Warm-up: None
Today:
- Last day of Physics 100!
- Please fill out the course evaluation if you have time
- Final Exam for seniors and anyone else who wants to take it early. Other students are still expected to be here on exam day. You could use it as a study hall.
- Review Materials PDF
Homework:
- Seniors -- have a great summer!
- The rest of you -- get ready for your final exam.
Warm-up: In order for this warmup to make sense, you first need to know something interesting about light...
Fred is conducting a laser experiment on a very, very, very fast train. He attaches a mirror to the roof of the train car and shines a quick pulse of laser light directly upward at the mirror. Hank is standing still outside the train. The train car is made of glass, so Hank can see the whole thing.
The pulse of laser light goes up, reflects off of the mirror, and then goes back down to the floor. There's enough dust in the air to make the laser pulse visible.
1) If Fred and Hank were to draw the laser pulse's "flight path" (as each of them sees it), what would each of them draw?
2) Who would see light travel a greater distance?
3) Assuming that the speed of the laser light is the same for both observers, who sees it travel for the longest amount of time?

Today:
- Final Exam Review -- get ready for senior final on Tuesday.
- Review Materials PDF
- Time for optional retake of Waves/Sound test -- or making up anything else that's missing.
Homework:
- Work on your final exam notes sheet. Senior final next class.
 Class
38:
Wednesday, 6/7/23
Class
38:
Wednesday, 6/7/23Warm-up:
What's happening in the picture on the right?
Today:
- Return tests and discuss.
- ??Reflection and Refraction Practice -- with laser ray boxes -- maybe
- Final Exam Review -- get ready for senior final on Tuesday.
- Review Materials PDF
Homework:
- Work on your final exam notes sheet.
Warm-up:
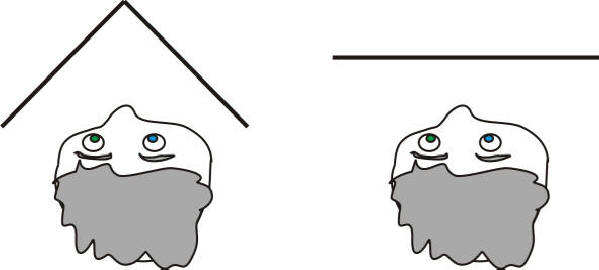
The diagram below shows top views of the same boy looking into mirrors. On the right, the mirror is a simple flat mirror. On the left, the mirror is two separate mirrors arranged at right angles. The boy has one blue eye and one green eye.
When he looks in the mirrors, where will his blue eye appear to be? Why?
Today:
- Return tests
- Review? -- but not the specific questions on the test -- similar ones, like the practice test.
- Test for the rest; retake for anyone who already took the test
Homework:
- None!
Warm-up:
Today:
- Test
Homework:
- None!
 Class
35:
Tuesday,
5/30/23
Class
35:
Tuesday,
5/30/23Warm-up: Does the Airzooka send a wave through the air? How can we tell if it's a wave?
Today:
- Return quiz 2 and review answers VIDEO
- Quiz 3 -- grade, return, and discuss VIDEO
- Quiz 1 -- Video
- Prepare for Thursday's test.
Homework:
- Test next class over...
- 1) Information on p. 1 of the packet, and the definitions of resonance and natural frequency. [This will be part 4 of the test] Unit 5 Handout PDF version
- 2) the information on quizzes 1, 2, and 3. Scroll down for more information about those quizzes. [This will be parts 1, 2, and 3 of the test. Each part will correspond to one of the three quizzes.] Here's a document with clean copies of all three Sound and Waves Quizzes.
 Class
34:
Thursday,
5/25/23
Class
34:
Thursday,
5/25/23Warm-up:
I am going to submerge an open pvc pipe in water. Then I will pull the pipe vertically out of the water, holding a ringing tuning fork next to it. At some point(s) the sound of the tuning fork will get louder and then quieter again.
1. Why will the sound get louder?
2. If we measure the pipe height at which the sound gets loud, we can calculate the speed of sound. How?
Today:
- Another example of wave properties and resonance? -- the Tacoma Narrows Bridge
- Check/review homework
- Quiz 2
- Practice Quiz 3 PDF Solutions
- Finish this later -- Play a specific note on an electric guitar (see directions in
Google Classroom)...
- Assemble a simple electric guitar.
- Strum a note and record its frequency.
- Mr. Stapleton will give you a new frequency to play. Play the new frequency by pressing down the string at the correct point and strumming. For full credit, your new frequency must be within 10% of the correct answer.
Homework:
- Prepare for quiz next class, like practice quiz 3. Solutions VIDEO from class
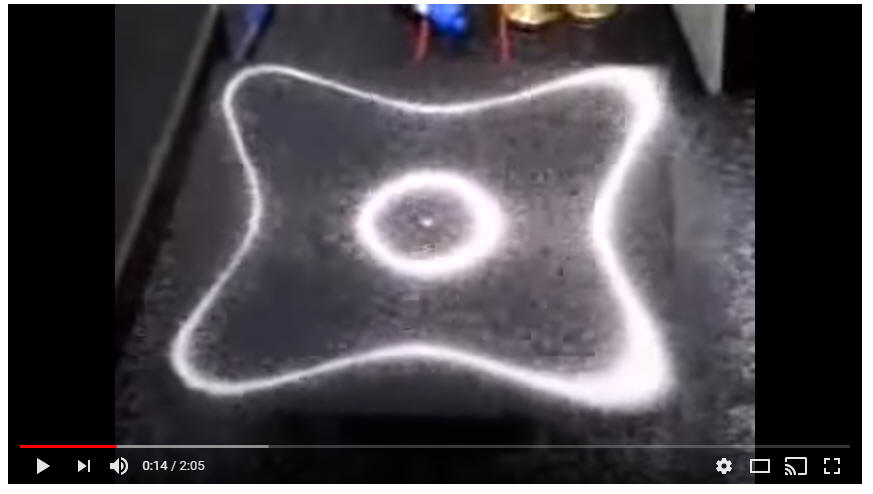 Class
33:
Tuesday,
5/23/23
Class
33:
Tuesday,
5/23/23Warm-up: This demonstration is like the demonstration of standing waves in a string. This piece of metal resonates with the speaker at a variety of natural frequencies.
