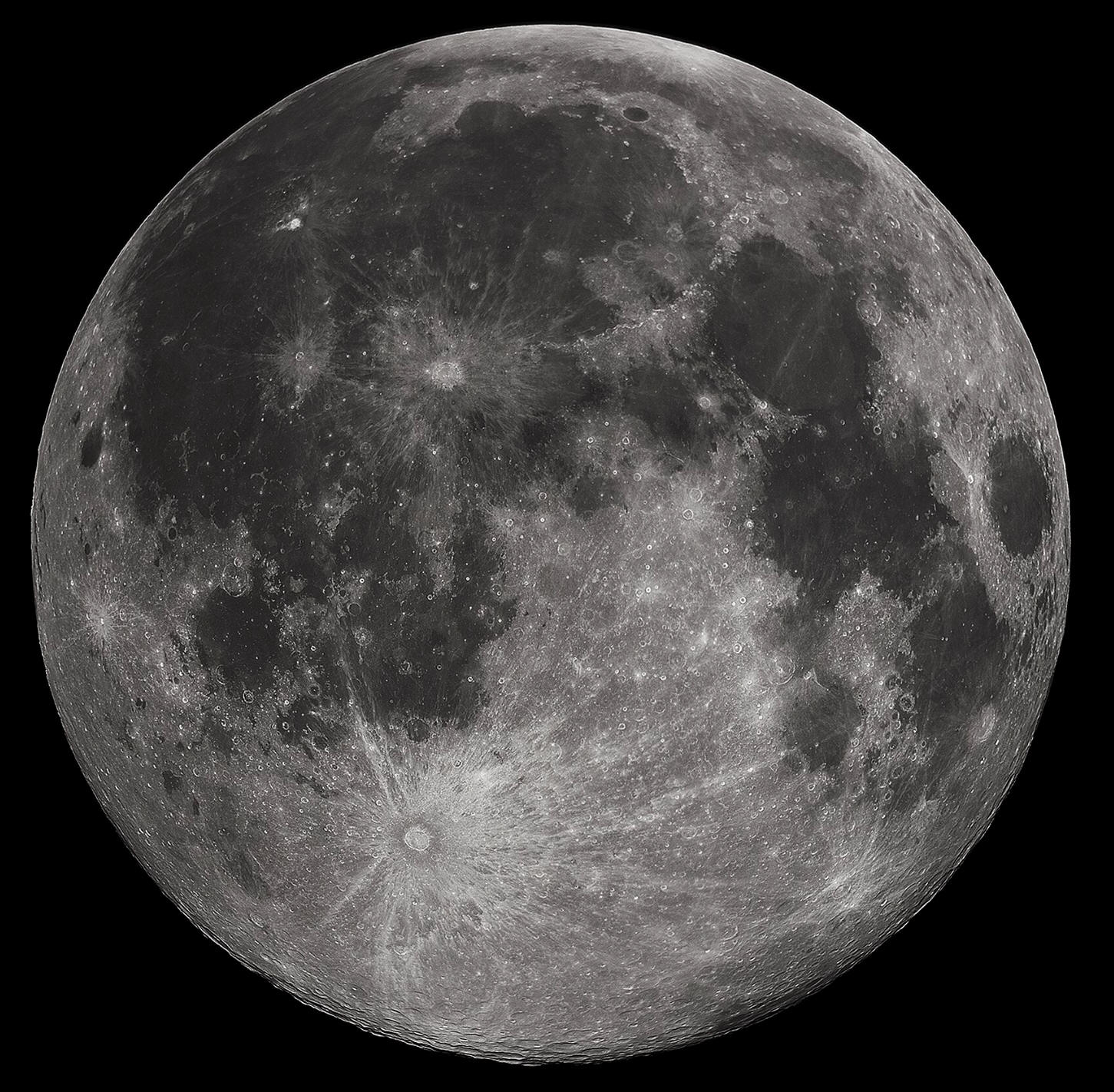
1. Why do clocks go clockwise?
2. Does the Moon rotate? Do we ever see a different side of the Moon?
3. On the diagram to the right, can you identify the rotation and revolution(s) of the Earth and Moon?

Today:
-
Check/review homework
-
System of the Earth, Moon, and Sun --
-
Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
Homework:
- Moon Phases Practice, on page 3 of today's handout
 Class
53:
Friday,
3/15/24
Class
53:
Friday,
3/15/24Warm Up:
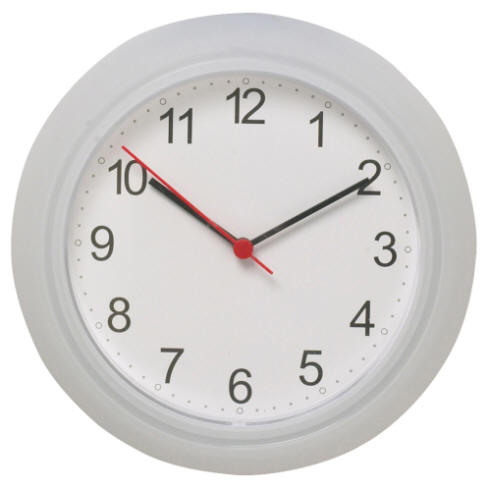
1.Why do we have time zones? 2.How many time zones are there?
3. Where is the International Date Line?
4. What happens at the International Date Line? What is its purpose?
Today:
-
Quiz -- Rock dating -- version 6
-
Quiz -- Rock Cycle
-
Notes and Practice: Begin System of Earth, Moon, and Sun
-
Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
Homework:
- Time of day practice (on the back of today's handout) Time of day Handout PDF Filled-in Version
 Class
52:
Wednesday,
3/13/24
Class
52:
Wednesday,
3/13/24Warm Up:
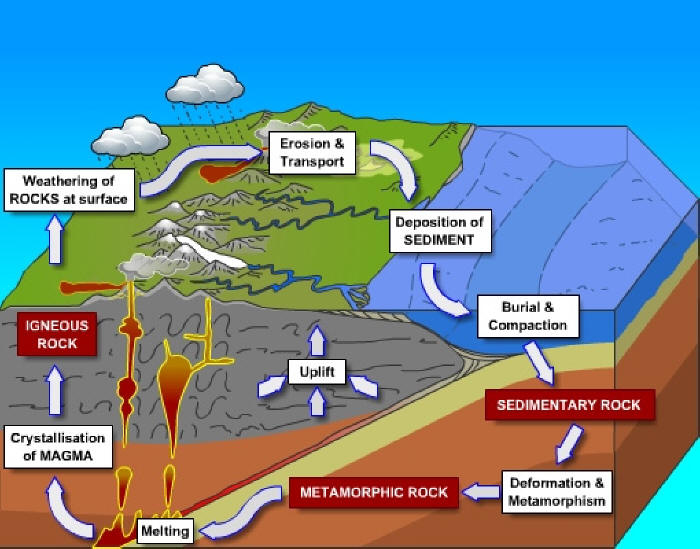
1. How is an igneous rock made?
2. How is a sedimentary rock made?
3. How is a metamorphic rock made?
Today:
-
Wrap up geology stuff and prepare to move on to the "System of the Earth, Moon, and Sun" (day/night cycles, moon phases, eclipses, tides, and maybe seasons). After that, the final unit is on climates.
-
Rock cycle review -- Another version of next class' quiz
-
Check homework -- go over Rock dating Quiz version 4 (Video)
-
One more rock dating practice quiz -- version 5
-
Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
Homework:
- Rock dating quiz next class (unless you're happy with your score)
- Rock cycle quiz next class -- just like the quiz in Google Classsroom ("Class #50, Part 2"), except that that the order will be diferent. See class 50, below, for more details. Here's another version of next class' quiz, for you to try.
Warm Up: Absolute Dating Review
1. What is a half-life? How are half-lives useful?
2. A rock sample contains 27 parent atoms and 123 daughter atoms. How many parent atoms did the rock have when it was new? What percentage of these atoms are parent atoms?
3. How many half-lives old is the rock sample from the previous question (approximately)?
Answer choices: 0-1 1-2 2-3 3-4 4-5
4. A rock sample has 30 daughter atoms and 65 parent atoms. What percentage of the atoms are parents?
5. How many half-lives old is the rock sample from the previous question (approximately)?
6. How would we determine the age of this sample, in years?
Today:
-
Rock Dating Quiz Practice
-
Rock Dating Quiz version 3 Quiz Version 4
-
Absent students, check out the class Youtube Playlist, and watch any videos from this class.
Homework:
- Finish Quiz version 4 -- unless you finished in class
 Class
50:
Wednesday,
2/23/24
Class
50:
Wednesday,
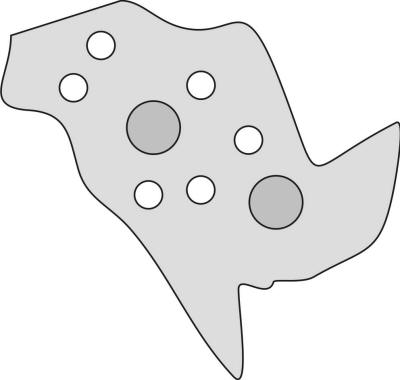
2/23/24Warm Up: The object on the right is a piece of rock. The big dots represent parent atoms in the rock, and the small dots represent daughter atoms. The half-life of the parent element is 2 million years.
1. What is the age of the rock sample, in half-lives?
2. What is the age of the rock sample, in years?
3. Does anyone in B5/6 want to try explaining this to B7/8?
Today:
-
Check/review the homework -- Google Quiz over the rock cycle
Rock dating -- Continue Absolute Dating Rock Dating Handout PDF
If you were gone, watch the video(s) and follow along in the handout on the Class YouTube Playlist.
Homework:
- None!
Warm Up: None -- Mr. Stapleton is gone today
Today:
-
Watch my rock cycle video from the early days of the pandemic.
-
Complete the "Class #50, Part 2" Google Quiz in Google Classsroom. It's on the rock cycle.
Homework:
- Finish the Google Quiz, if you haven't done it already.
Warm Up:
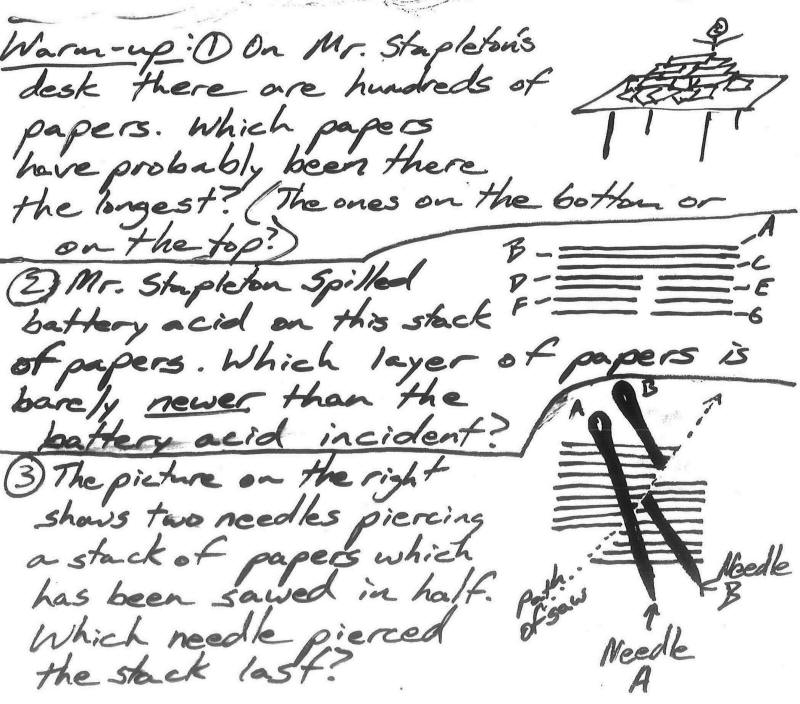
The diagrams on the right show some rock layers in two different parts of the world.
1. What do the buried fish, snail, plant, bug, and human represent?
2. Which layer is probably older, Layer S (in diagram A) or layer H (in diagram B)?
3. Which layer is probably the oldest of all? Why?
4. Which layer is probably the youngest of all? Why?
Today:
-
Test
-
Rock dating -- Start Absolute Dating Rock Dating Handout PDF
-
If you were gone, watch the video(s) and follow along in the handout on the Class YouTube Playlist.
-
Mr. Stapleton will be gone for jury duty on Wednesday. I'm not sure what sort of plan I will leave.
Homework:
- None!
Warm Up:
Today:
-
Return tests -- easy version
-
Begin Relative Dating -- Rock Dating Handout PDF
-
If you were gone, watch the 3 rock dating videos from class on the Class YouTube Playlist.
-
Homework:
- Test on Monday
- Practice/review the test preparation that we're working on in class. You can practice using the links from last class. You can check your solutions with those links. You can also watch the videos from class on the 23-24 ESS Youtube Playlist.
 Class
47:
Tuesday,
2/13/24
Class
47:
Tuesday,
2/13/24Warm Up:
What would each of these features look like from a satellite view?
A. Continent/Continent Convergent
B. Continent/Ocean Convergent
C. Continent/ Continent Divergent
D. Ocean/Ocean Convergent
E. Ocean/Ocean Divergent
F. Ocean Hotspot
G. Transform boundary
Today:
-
Return old assignments
- Prepare for the test. Finish the hardest option (bonus option) together. Make a video.
- Take a look at the test Options -- I have adjusted the possible
points.
- Hardest Version (earn up to 105%) Hardest solution
-
Medium Version (earn up to 95%)
Medium Version Diagram Here's what it looks like,
assembled --
 Medium Solution
Medium Solution -
Easier Version (earn up to 80%)
Easier
Version Diagram Here's what it looks like, assembled --
 Easier Solution
Easier Solution
- Try the easy version of the test. I will grade it and return it next class. The real test will be next Monday, but you can keep this score if you like it (though it can't be higher than 80%).
Homework:
- Practice/review the test preparation that we're working on in class. You can practice using the links above. You can check your solutions with the solution links above. You can also watch the videos from class on the 23-24 ESS Youtube Playlist.
- Test on Monday
 Class
46:
Friday,
2/9/24
Class
46:
Friday,
2/9/24Warm Up:
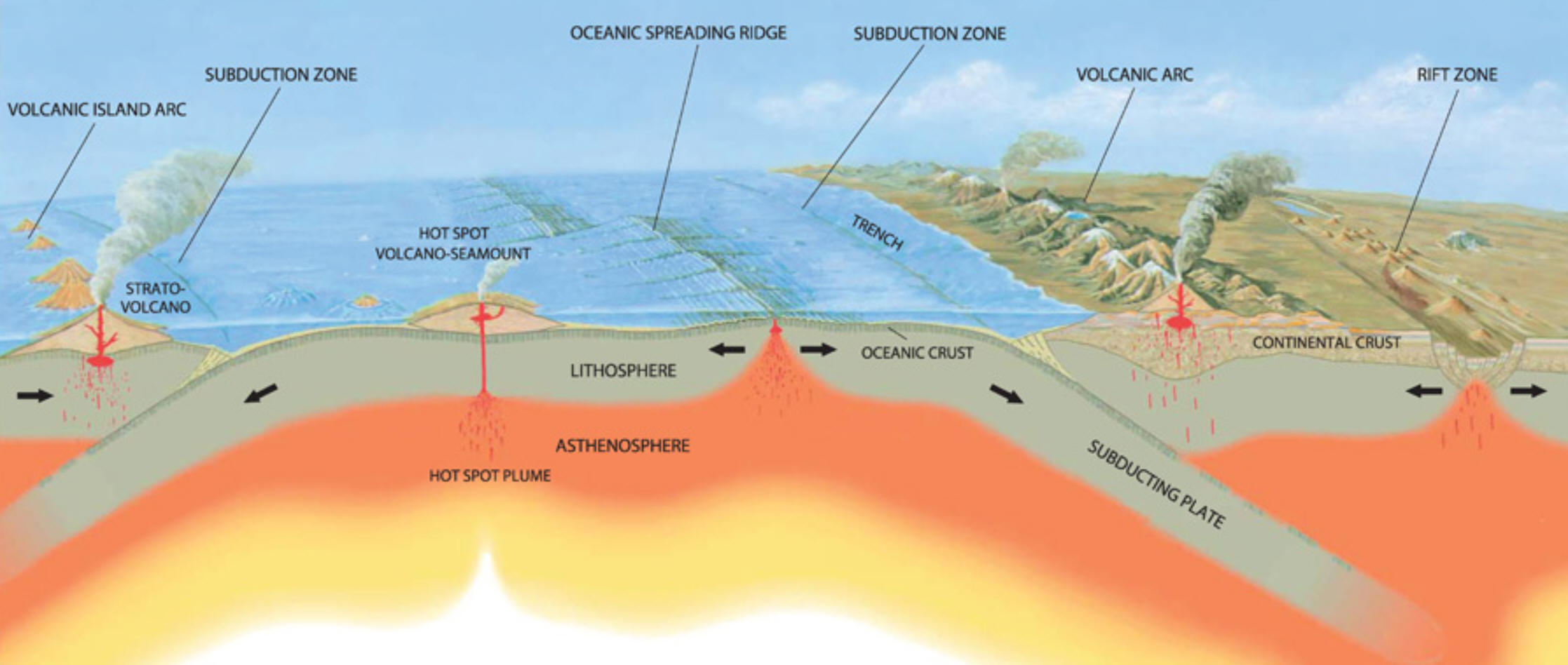
We have covered 7 different plate boundaries (or features).
1. How many can you find in this diagram?
2. How could we add the remaining one(s) to the diagram?
Today:
-
Return old quizzes
- Finish National Geographic Volcano!, and answer questions -- Questions PDF
- Prepare for the test. Complete the hardest option (bonus option) together. Make a video.
- Easier Solution; Medium Solution, Difficult solution
Homework:
- Practice/review the test preparation that we're working on in class.
 Class
45:
Wednesday,
2/7/24
Class
45:
Wednesday,
2/7/24Warm Up:
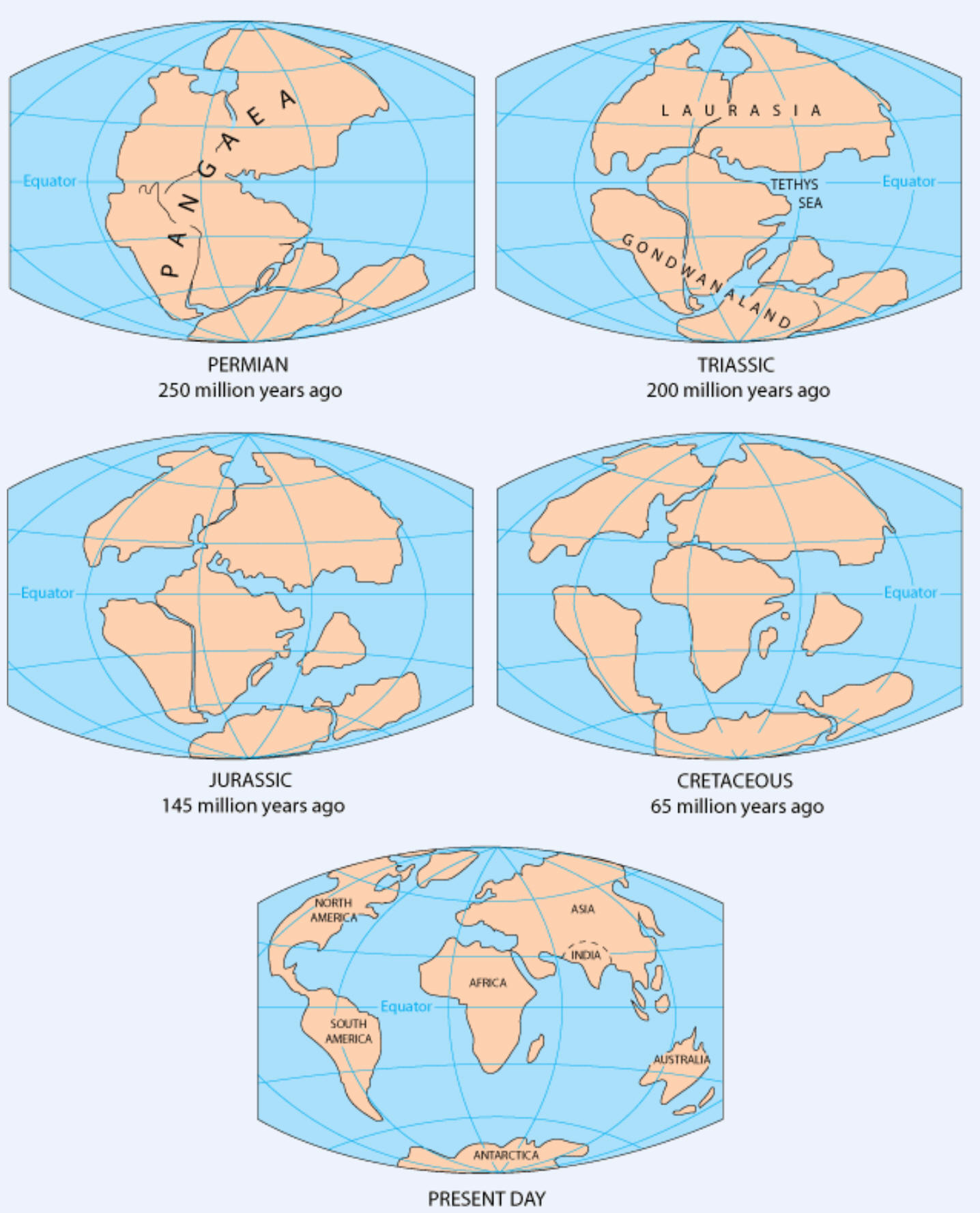
1. When did the scientific community first accept the theory of Plate Tectonics?
2. What was Pangaea?
3. What evidence first convinced the scientific community that Plate Tectonics was a valid theory?
Today:
-
Return old quizzes
-
Plate boundary quiz
- See some plate tectonics in action, in National Geographic Volcano!, and answer questions -- Questions PDF
Homework:
- None
 Class
44:
Monday,
2/5/24
Class
44:
Monday,
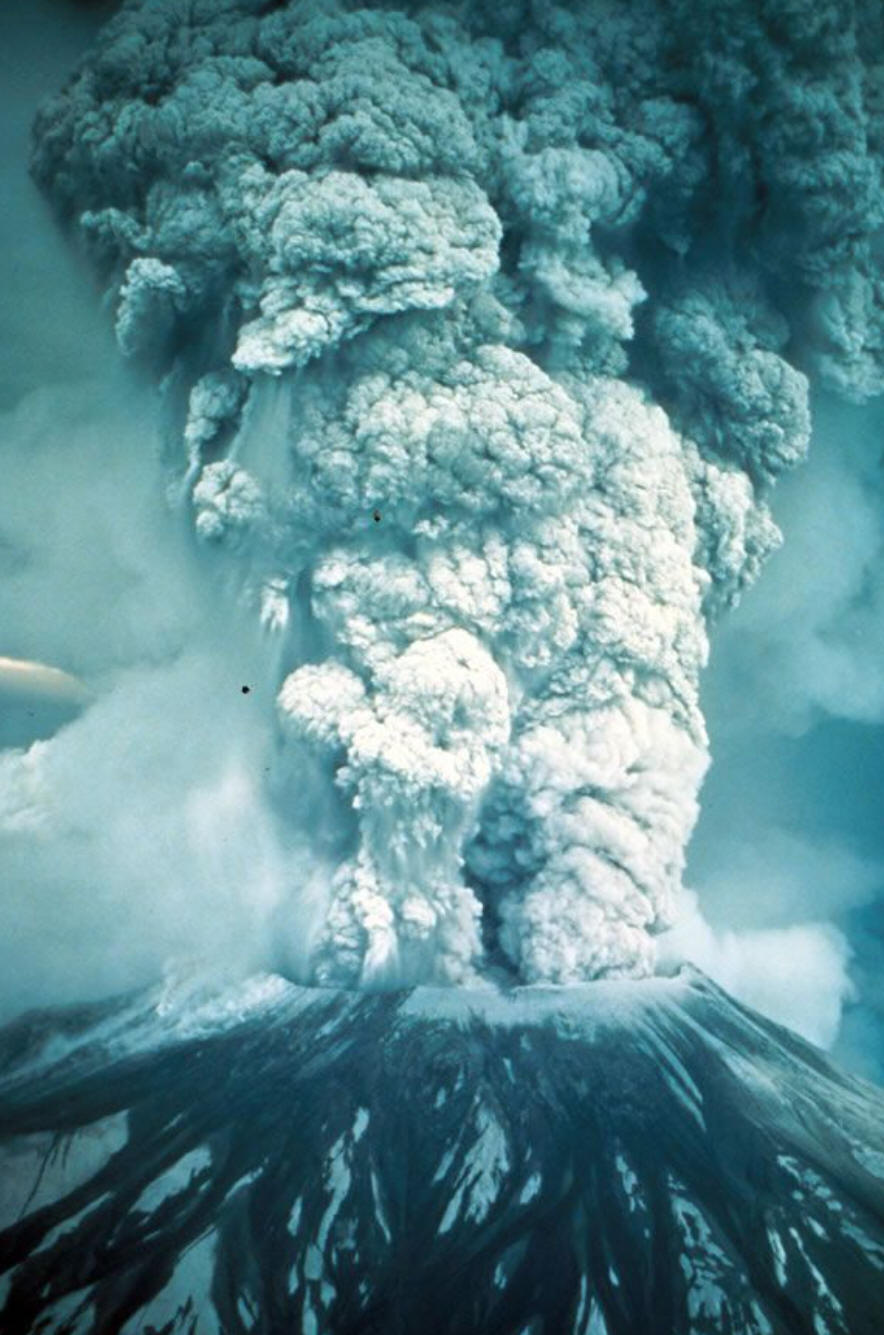
2/5/24Warm Up:
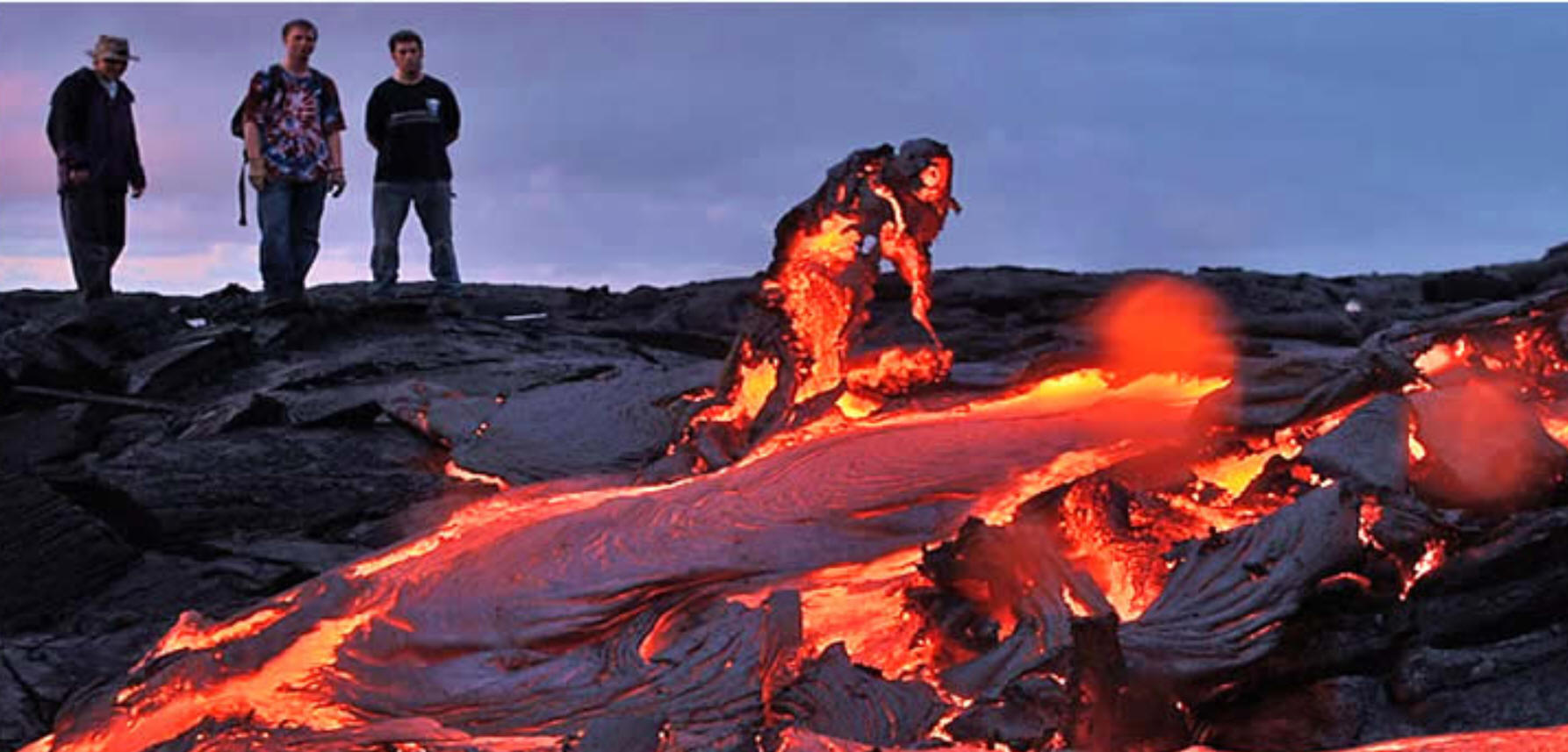
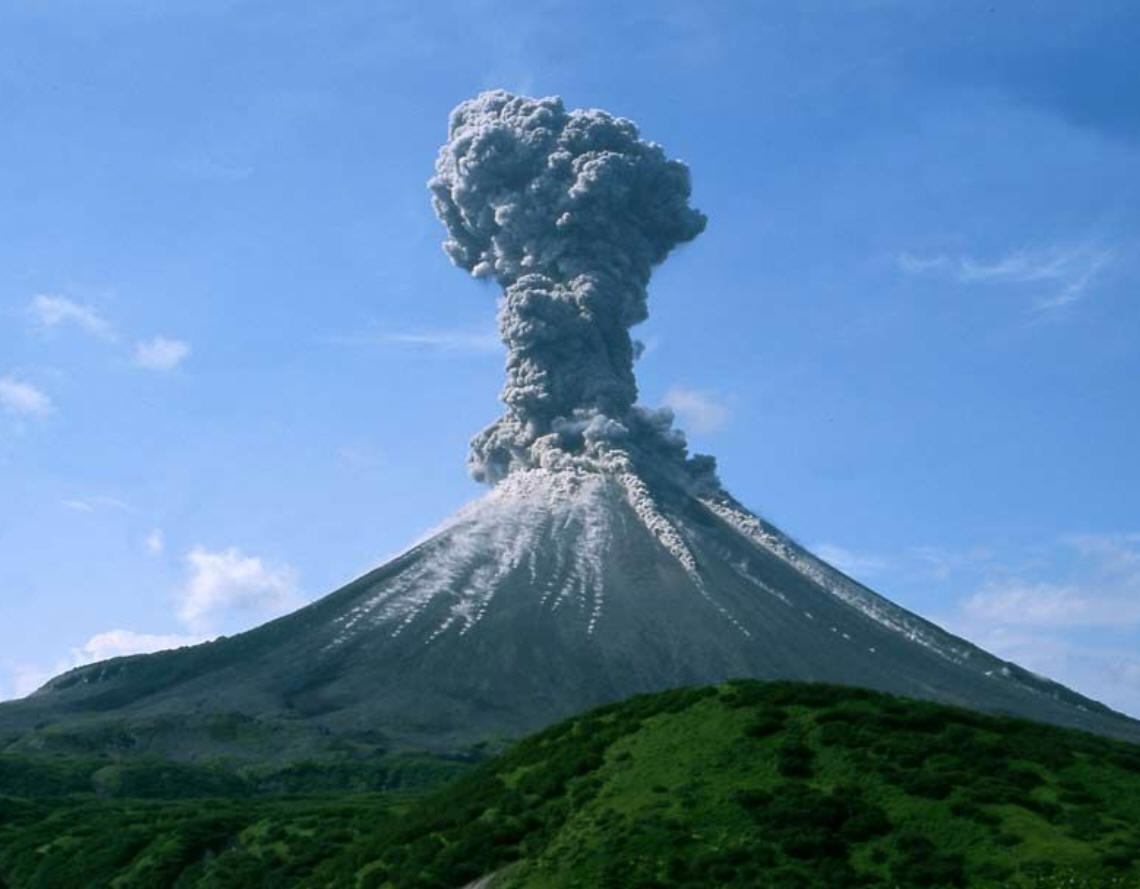
1. At what type of plate boundary(ies) might each of these eruptions have taken place?
2. What is the difference between magma and lava?
Today:
-
Check/review homework
-
Mafic/felsic rock types quiz -- unless you like your score from last class
-
Draw the rest of the plate boundary features
- plate boundary drawing template
- The final boundary -- Transform boundary
- Practice with names and locations
- Practice quiz (PDF)
- Maybe? Start watching National Geographic Volcano! Questions PDF
Homework:
- Study the Quizlet over plate feature names and locations -- and submit in Google Classroom.
- Quiz next class, similar to the quizlet.
 Class
43:
Thursday,
2/1/24
Class
43:
Thursday,
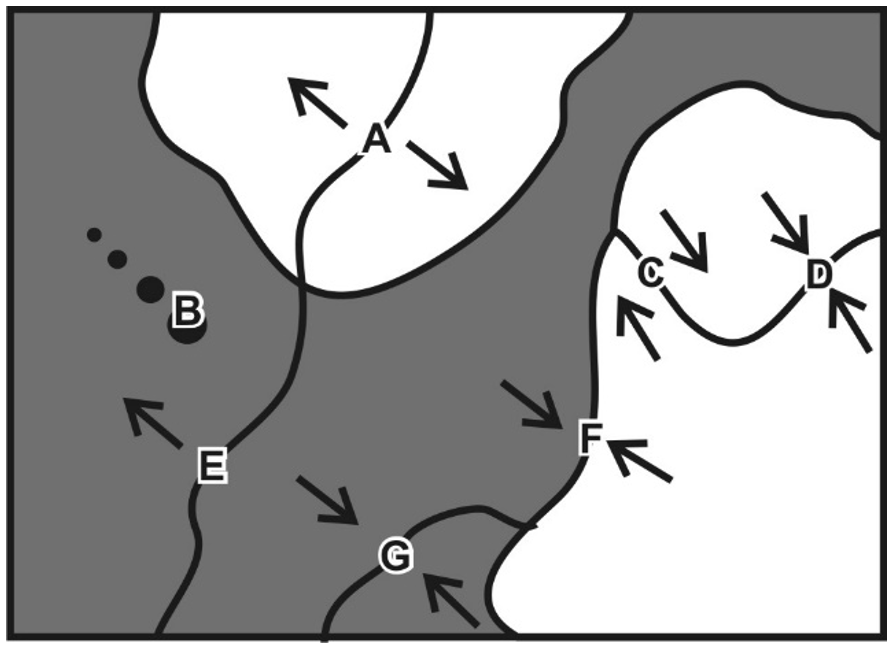
2/1/24Warm Up:
1. Which lettered item on the right is not a plate boundary?
2. Name all of the plate boundaries in the diagram on the right.
3. Which of the convergent plate boundaries will be subduction zones?
4. Why won't the other convergent plate boundary be a subduction zone?
Today:
-
Return Quizzes
-
Practice with Mafic/Felsic. If you like your score you can keep it.
-
Draw the rest of the plate boundary features
- Work time -- "Understanding a plate boundary." pdf version
Homework:
- Quiz next class over the mafic/felsic rock types quizlet -- unless you like today's score.
- Finish "Understanding a plate boundary." pdf version


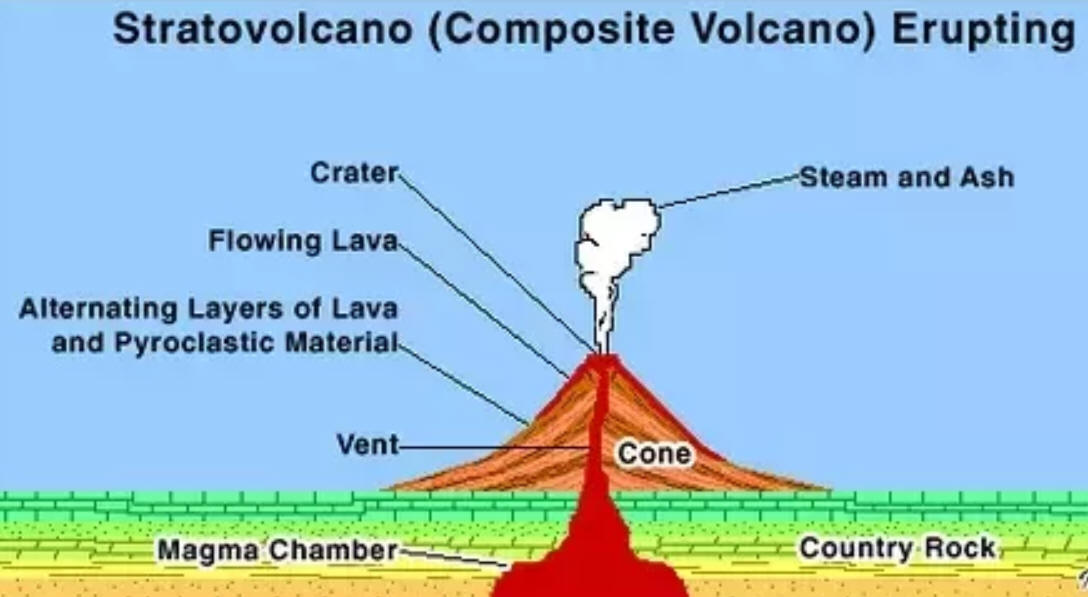 Class
42:
Tuesday,
1/30/24
Class
42:
Tuesday,
1/30/24Warm Up:
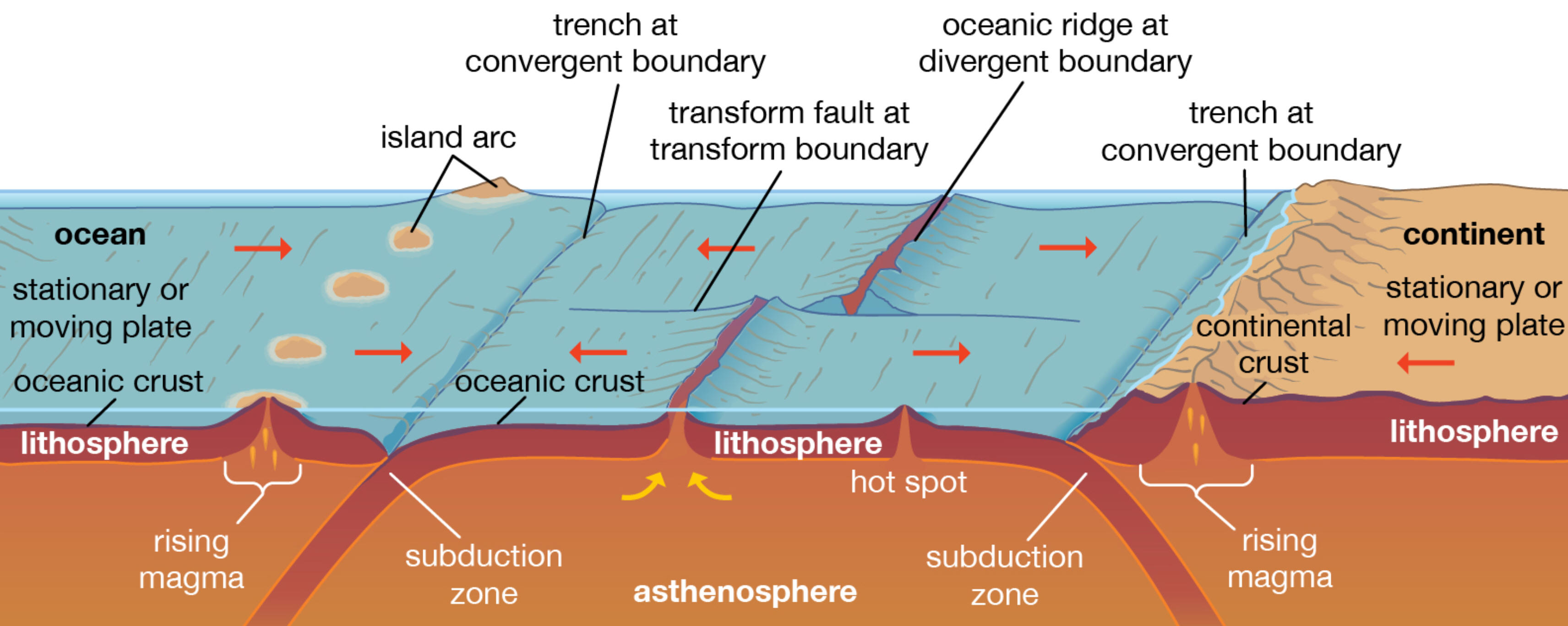
1. How are the items on the right similar? How are they different?
2. In the bottom picture, what makes the "diapirs" rise
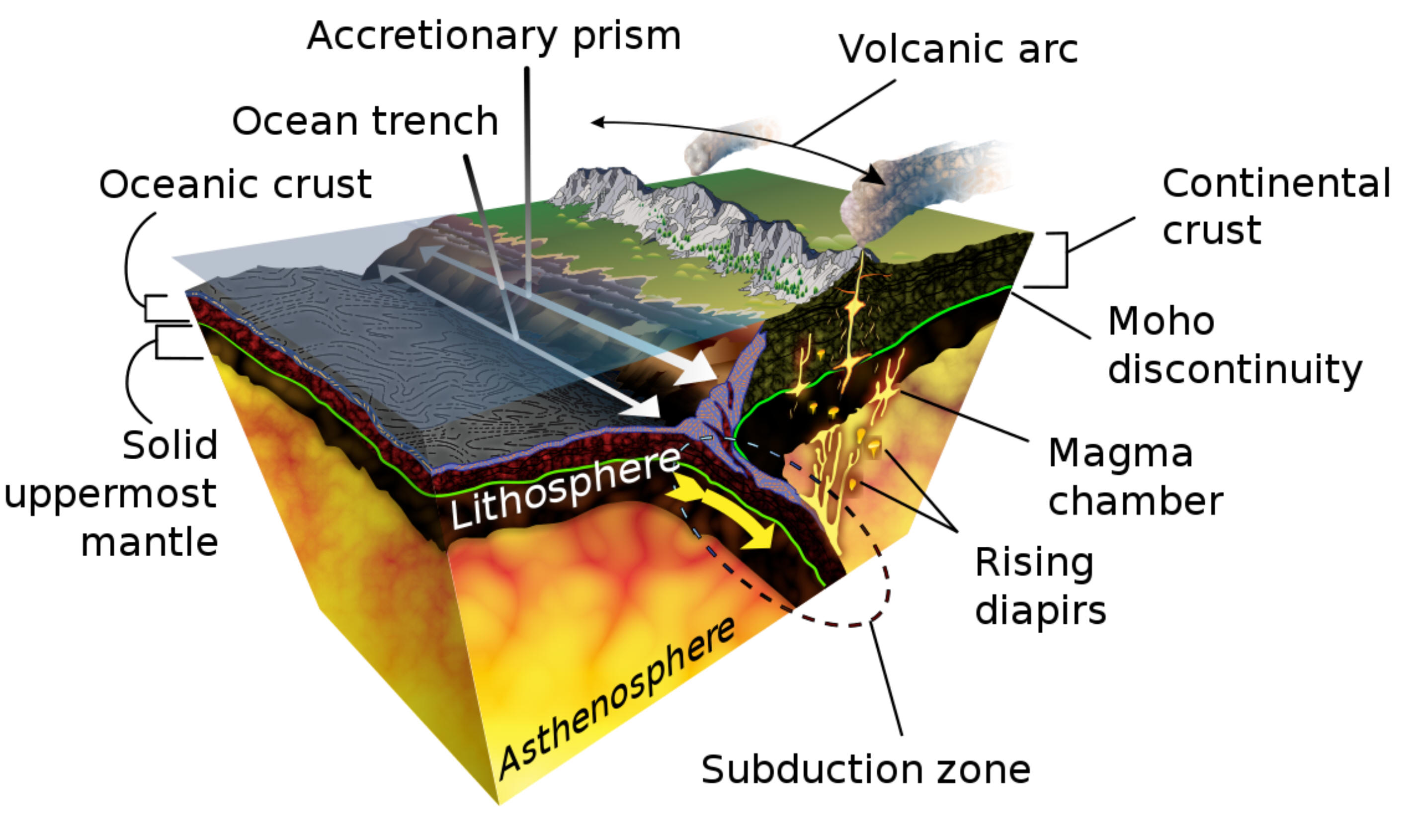 from the ocean
crust in the subduction zone?
from the ocean
crust in the subduction zone?Today:
-
Quiz -- Layers of the Earth and Plate Tectonics Basics
-
Mafic and Felsic Rock Types
-
Draw more plate features.
Homework: Study the Rock Types Quizlet


Warm Up:
1. If I boil some water and some spaghetti sauce, which one will splatter more?
2. What causes the little explosions that power the splatters?
3. Why are some of those explosions more powerful?
Today:
-
Check/review homework -- practice quiz
-
Notes on Earth's layers, plate boundaries, and convection currents.
-
Mafic and Felsic Rock Types
-
Learn to draw plate features -- start practicing.
Homework: Quiz next class -- study the first two pages of notes, the quizlet, and today's practice quiz.
Warm Up: Oops! I forgot the warm up!
Today:
-
Take a look at midterms
-
Notes on Earth's layers, plate boundaries, and convection currents.
Homework: Study this quizlet
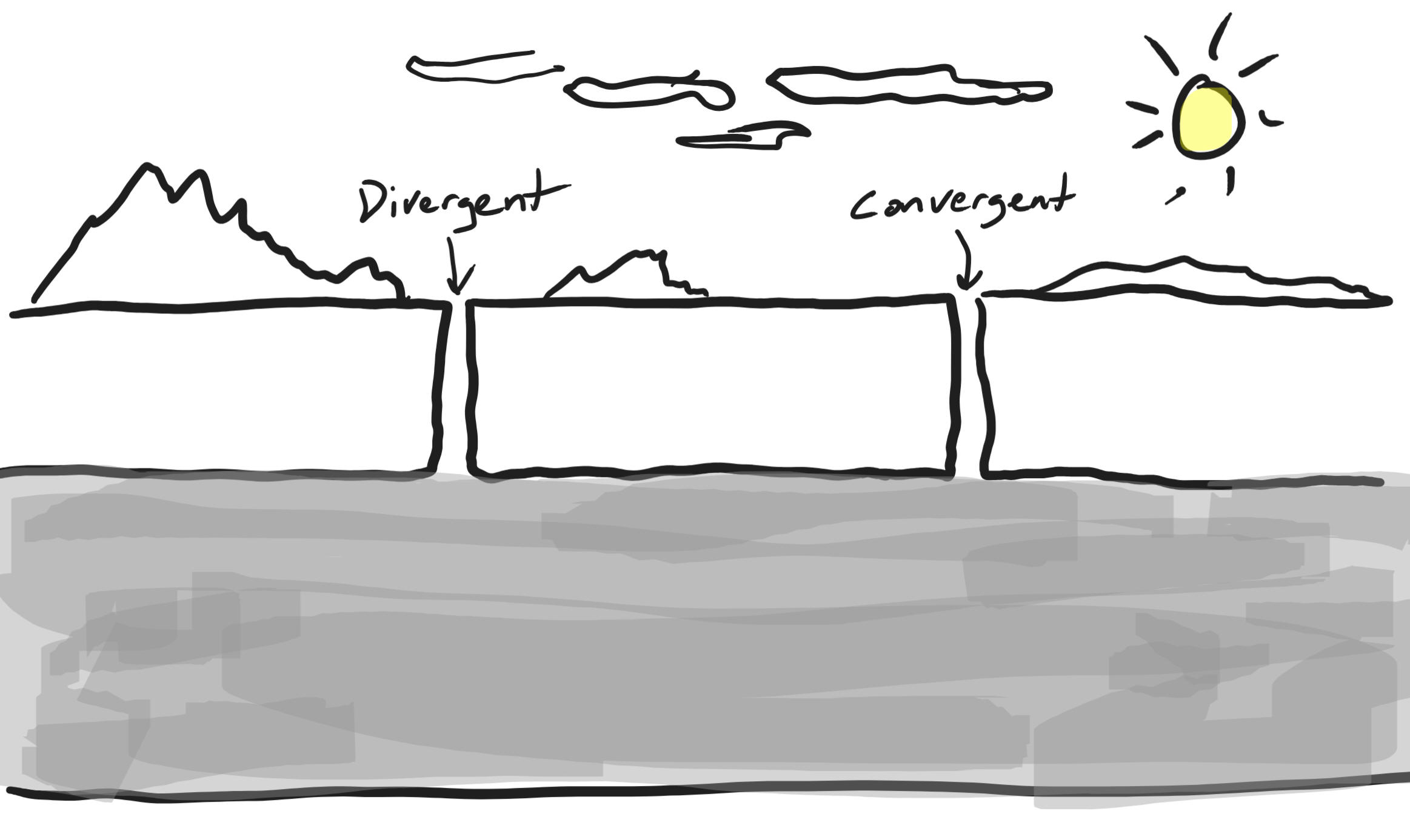 Class
39:
Tuesday,
1/9/24
Class
39:
Tuesday,
1/9/24Warm Up:
1.How many plates are shown in the picture on the right? What kind of plates are they?
2. In which direction is each plate moving?
3. Where is there a rising current in the mantle? Where is there a sinking current?
4. Which plate boundary sits over a particularly cool part of the mantle?
5. Where is lava most likely to come to the surface?
6. Where are tall mountains likely to form? Will there be a volcano?
Today:
-
Check/review homework
-
Check on PLP Reflection Submissions -- some of you have zeroes. Fix those now.
-
Midterm Exam Review
-
Work on Midterm Review, Part 3 PDF Answers
-
-
Midterm Preparation Materials:
-
Star Stuff -- Google Classroom Links:
Homework: Prepare for the midterm. Work on your notecard. Review.
 Class
39:
Tuesday,
1/9/24
Class
39:
Tuesday,
1/9/24Warm Up:
1.How many plates are shown in the picture on the right?
2. Which is more dense, the crust or the mantle?
3. Which type of crust is most similar to the mantle?
4. There's light colored sediment on top of the ocean crust. Where did that come from?
5. Which plate boundary is convergent, and which is divergent?
6. Where is a very tall volcano likely to form? Why?
Today:
-
Check/review homework
-
Check on PLP Reflection Submissions -- many of you have zeroes. Fix those now.
-
Note about Hadean Era postcard
-
Midterm Exam Review
-
Work on Midterm Review, Part 3 PDF
-
-
Midterm Preparation Materials:
-
Star Stuff -- Google Classroom Links:
Homework:
- Complete 1-29 of Midterm Review, Part 3 PDF
 Class
38:
Friday,
1/5 /24
Class
38:
Friday,
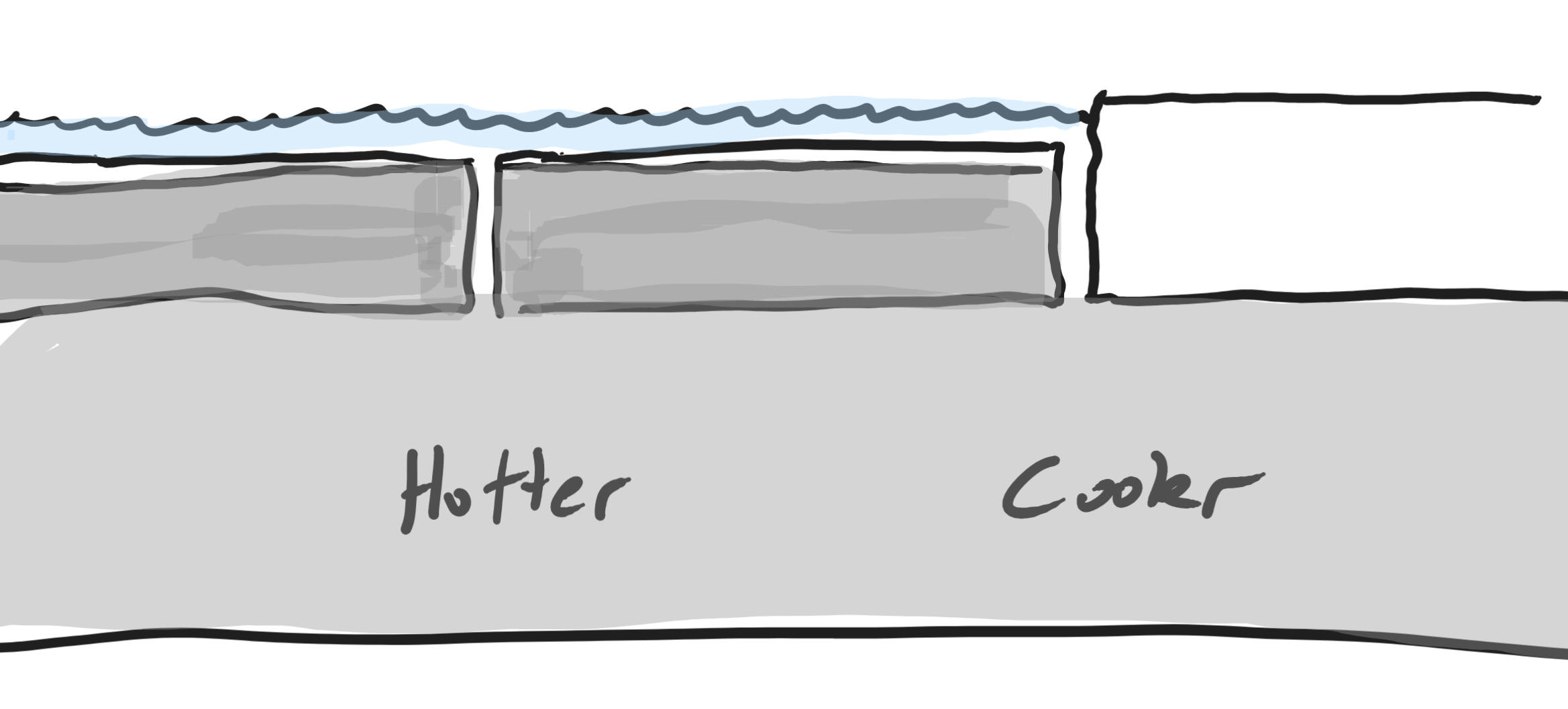
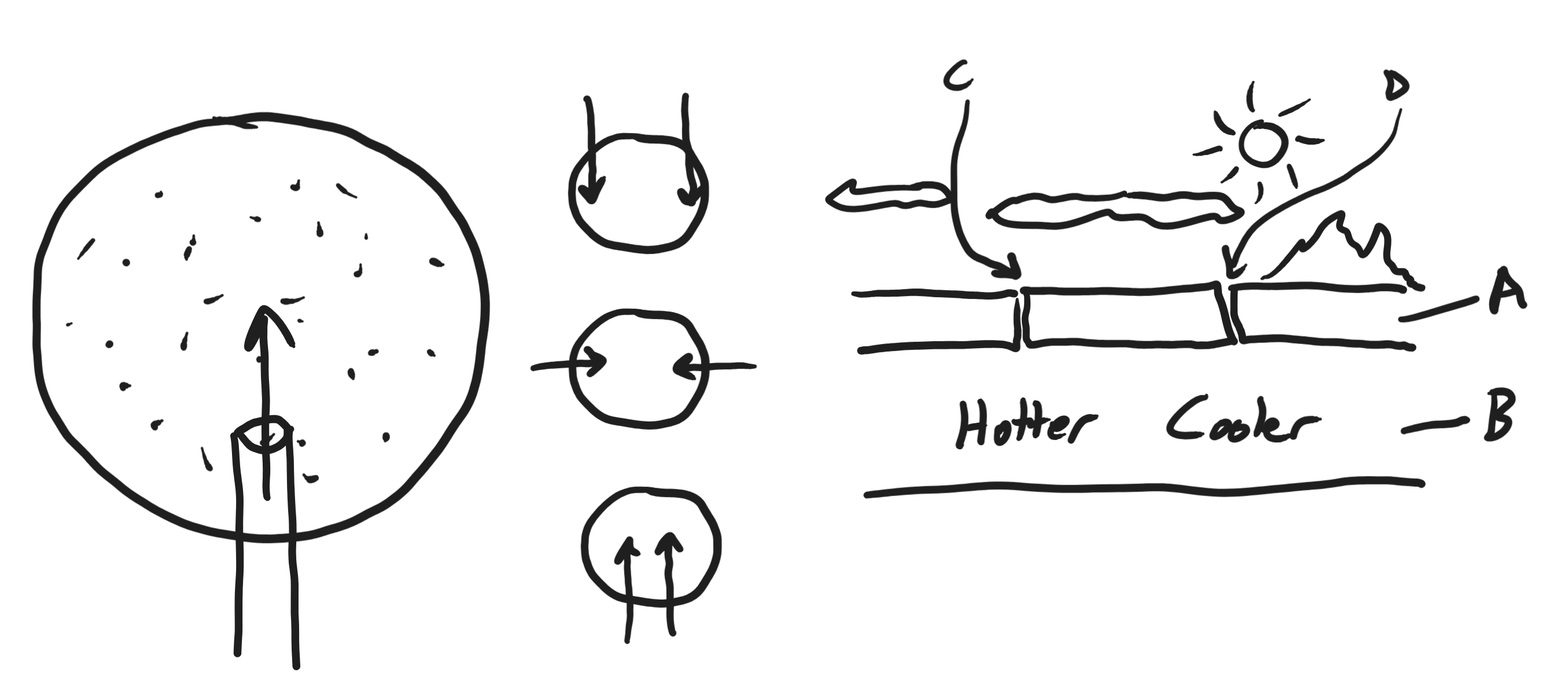
1/5 /24Warm Up: The first picture on the right shows an air current being blown across a dish of water sprinkled with pepper.
1. What currents will form?
2. What currents will form in the other 3 situations?
3. What are the names of the Earth layers labeled A and B?
4. What are the pieces of layer A called?
5. What currents will form in layer B?
6. Which letter points to a convergent plate boundary, and which points to a divergent plate boundary?
Today:
-
Check/review homework
-
Return stuff
-
Check on PLP Reflection Submissions -- many of you have zeroes. Fix those now.
-
Note about Hadean Era postcard
-
Midterm Exam Review
-
Note card work / study time
-
Quizzing -- note cards allowed
-
Quizzing over space Quizlets
-
Quizzing over physical properties and air pressure
-
-
-
Midterm Preparation Materials:
-
Star Stuff -- Google Classroom Links:
-
Begin Plate Tectonics? Probably not yet; we need to get ready for the midterm.
-
Notes on Earth's layers, plate boundaries, and convection currents. Plate Tectonics Notes, Part 1 -- Filled-in version
-
Homework:
- Complete the Hot air balloon practice Questions PDF . Check your answers and add anything to your note card that you think would be helpful. Answers
 Class
37:
Wednesday,
1/3/24
Class
37:
Wednesday,
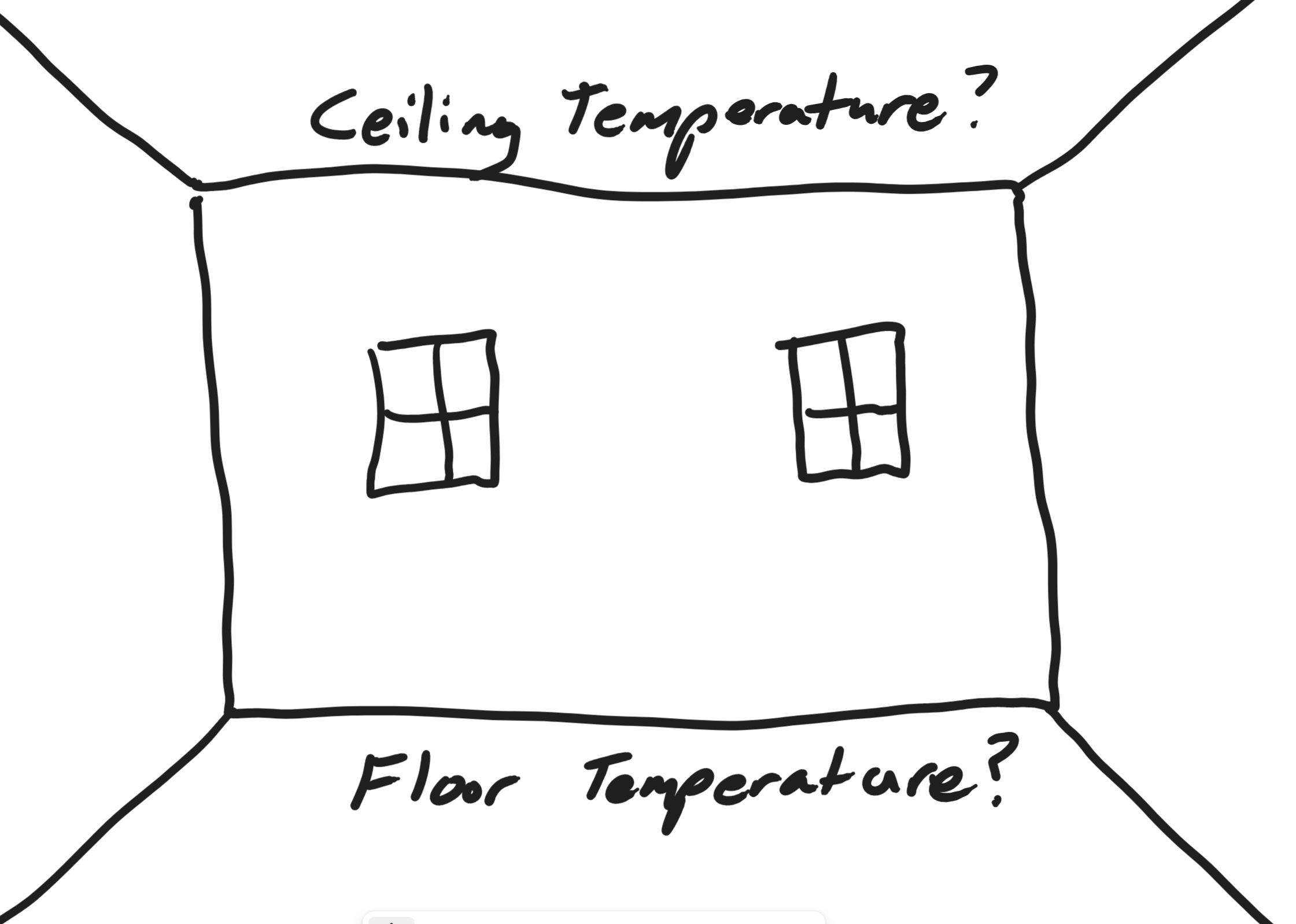
1/3/24Warm Up:
1. Guess the difference in temperature between a thermometer at floor level and a thermometer at the ceiling.
2. Why should there be a difference?
Today:
-
Return stuff
-
Check on PLP Reflection Submissions -- many of you have zeroes. Fix those now.
-
Course recommendations -- what science class(es) would you like to take next year?
-
Midterm Exam Information
-
Test Format:
-
40-50 Multiple Choice Questions
-
5-8 Short Answer Questions
-
Whatever notes you want to fit on a large note card, front and back (or one side of a regular sheet of copier paper)
-
-
Material on The Test:
-
Google Classroom Links:
-
-
Begin Plate Tectonics
-
Notes on Earth's layers, plate boundaries, and convection currents. Plate Tectonics Notes, Part 1 -- Filled-in version
-
Homework:
 Class
36:
Friday,
12/22/2023
Class
36:
Friday,
12/22/2023Warm Up: What happened at 10:27PM, last night? What does this mean for us? What does it not mean?
Today:
-
Quiz retakes
- Check on PLP reflections in Classroom -- how to see if you have 200 words for numbers 3, 4, and 5. If you have 200 or more words on #3-5, you get 100% on a quiz grade. If you have between 100 and 200 words on #3-5, you get 100% for a homework grade. If you don't turn this in, it counts as a zero for a homework grade.
- Play Scattergories
Homework:
- Finish the PLP reflection by tonight!
 Class
35:
Wednesday,
12/20/2023
Class
35:
Wednesday,
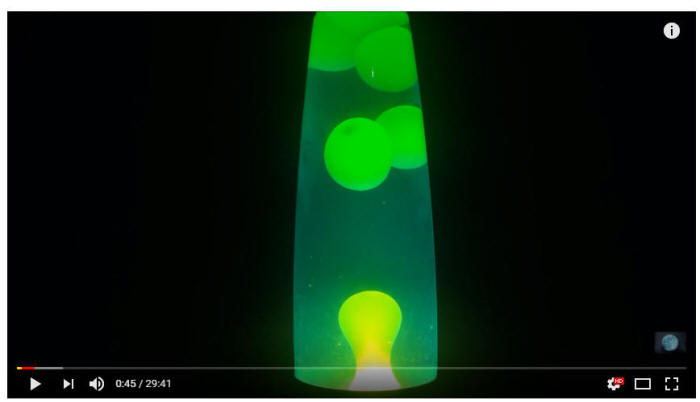
12/20/2023Warm Up: Why do the blobs in a lava lamp rise and sink?
Today:
-
Go over quizzes -- you can retake the quiz on Friday, during class.
-
Look at grades in PowerSchool
-
Write Reflections for your PLP -- the assignment is in Google Classroom (9th graders only) -- If it's submitted and you meet all of the grading requirements, it will be entered as a 100% quiz grade. If not, you won't get credit, but you'll still have to do it.
Homework:
- Finish the PLP reflection
- If you want to make up or retake any quizzes, prepare to do that next class.
Warm Up: Can you identify any of these locations on Earth? Do you know how they formed?




Today:
-
Quiz: Waves and The Big Bang
-
Celebrate the end of the Astronomy Unit -- Watch Cosmos?
Homework: None

 Class
33:
Thursday,
12/14/2023
Class
33:
Thursday,
12/14/2023Warm Up:
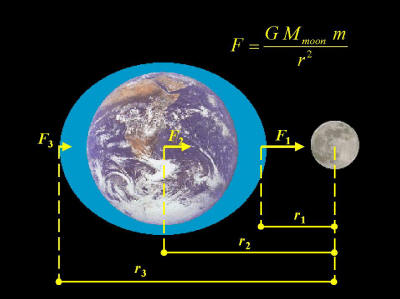
If you fell into a black hole, you would be spagettified. The Sun, Earth, and Moon are continually spaghettifying one another. We see the effects of this spaghettification in the form of tides.
1. What is spaghettification, and what causes it?
2.
Which
object exerts greater gravitational force on us, the Moon or the
Sun?
Today:
-
Check/review homework.
-
B5/6 new seats
-
Finish the Notes: Evidence for The Big Bang pdf version filled-in version
-
Finish the Practice: Waves and The Big Bang PDF
-
Quiz review -- Jeopardy
Homework: Quiz next class over waves and The Big Bang (similar to notes and practice)
 Class
32:
Tuesday,
12/12/2023
Class
32:
Tuesday,
12/12/2023Warm Up: What's this?
Today:
-
library vs. bathroom
-
Notes: Doppler Effect pdf version filled-in notes
-
Doppler Effect Videos and Simulations
-
- Notes: Evidence for The Big Bang pdf version filled-in version
Homework: #1-15 of Practice: Waves and The Big Bang PDF
 Class
31:
Friday,
12/8/2023
Class
31:
Friday,
12/8/2023Warm Up:
The picture on the right shows an explosion. This explosion shares some similarities with the Big Bang theory of the Universe's formation.
1. In the picture, which bits of matter are traveling fastest? How can you tell?
2. One result of this explosion is the movement of bits of matter. What are some other results of this explosion?
The expansion of the Universe after the Big Bang was not like the expansion after the explosion above. It was more like the expansion of the surface of a balloon. Coins glued to the balloon represent galaxies.
3. If we drew some waves between the coins, what would happen to the wavelengths as the balloon expanded?
Today:
- Quiz: Large Stars
-
Finish waves notes
-
Notes:
Waves part 1
pdf version
Filled-in notes
- Roy G. Biv song
- Powerpoint: Waves, Stars, Etc.
- RGB color model -- adding light
- CMYK color model -- adding pigment (paints)
Homework: None
 Class
30:
Wednesday,
12/6/2023
Class
30:
Wednesday,
12/6/2023Warm Up: If you're standing next to a race track, which of the following do you hear as the cars pass you?
a. The cars' pitch changes from high to low.
b. The cars' pitch changes from low to high.
c. There is no change in pitch.
Today:
- Quiz: Medium-Sized Stars
- Practice Quiz: The Lives of Large Stars PDF
Homework: Study -- quiz next class over the lives of large stars
 Class
29:
Monday,
12/4/2023
Class
29:
Monday,
12/4/2023Warm Up:
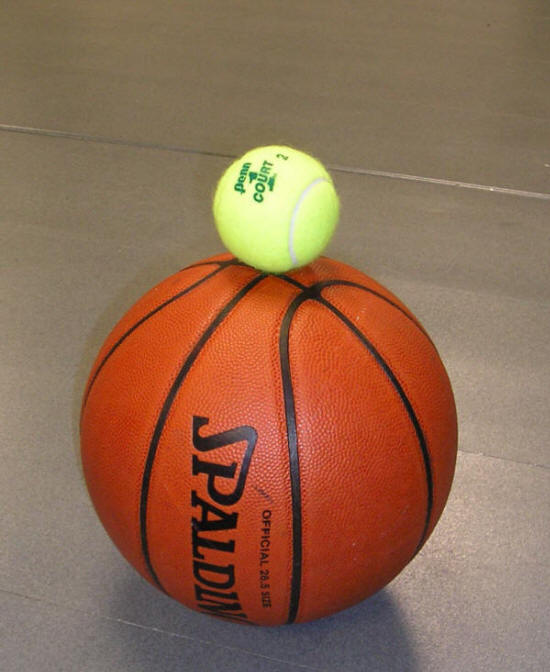
1. Do this: hold a tennis ball on top of a basketball and drop them to the floor together? See what happens.
2. Guess why it happens.
3. Watch this video to find the answers and to see how this relates to supernovas.
Today:
- Return Quizzes.
- Practice Quiz over the life stages of Medium-Sized Stars (like our Sun) (PDF) Answer Key
- Notes: Life Stages of large stars pdf version filled-in version
- Neutron Stars
- Black Hole Spaghettification
Homework: Study for a quiz next class over medium-sized stars
 Class
28:
Thursday,
11/30/2023
Class
28:
Thursday,
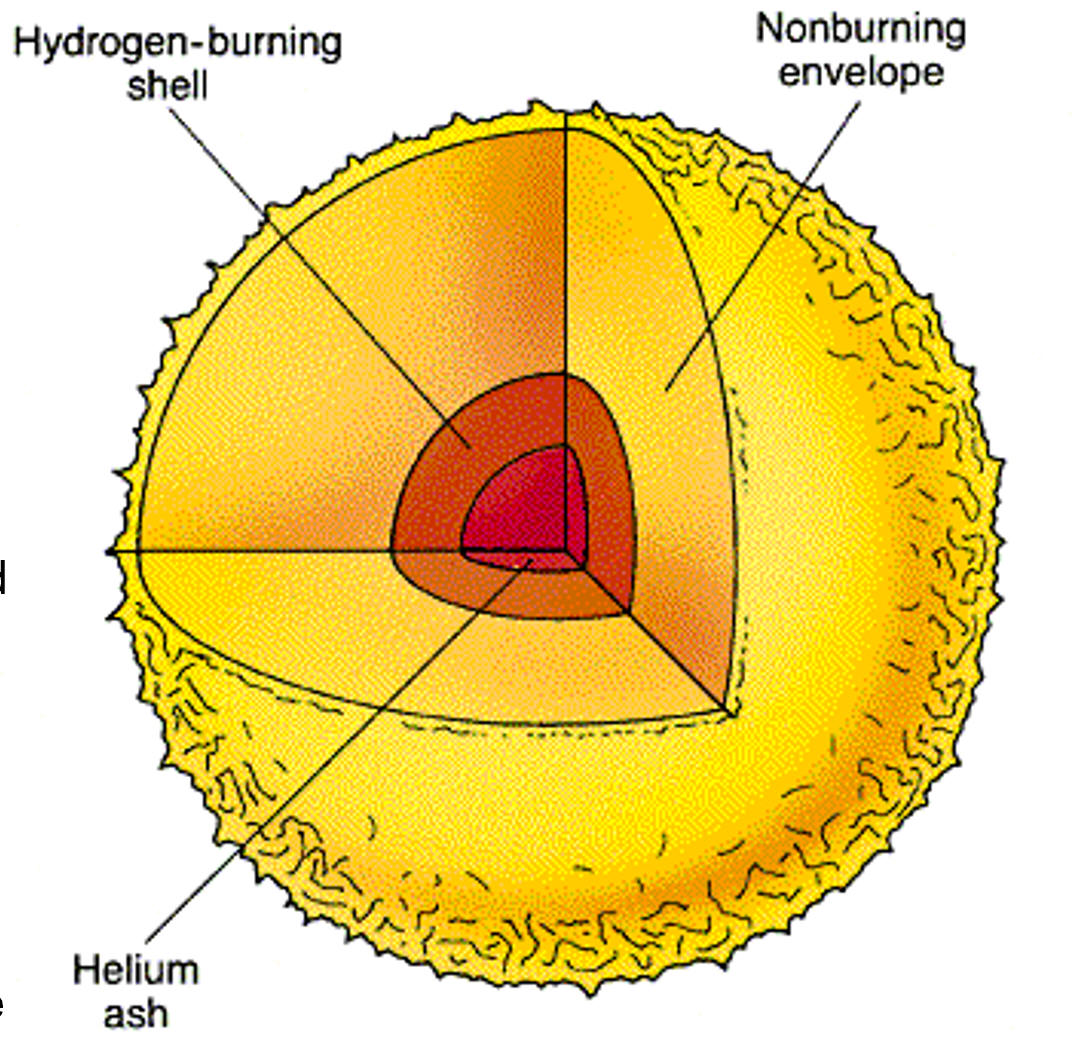
11/30/2023Warm Up: Where does the "helium ash" come from, and how does it get to the center of the Sun?
Today:
- Quiz over Solar System formation, part 2
- Continue Notes: Medium Star Life Cycles pdf version filled-in version
Homework: None
 Class
27:
Tuesday,
11/28/2023
Class
27:
Tuesday,
11/28/2023Warm Up: What are the hottest and coolest parts of this picture? How can you tell?
Today:
- Return papers, discuss missing work. Some of you should sign up for FLEX to take or retake quizzes.
- Practice Quiz: Solar System Formation, Part 2 (PDF)
- New Notes: Medium Star Life Cycles pdf version filled-in version
Homework: Quiz next class over the information on today's quiz review. Study!
 Class
27:
Friday,
11/17/2023
Class
27:
Friday,
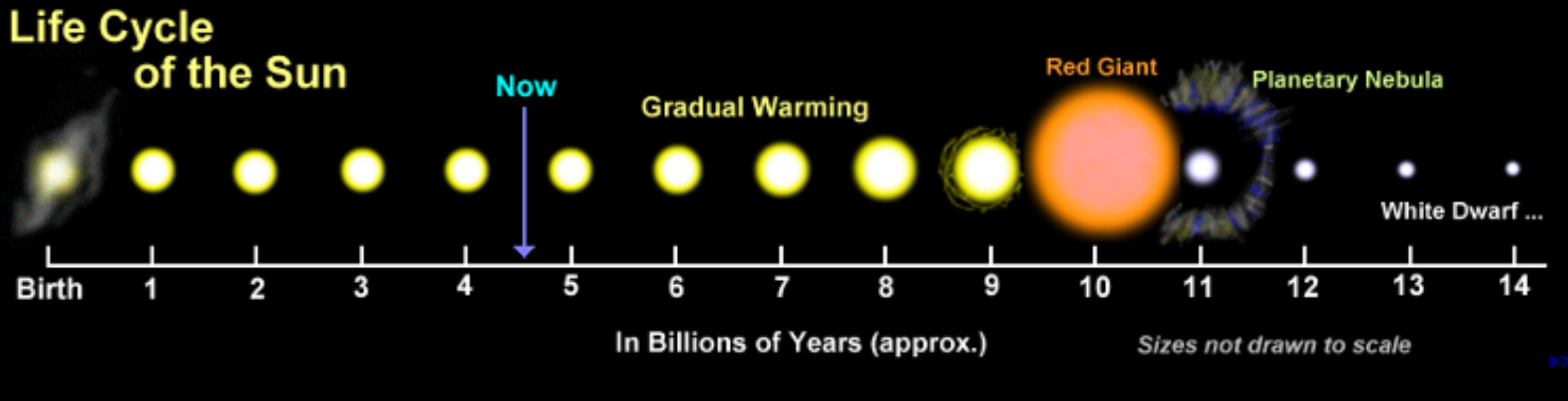
11/17/2023Warm Up: The diagram on the right shows the life cycle of a star like our Sun. What's wrong with the diagram?
Today:
- Return Quizzes
- Finish notes: Formation of The Solar System, part 2 (PDF) Filled-in Notes
- Watch
The Sun and Stars -- start at 1:00.
- Username: ehscte
- Password: hornets
Homework: None!
 Class
26:
Wednesday,
11/15/2023
Class
26:
Wednesday,
11/15/2023Warm Up: How can you demonstrate static electricity with ordinary clear tape? Good YouTube demo
Today:
- Quiz over Solar System Formation practice questions (PDF)
- Formation of The Solar System, part 2 (PDF)
Homework: None!
 Class
25:
Monday,
11/13/2023
Class
25:
Monday,
11/13/2023Warm Up:
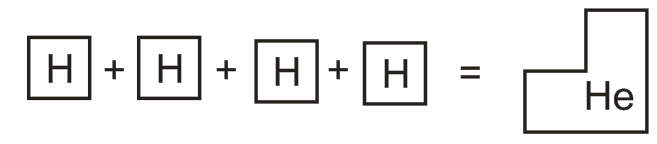
1. The first diagram on the right shows four hydrogen
atoms that combine to make one
 helium atom.
This is what happens in nuclear fusion. What looks
wrong?
helium atom.
This is what happens in nuclear fusion. What looks
wrong?
2. E = mc2 is a famous equation. What do each of the letters in the equation represent?
Today:
- Return quizzes
- Return Stirling Engine grading sheets and go over the answers. Make a VIDEO and put it in the Google Classroom assignment.
- Review the questions from last class (homework if you didn't finish). Make a VIDEO and put it in the Google Classroom assignment.
- Work on correcting the Stirling Engine Slideshows. Turn in your corrected slideshow by Friday.
Homework:
- Study for a Quiz next class over the practice questions that were due today.
- Correct the Stirling engine slideshows -- make sure that you put things into your own words.
 Class
24:
Thursday,
11/9/2023
Class
24:
Thursday,
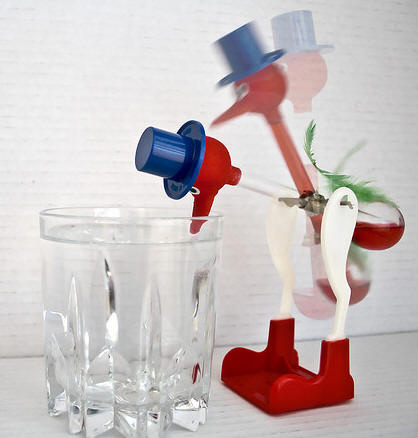
11/9/2023Warm Up:
Why does the bird keep drinking?
Today:
- Quiz -- Earth's Formation
- Finish Notes: Formation of The Solar System Part 1 -- Gravitational Contraction PDF Filled-in notes
Homework: Complete the Solar System Formation practice questions (PDF)-- If we didn't finish them in class.
 Class
23:
Tuesday,
11/7/2023
Class
23:
Tuesday,
11/7/2023Warm Up:
1. If you rub a balloon on your head and then hold it next to your hair, your hair is attracted to the balloon. Why?
2. Your hair may also stand on end after being rubbed by a balloon. Why?
3. How can we produce this same effect with tape?4. How does this relate to the Earth's formation?
Today:
- Stirling Engine Slideshows are due by midnight tonight.
- Finish the "Birth of the Earth" video
- Start Formation of the Solar System
- New Unit -- History of Space
- Formation of the Solar System (including Earth)
- Stars, from birth to death (various types of stars)
- Formation of the Universe (the Big Bang)
Homework: Study for the uiz next class over Birth of The Earth questions
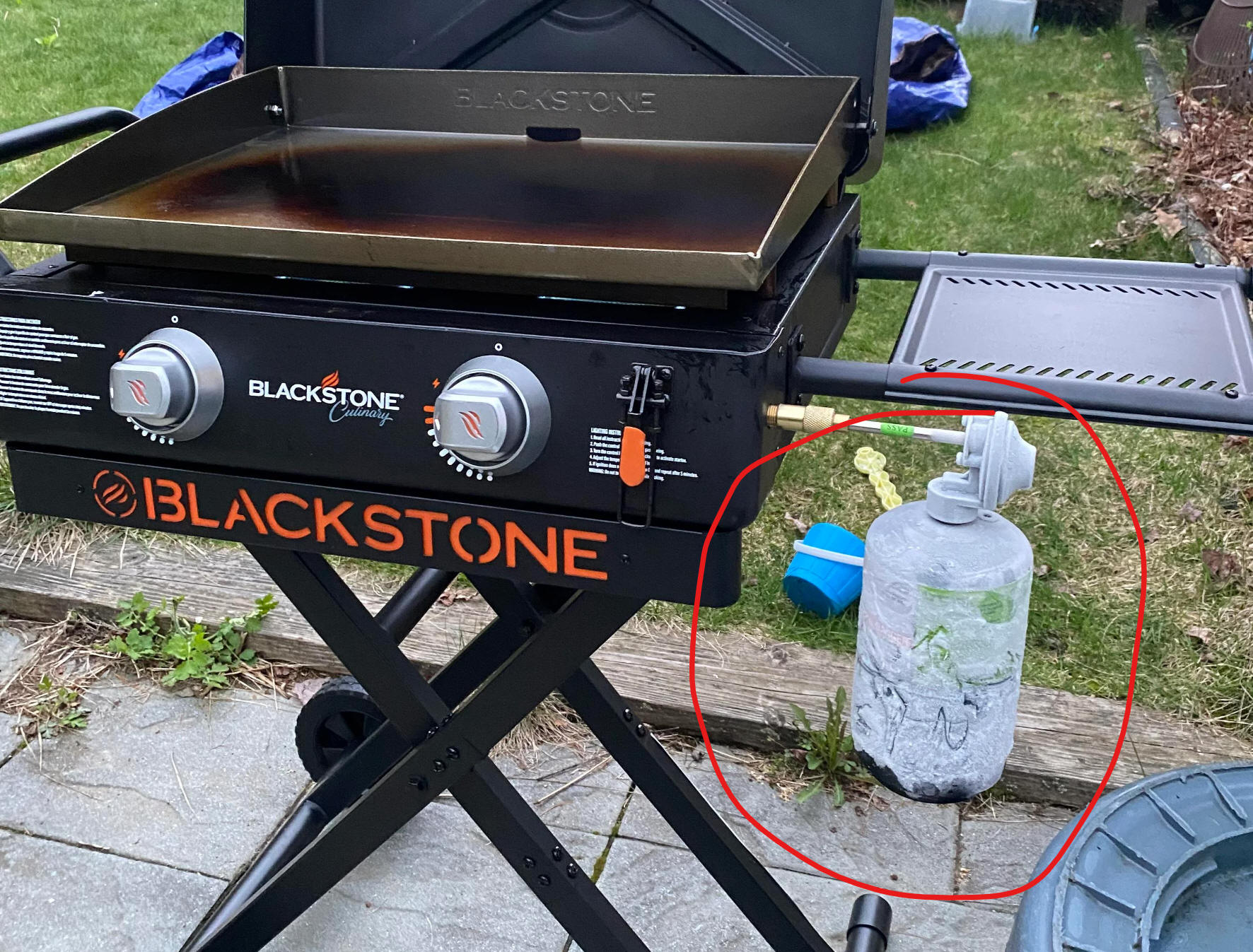

Warm Up:
1. Why does frost sometimes form on propane tanks, even when the weather isn't very cold?
2. Does this frost make the propane tank perform better or worse? Explain why.
3. Is the propane in a tank solid, liquid, gas, or a combination of states of matter?
Today:
- Work on Stirling Engine Slideshows. They are due on Tuesday, but you won't have class time on Tuesday to work on them.
- Finish the "Birth of the Earth" video?
- Next Unit -- History of Space
- Formation of the Solar System (including Earth)
- Stars, from birth to death (various types of stars)
- Formation of the Universe (the Big Bang)
Homework: Stirling Engine Slideshows are due on Tuesday, by midnight. There won't be class time to work on this on Tuesday, but I will remind you.
 Class
21:
Tuesday,
10/31/2023
Class
21:
Tuesday,
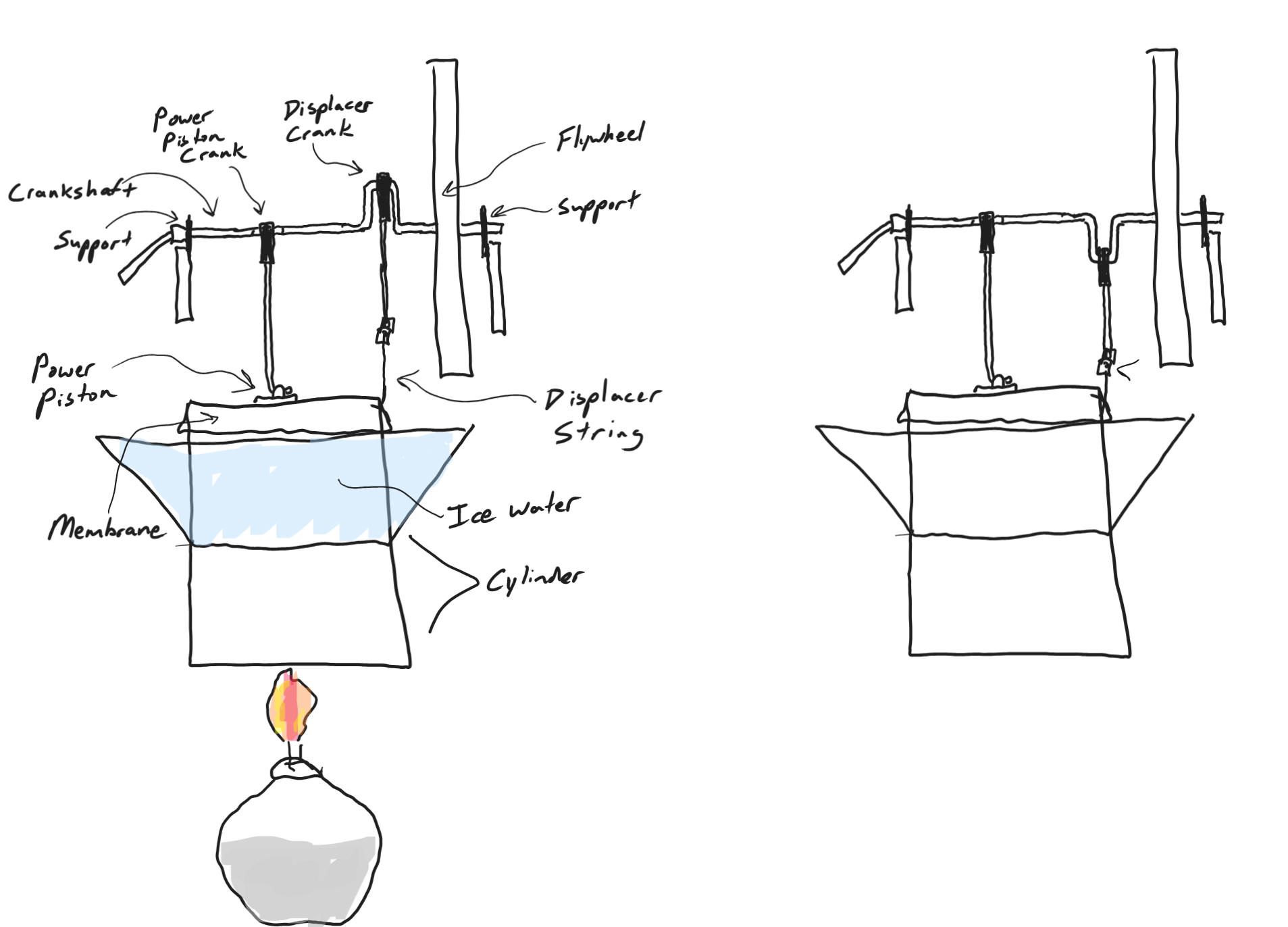
10/31/2023Warm Up: If you add heat and coolness to a Stirling engine, this generates force and causes movement. You can reverse the process if you add force, turning the flywheel of a Stirling engine to cause heating and cooling. Explain.
Today:
- Return make-up stuff.
- Look at grades
- Work on Stirling Engine Slideshows (in Google Classroom -- Due next Tuesday)
- What kind of donuts?
Homework: Stirling Engine Slideshows are due on Tuesday
 Class
20:
Friday,
10/27/2023
Class
20:
Friday,
10/27/2023Warm Up:
1. How does a simple D.C. electric motor work?
2. What does D.C. mean?
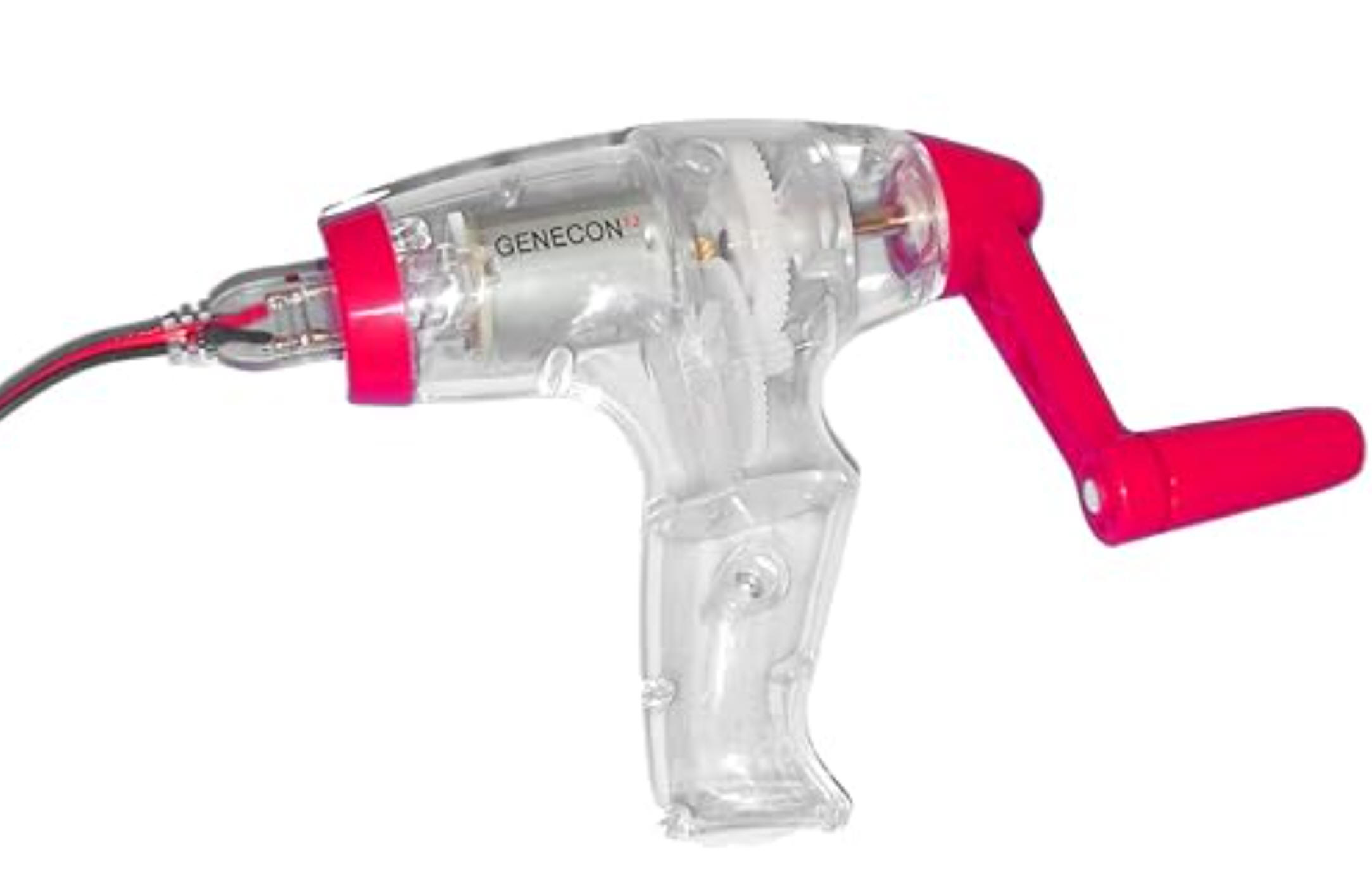 3.
How does this Genecon generator work?
3.
How does this Genecon generator work?4. What interesting thing can we do with two Genecon generators?
Today:
- Make-up day
- Work on Stirling Engines. Remove the flywheel when you're done, but leave the rest on the stand. Do label it with your names!
Homework: None!
 Class
19:
Wednesday,
10/25/2023
Class
19:
Wednesday,
10/25/2023Warm Up:
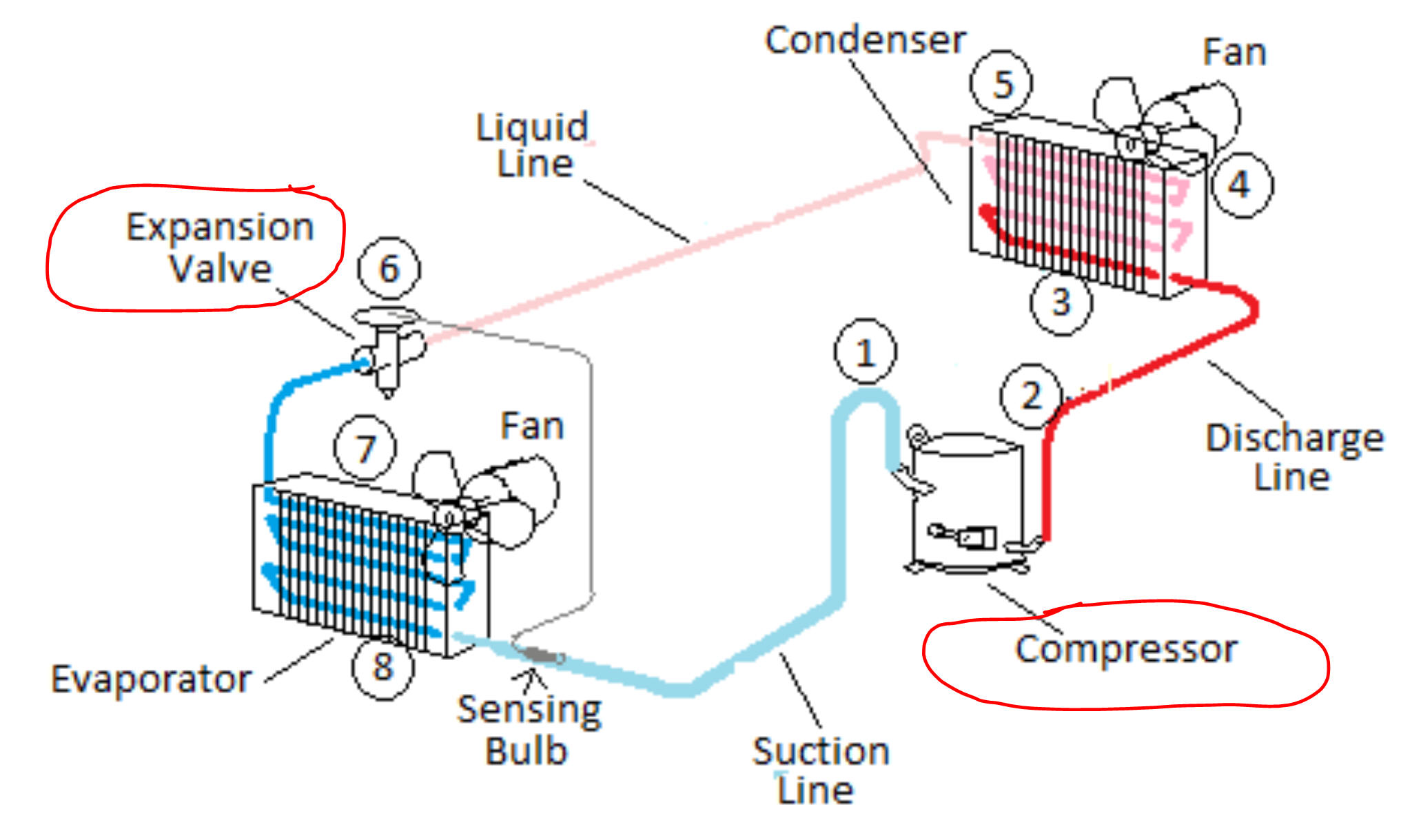
The diagram on the right shows a basic refrigeration unit. I have circled the compressor and the expansion valve. In this system, a substance called a refrigerant, moves through the pipes.
1) What happens to the temperature of the refrigerant when it is compressed?
2) What happens to its temperature when it is allowed to expand?
3) In which direction is the refrigerant flowing through the pipes?
4) Can you guess the purposes of the fans and radiators? Do you know what a radiator does?
Today:
- Return quizzes
- Stirling Engine Update:
- I think I patched most (hopefully all) of the reservoir leaks.
- I want to make some more stands, so that you don't have to take your engine apart between classes -- so we're pausing the project for today. The plan is to resume on Friday.
- Today we will watch a video that we would usually watch later on, but this will be a good time to do it, so we're not wasting time while we wait on me to make new Stirling Engine Stands.
Homework: Friday's class will be a make-up day, when you can make up any missing assignment or retake any quiz. Take a look in PowerSchool and decide what you might need to do to prepare for Friday. Here are some materials to help you prepare for a retake...
- Quiz 1: Universe Structure and Objects Orbiting the Sun (Quizlets 1 and 2)
- Quiz 2: Universe Structure and Objects Orbiting the Sun (Quizlets 3 and 4)
- Quiz 3: Physical Properties and Air Pressure
- Quiz 4: Beyond The Solar System (Quizlet 5)
- Balloon Video Make-up: Earn UP TO 80% by answering the balloon video questions in writing. Submit by email or in person.
 Class
18:
Monday,
10/23/2023
Class
18:
Monday,
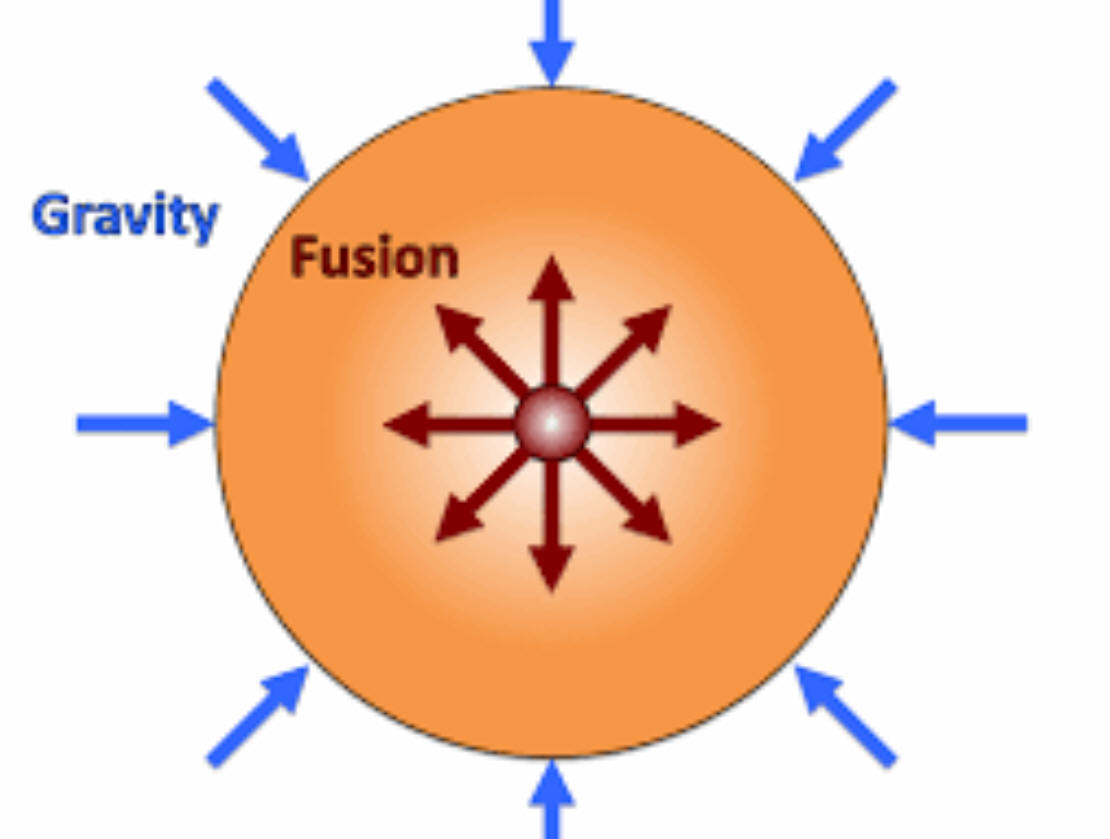
10/23/2023Warm Up: Nuclear fusion happens when the core of the star is hot enough to fuse Hydrogen into Helium. This diagram was made to help explain how stars keep "burning" evenly, without cooling off or heating up. For most of their lives, stars don't overheat, and they don't cool off. These questions explore why this happens...
- Suppose the star happened to cool off a little. How would the star's volume change? Why?
- What force would cause the star's volume to change?
- Explain why that volume change would cause the star to heat back up?
- Now suppose the star
Today:
- Quiz
- Check/review page 2 of the stirling engine questions
- Copy notes
- Finish the stirling engines?
Homework: Friday's class will be a make-up day, when you can make up any missing assignment or retake any quiz. Take a look in PowerSchool and decide what you might need to do to prepare for Friday.
 Class
17:
Thursday,
10/19/2023
Class
17:
Thursday,
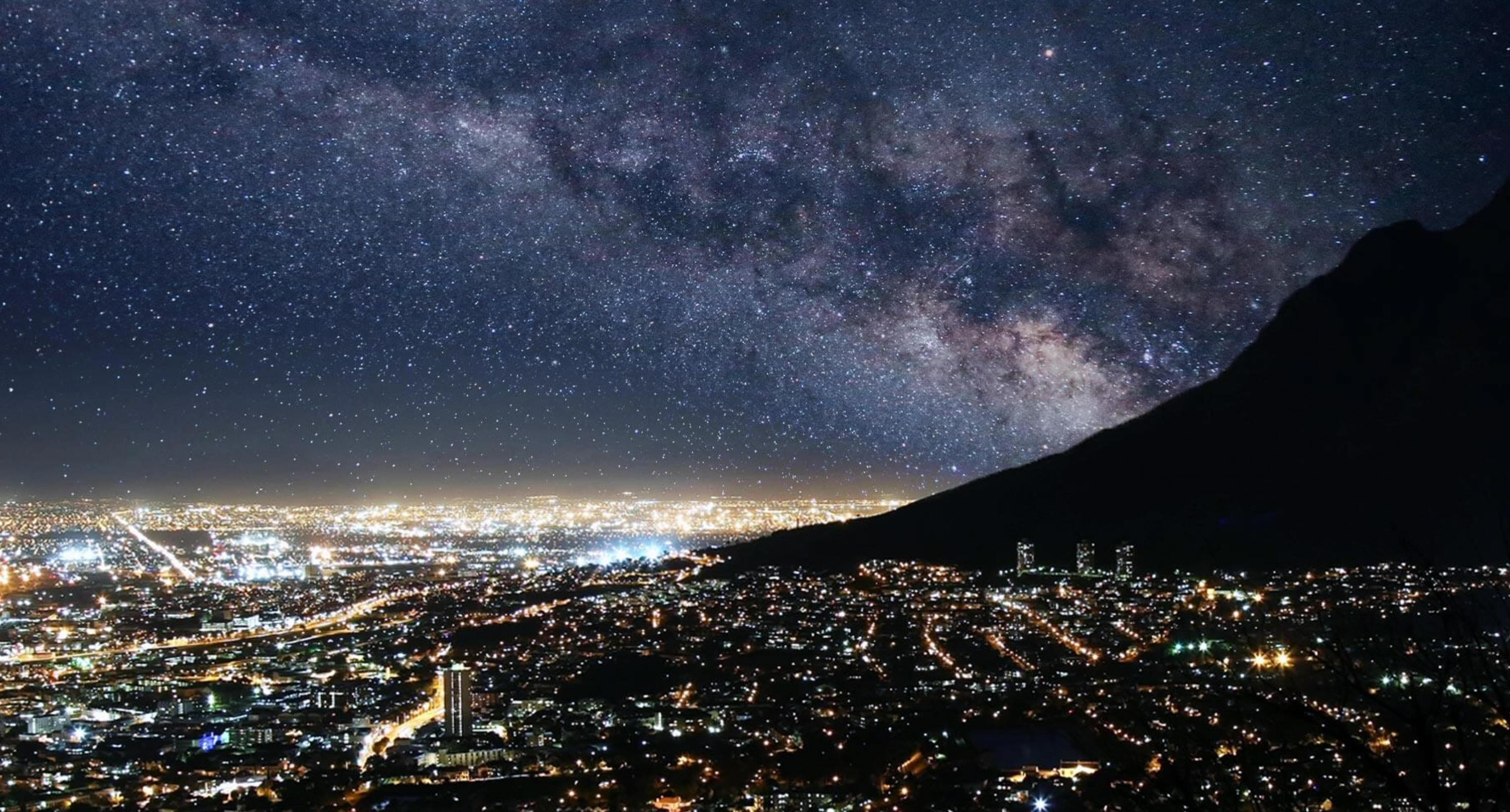
10/19/2023Warm Up:
When you go outside on a clear, moonless night, how far away are the closest and farthest objects that you can see with your "naked eyes?"
Today:
- Add ice water reservoirs to your stirling engines. Secure the reservoir with tape. Caulk the seams and set the cylinder aside to cure. We will finish the stirling engines on Monday.
- Check out
the
5th and Final Objects In Space Quizlet:
Beyond The Solar System together.
- Look at the links on this page that go with the 3rd Quizlet.
- Stirling Engine Questions (PDF)
Homework:
- Part 1: Study Quizlet #5 to prepare for a short quiz next class. Then submit the assignment in Google Classroom. This quiz will be fill-in-the blank, just like the flash cards. There will be one bonus.
- Part 2: Finish the Stirling Engine Questions, if you didn't finish them in class.
Warm Up:
How can we make a stirling engine go even faster?
Today:
- hand out old work
- Stirling engine work time
Homework:
- no homework
 Class
15:
Friday,
10/12/2023
Class
15:
Friday,
10/12/2023Warm Up:
1. What is the purpose of a flywheel?
2. How do gasoline engines work?
 3.
What are some differences between
2-stroke engines
and 4-stroke engines?
(better 4 stroke
animation)
3.
What are some differences between
2-stroke engines
and 4-stroke engines?
(better 4 stroke
animation)4. How is this diesel engine different? Is it a 2-stroke or a 4-stroke?
5. What does a crankshaft do? How many cylinders does the engine in the video have?
Today:
- Cell phones in the caddy.
- Return Quizzes
- Finish your displacer.
- Add a string to your displacer.
- Duct tape the hole, thread the string, and add a plastic connector to your string.
- Add a connector to your membrane.
- Get a stand and write down the number next to your name on the board.
- Test your displacer. Add a decapitated balloon to your cylinder. Put your cylinder on the stand. Light an alcohol burner. Raise and lower your displacer, using the string, and observe.
- Measure the movement of your balloon and displacer, in cm. Divide those numbers by 2.
- Make a crankshaft.
- Connect your crankshaft to a flywheel. Write your flywheel number on the board.
- Connect the power piston to the crankshaft with wire rod.
- Connect the displacer to the crankshaft.
- Test your engine!
Homework:
- None! Enjoy your weekend!
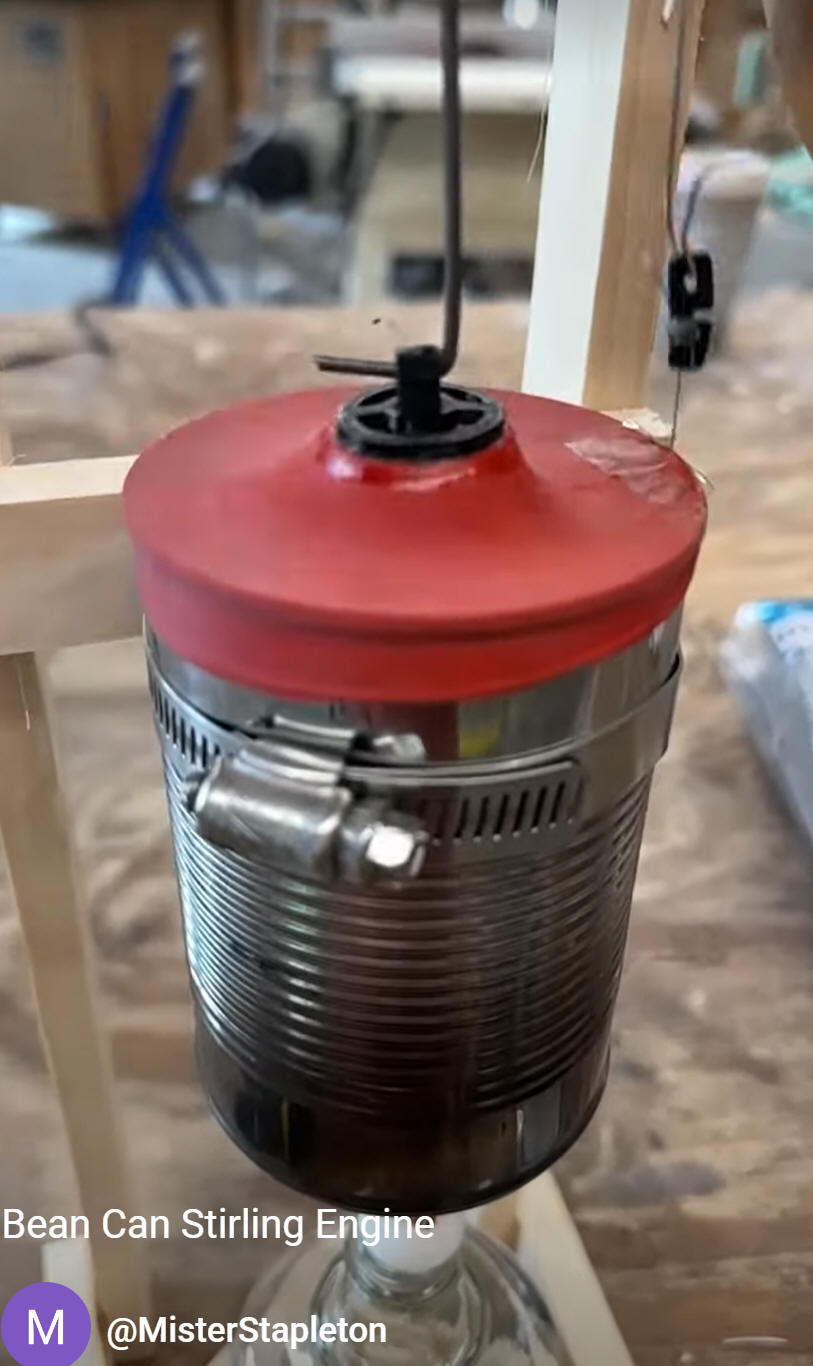 Class
14:
Wednesday,
10/11/2023
Class
14:
Wednesday,
10/11/2023Warm Up:
What makes this Stirling engine puff out and "suck in?"
Today:
- Cell phones in the caddy.
- Quiz
- We will be making Stirling Engines similar to this one
- Get a can
- Make a displacer
- Install the displacer
Homework:
- None!
 Class
13:
Thursday,
10/5/2023
Class
13:
Thursday,
10/5/2023Warm Up:
I measure the amount of force it takes to open my freezer door. I close the door again. Then I measure how much force it takes to open the freezer door a second time. Video
1. How is the required force different the second time?
2. Why?
Today:
- Cell phones in the caddy.
- Return papers
- Check/review homework
- Modeling Astronomy Concepts: practice quiz
Homework:
- Study for a quiz next class (next Wednesday), very similar to the practice quiz from today (and similar to the homework that was due today). Then submit the assignment in Google Classroom.
 Class
12:
Tuesday,
10/3/2023
Class
12:
Tuesday,
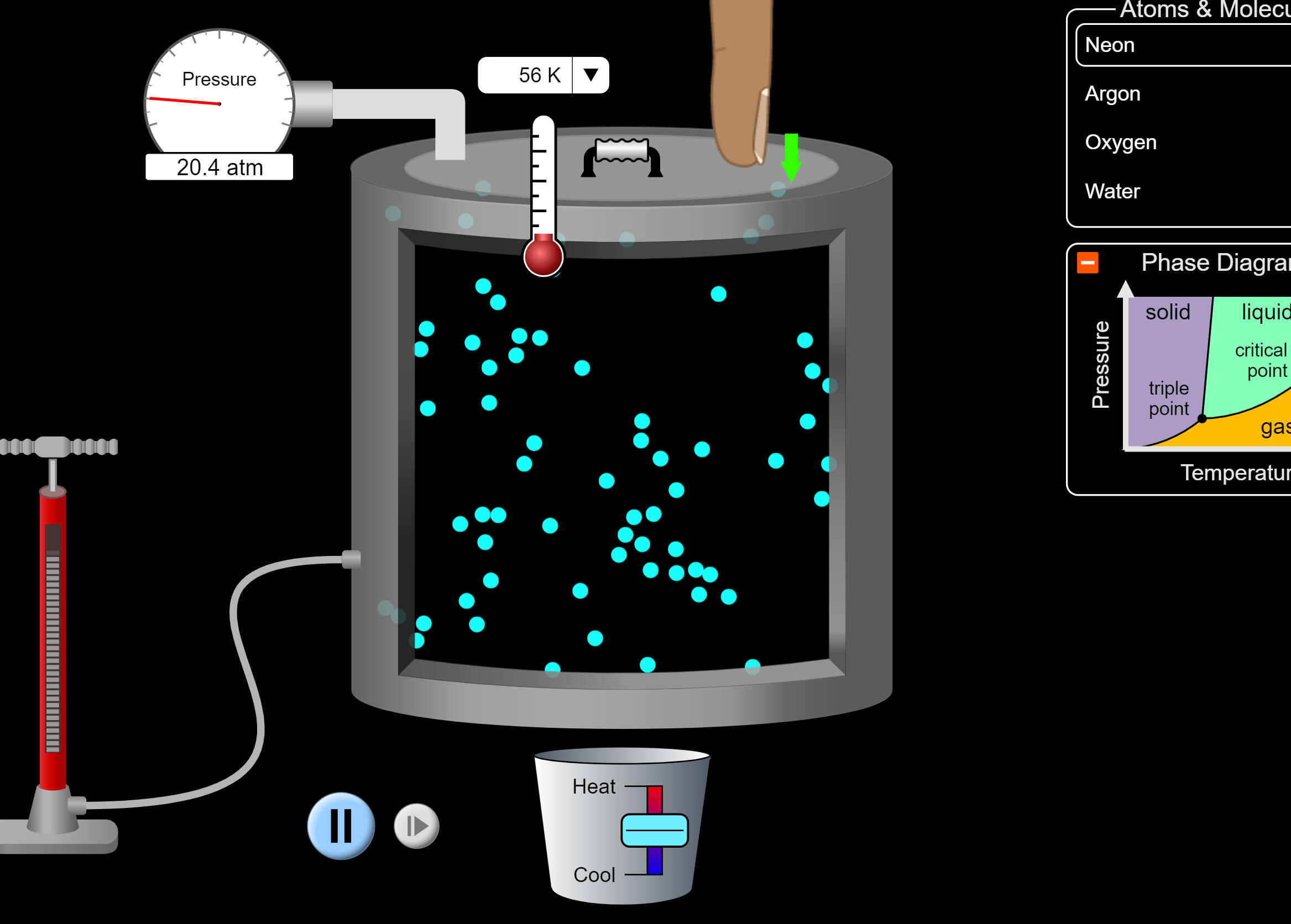
10/3/2023Warm Up: In the Phet States of Matter simulation, the container has a movable lid. What happens if you use the finger to push the lid downward when the substance is in gas phase?
1. What happens to the volume?
2. What happens to the pressure?
3. What happens to the temperature?
4. Why?
Today:
- Cell phones in the caddy.
- Return Quizzes. You can retake the quiz any time in FLEX. I haven't finished grading the video resubmissions.
-
Modeling Astronomy Concepts:
- Handout Part 3: How Changes in Pressure and Volume Affect Temperature (p. 9 of Astronomy Concepts Handout (PDF))
- Cloud in a Bottle (p. 10)
Homework:
- Packet p. 12, (#17-28)
 Class
11:
Friday,
9/28/2023
Class
11:
Friday,
9/28/2023Warm Up:
1. What would happen if you made a hole through the center of the Earth, and you jumped in?
2. If you made it all of the way through, where would you come out? (antipodes map)
Today:
- Cell phones in the caddy.
- Quiz
- Return (original copies of) the hot air balloon video grading sheets. Go over the answers. Prepare to do video corrections.
Homework:
- Unless your score was 36/36, correct your video for more points.
 Class
10:
Wednesday,
9/25/2023
Class
10:
Wednesday,
9/25/2023Warm Up:
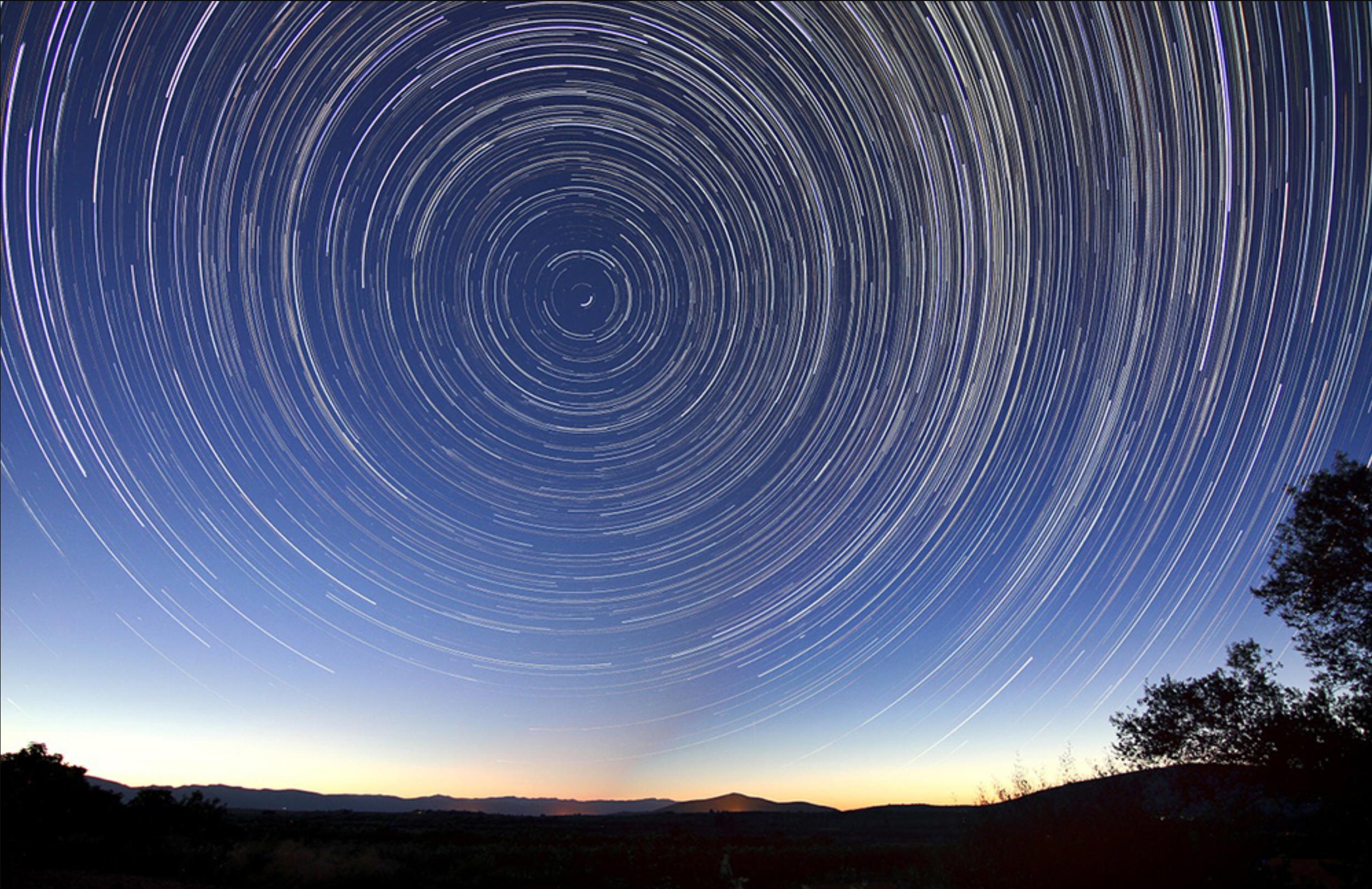
- What are the lines in the sky?
- How was the picture created?
- Why are the lines arranged in a circular pattern?
- If this picture was taken in the Northern Hemisphere, in which direction did the circles form? (clockwise or counter-clockwise)
- Which stars are moving faster, the inner ones or the outer ones? ** this is a trick question**
- If there is a star near the center, what is its name?
- Why did the photographer have to stop the picture before the stars made a complete circle?
Today:
- Cell phones in the caddy. If they're ever needed, ask Mr. S. first.
- Check to see that the videos are submitted correctly in Google Classroom. Make sure that I have access.
- Look at the links on this page that go with the 4rd 4th Quizlet: The Sun and Other Stars.
- How should you study? Do some quiz preparation together -- practice studying.
Homework:
- Study for the quiz next class (over Quizlets #3 and #4). When you're done, submit the assignment in Google Classroom.
 Class
9:
Monday,
9/25/2023
Class
9:
Monday,
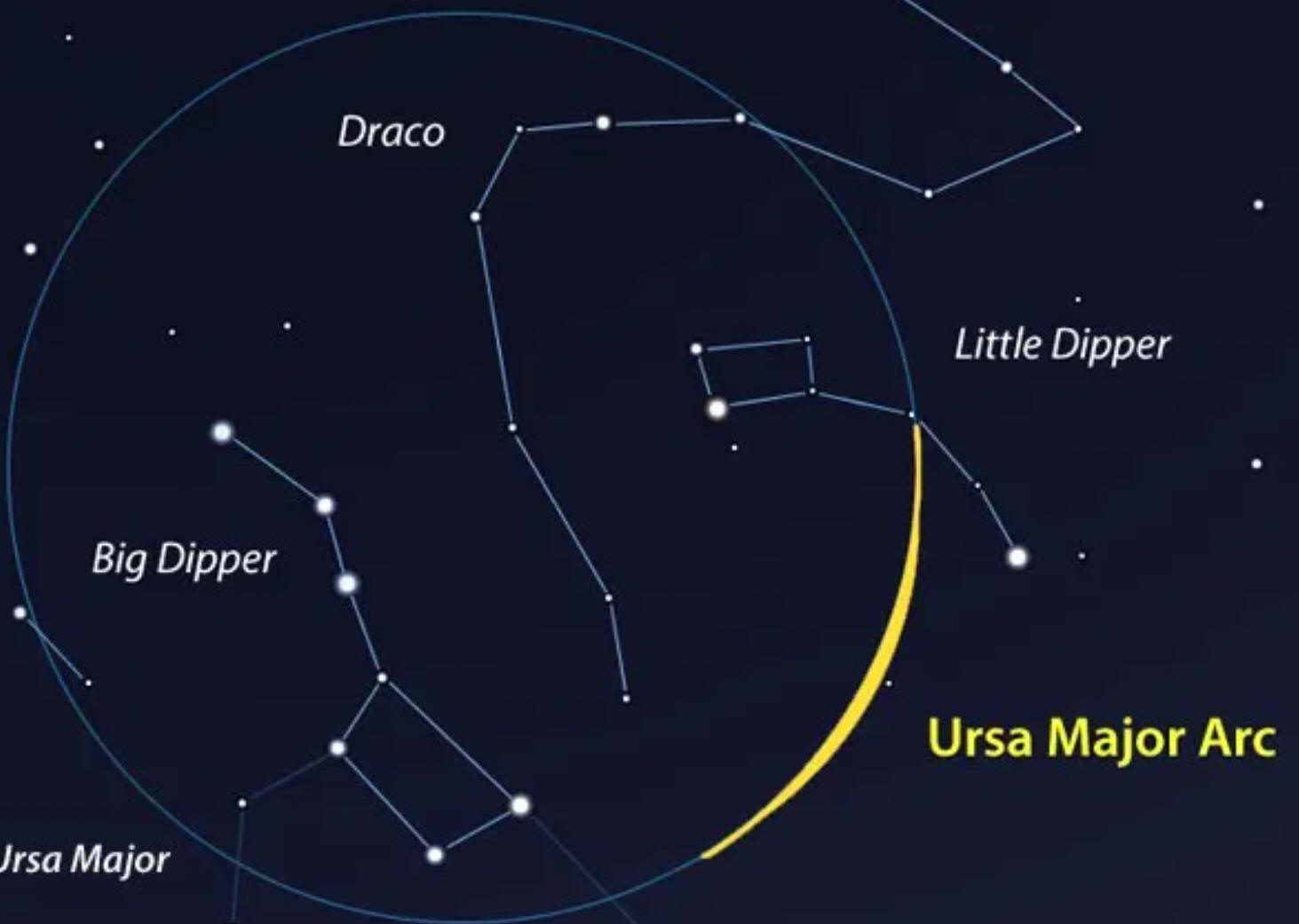
9/25/2023Warm Up:
1. Find Polaris (the North Star) in the picture on the right
2. Why might Polaris be harder to find tonight?
3. Suppose you went out last night and looked at the night sky, and it looked like the picture on the right. What time was it? Follow these directions for telling time with the Big Dipper.
Did you know that the Big Dipper isn't a constellation -- it's an asterism?Today:
- Cell phones in the caddy. If they're ever needed, ask Mr. S. first.
- Return quizzes -- don't forget this time!
- Check/review the Hot Air Balloon Practice homework from two classes ago. Hot air balloon practice Questions PDF Answers
- Look at grades in PowerSchool
- Look at the class YouTube playlist.
- Begin work on the hot air balloon
discussion video. It's due before next class.
- Example of a narrated video clip that I made using Screencastify.
Homework:
- See Google Classroom -- submit your hot air balloon discussion video before next class
 Class
8:
Thursday,
9/21/2023
Class
8:
Thursday,
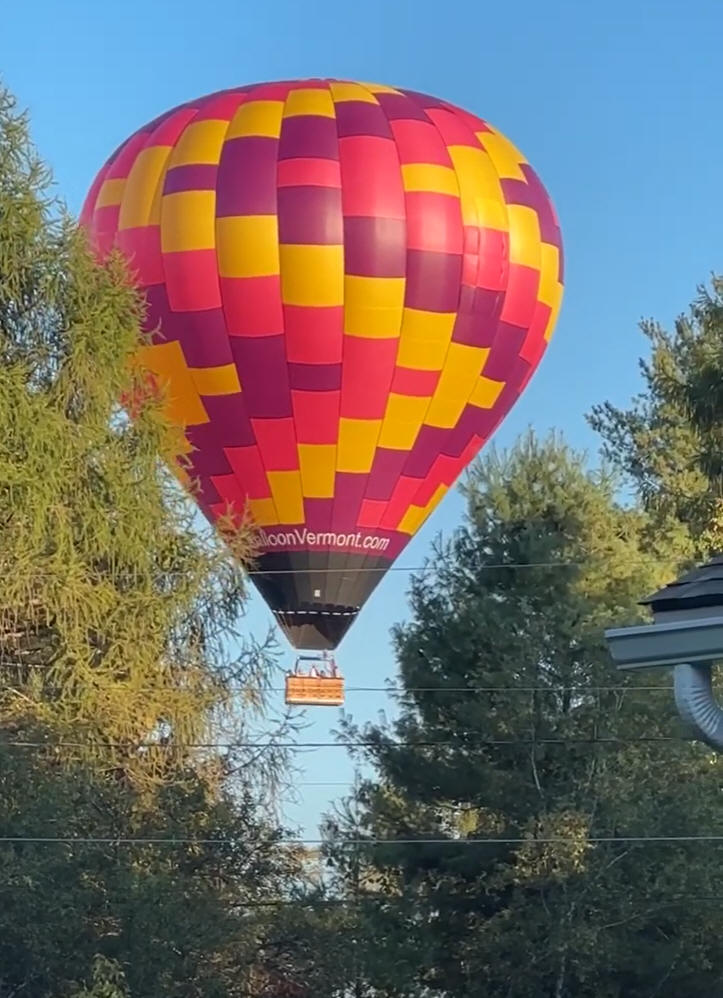
9/21/2023Warm Up:
What do you notice about this hot air balloon that I saw yesterday?
Today:
- Return quizzes.
- Check/review homework
- Hot Air Balloon Activity
- Make a hot air balloon.
- Make (and save) a video of your balloon being heated, beginning to fly, and then flying. Let's try to use Screencastify.
- Next class: Create a presentation explaining what's going on.
Homework:
- No homework!
 Class
7:
Tuesday,
9/19/2023
Class
7:
Tuesday,
9/19/2023Warm Up:
1. What will happen if I put a balloon over a flask of water and then boil the water?
2. What will happen if I put the flask on ice?
3. Will the balloon behave differently if I put it on after the water is already boiling?
4. What will happen if I inflate a balloon, tie it off, and then place it in cold water?
5. Why does all of this happen?
Today:
- Warm-up/Attendance
- Optional Quiz retake
-
Modeling Astronomy Concepts:
- Part 2: How Temperature Affects Volume and Pressure (p. 7-8 of Astronomy Concepts Handout (PDF)) FILLED-IN NOTES
Homework:
- Complete the Hot air balloon practice Questions PDF Answers
 Class
6:
Friday,
9/15/2023
Class
6:
Friday,
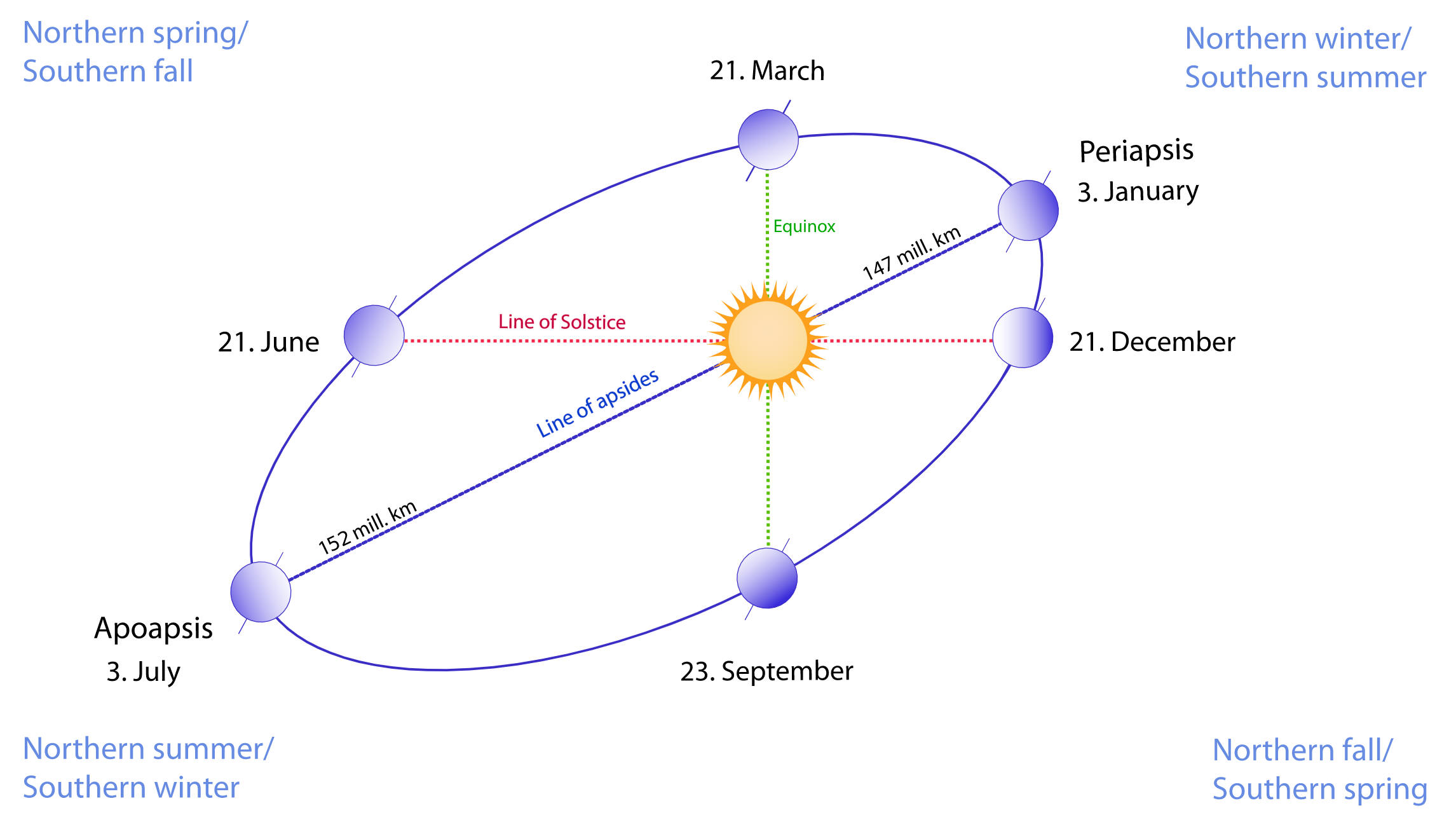
9/15/2023Warm Up:
1. According to this diagram from Wikipedia, on what date are we closest to the Sun?
2. Is this diagram correct?
3. Seasons on the Earth are not the same length. In Vermont, which of our seasons would you guess is the longest? Which is the shortest?
Orbit Simulation -- Explore a bit... Can you make the basic orbit more ellptical? When, why, and how does the speed of the satellite change? Is the Moon's orbit circular? What happens if we get rid of gravity?
Today:
- Warm-up/Attendance
- Return Quizzes -- do you like your score? What happened? Does it need to be fixed, and if so, how?
- Take another look in PowerSchool.
-- what will your grade be when I put the quiz in?
- Let's make sure everybody understands the grade they're seeing.
- Let's make sure everything is correct.
- Finally, if you need to fix something or complete a missing assignment, let's make sure that you know how to do that.
- New Objects in Space --
- Check out the 3rd Quizlet: Satellites, Moons, Comets, and Orbits together.
- Look at the links on
this page
that go with the 3rd Quizlet.
- Try the orbit simulation, to see what you can learn about orbits.
- Take a walk through a scale model of the solar system -- experience the vastness of space!
- PUT UP CHAIRS
Homework:
- Practice the 3rd Quizlet: Satellites, Moons, Comets, and Orbits until you can answer the questions. When you're done, submit the assignment in Google Classroom.
- Optional: If you want to improve your quiz score, study for a quiz retake next class.
 Class
5:
Wednesday,
9/13/2023
Class
5:
Wednesday,
9/13/2023Warm Up:
1. Suppose you hold an object at arm's length and use it to cover up the moon. How large does the object need to be to perfectly cover up the moon? Quarter sized? Dime sized? Something else?
2. What if you wanted to cover up the Sun? What object would be just the right size?
3. This picture shows how eclipses happen as the moon revolves around the Earth. Why don't we have two eclipses every month?
Today:
- Attendance
- Discuss homework
- Quiz over the first two Quizlets
- Practice with:
- Google Classroom
- PowerSchool
- Postponed for a drier day...Walk through a scale model of the solar system
Homework:
- None!
 Class
4:
Monday,
9/11/2023
Class
4:
Monday,
9/11/2023Warm Up:
1. How can I crush a soda can using a hot plate and ice water?
2. Forces are either pushes or pulls. Is the force that crushes the can a push or a pull?
3. What exerts that force?
Today:
- Attendance
- Check/review homework (VIDEO of us going over this). Talk about what to do if you get a zero because you didn't complete an assignment.
- Quick quiz (ungraded) to see how we're doing with mass, volume, density, and weight.
- New Objects in Space --
- Check out the "Planets (and other rocks orbiting the Sun)" Quizlet Together. Look at these links at the same time.
- Mr. Stapleton Slideshow -- photos I've taken in the last year
Homework:
- Study the second quizlet.
- Quiz next class over the first two quizlets.
 Class
3:
Thursday,
9/7/2023
Class
3:
Thursday,
9/7/2023Warm Up:
1. Why can't we see our breath right now?
2. What can I do so that you can see my breath?
3. How does that work?
4. How does this relate to meteors?
Today:
- Attendance
-
Modeling Astronomy Concepts:
- Finish the The Floating, Sinking, Floating, Sinking, Floating Challenge! -- fill out a neater version of the worksheet. 20 minutes of work time.
- Test your methods and award fruit snacks to the ones that work.
- New seats
- Check/review homework
Homework:
- Complete the Physical Properties Practice, on page 6 of the Astronomy Concepts Handout (PDF).
 Class
2:
Tuesday,
9/5/2023
Class
2:
Tuesday,
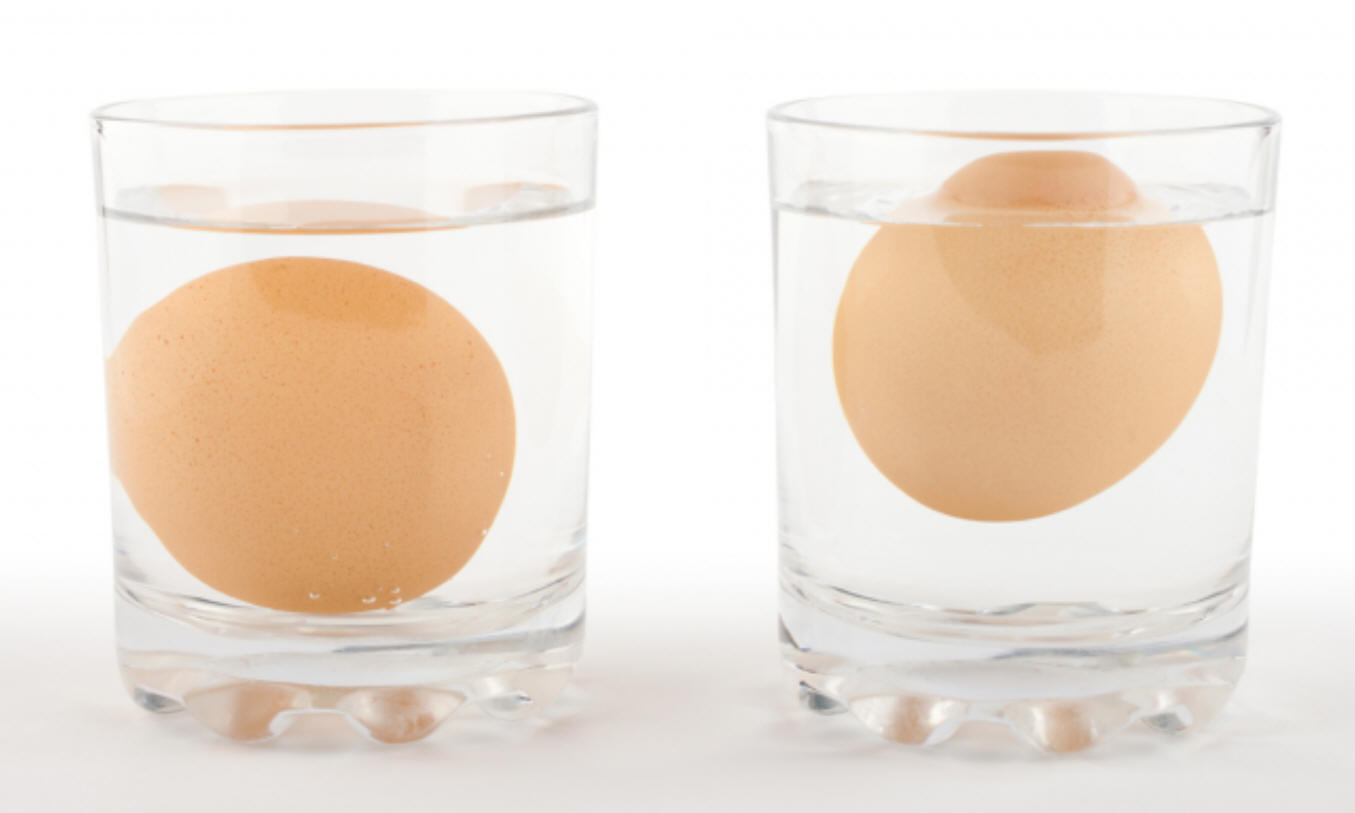
9/5/2023Warm Up: Suppose one egg floats, one egg sinks, and one egg neither sinks nor floats. What can you infer from this?
Today:
- Phones in the caddy
- Check/review homework
- Note: Tardies count, starting today!
- Same seats -- I'm still working on names -- I read about some of your seating preferences, and I will try to accommodate those on Thursday.
- Check/review homework
- Warm-up
- Objects in Space -- I added
a little to the Quizlet. Check out the new bonus questions.
- Check out Quizlet Together. Look at these links together.
-
Modeling Astronomy Concepts: Exploring
Physics and Chemistry concepts that help explain astronomy
- Get Astronomy Concepts Handout (PDF)
- Start physical properties practice -- Video from today's class
- Work on The Floating, Sinking, Floating, Sinking, Floating Challenge!
- Get phones.
Links
- All Unit 1 Quizlets (online flash cards) to study the objects in space facts.
- All unit 1 Objects In Space Facts, in the form of a list.
Homework:
- Finish the physical properties practice -- #20-24 on the third page of today's handout. Astronomy Concepts Handout (PDF)
 Class
1:
Thursday,
8/31/2023
Class
1:
Thursday,
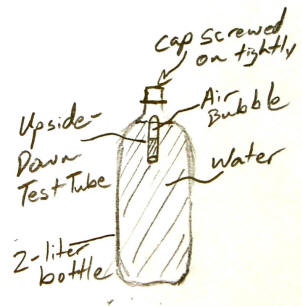
8/31/2023Warm Up:
The bottle on the right contains a "cartesian diver." The diver dives when the bottle is squeezed, and the diver rises when the bottle is released.
1. Why does this happen?
2. How does this relate to space science?
Today:
- Phones in the caddy
- Seating chart -- so I can learn names of students without pictures
- Warm-up
- Discuss passes
- Practice names/pronunciations. Get into seats (front rows).
- Fill out the Student info sheet (PDF)
- Get the
ESS Course Expectations.
Important things you need to know...
- Phones
- Hall passes
- The plan for the next few weeks:
- "Objects in Space"
- Modeling Astronomy Concepts: hands-on activities to experience some of the same processes that happen inside stars and during the Earth's formation
- Objects in Space -- Begin Structure and Scale of The
Universe -- making sense of the Quizlet facts
- Check out Quizlet Together. Look at these links together.
- Maybe watch one of these...
-
Modeling Astronomy Concepts: Exploring
Physics and Chemistry concepts that help explain astronomy
- Begin Film Canister Submarine lab.
- Clean up (B5/6 -- 1:05, B 7/8 --3:05)
- Wait to get phones.
- Links
- All Unit 1 Quizlets (online flash cards) to study the objects in space facts.
- All unit 1 Objects In Space Facts, in the form of a list.
- My info
- My Class goals
- Slideshow -- photos I've taken in the last year
- Homework:
- Study today's space facts, using the
"Structure and Scale of The Universe" Quizlet
- Go through the flash cards until you can answer at least the first 6. The rest may only appear as bonus questions.
- Try reverse mode at least once.
- Mark this assignment complete in Google Classroom!
- Study today's space facts, using the
"Structure and Scale of The Universe" Quizlet