1. Where are the nodes and where are the antinodes?
2. What's your reasoning?
Today:
- Check/review homework VIDEO
- Continue More Waves Notes (PDF) -- physics of string instrument pitch VIDEO
- Play a specific note on an electric guitar (see directions in
Google Classroom)...
- Assemble a simple electric guitar.
- Strum a note and record its frequency.
- Mr. Stapleton will give you a new frequency to play. Play the new frequency by pressing down the string at the correct point and strumming. For full credit, your new frequency must be within 10% of the correct answer.
Homework:
- "more practice" #5, on the "more waves notes" handout
- Quiz next class over the concepts represented in #6-24 on p. 11-13 of the packet Answers to p. 11-13
 Class
32:
Friday,
5/19/23
Class
32:
Friday,
5/19/23Warm-up: The red wave is traveling rightward along a string that is tied to a post. When it hits the post, the wave will reflect (echo) and travel backward through itself.
What will it look like when two identical waves pass through one another?
Today:
- Check/review homework. VIDEO of homework
- Return Quizzes VIDEO of quiz
- More Waves Notes (PDF) --
- Resonance
- Unit 5 Handout PDF version
- Mechanical waves links
- Work on homework
Homework:
- "more practice" 1-4, on today's handout
 Class
31:
Wednesday,
5/17/23
Class
31:
Wednesday,
5/17/23Warm-up:
If you're standing next to a race track, what do you hear as the cars pass you?
a. The cars' pitches change from high to low.
b. The cars' pitches change from low to high.
c. There is no change in pitch.
Today:
- Check/review homework.
- Quiz
- Doppler Effect Notes -- p. 10 VIDEO
- Unit 5 Handout PDF version
- Mechanical waves links
- Work on homework
Homework:
- #1-28 on the 2014-2015 test (packet p. 11-14)
 Class
30:
Monday,
5/15/23
Class
30:
Monday,
5/15/23Warm-up: Is this a real photo of a string?
Today:
- Check/review homework.
- Practice Quiz Questions and Solutions
- Notes and practice with standing waves (p.6...)
- Unit 5 Handout PDF version
- Mechanical waves links
Homework:
- Prepare for the quiz next class
 Class
29:
Thursday,
5/11/23
Class
29:
Thursday,
5/11/23Warm-up: If you see lightning strike a point 1 mile away, how long can you expect to wait before you hear thunder? Why?
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Notes and Practice
- Unit 5 Handout PDF version
- Mechanical waves links
Homework: Two things...
- #17-22 on p. 9 (and maybe #23, also)
- #31-33 on Packet p. 14-15
 Class
28:
Tuesday,
5/9/23
Class
28:
Tuesday,
5/9/23Warm-up:
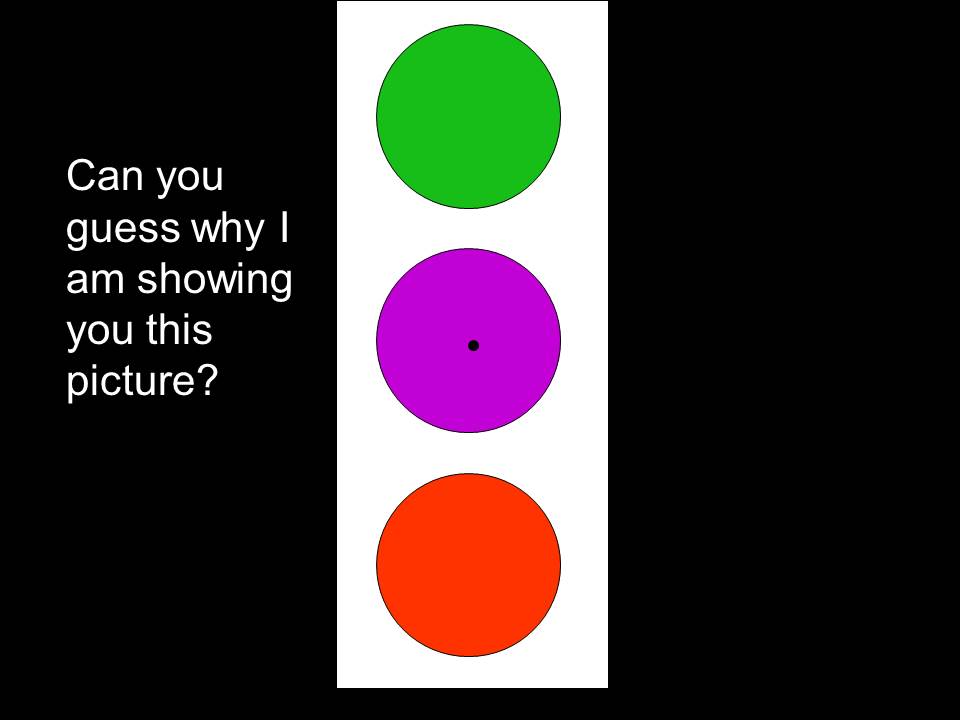
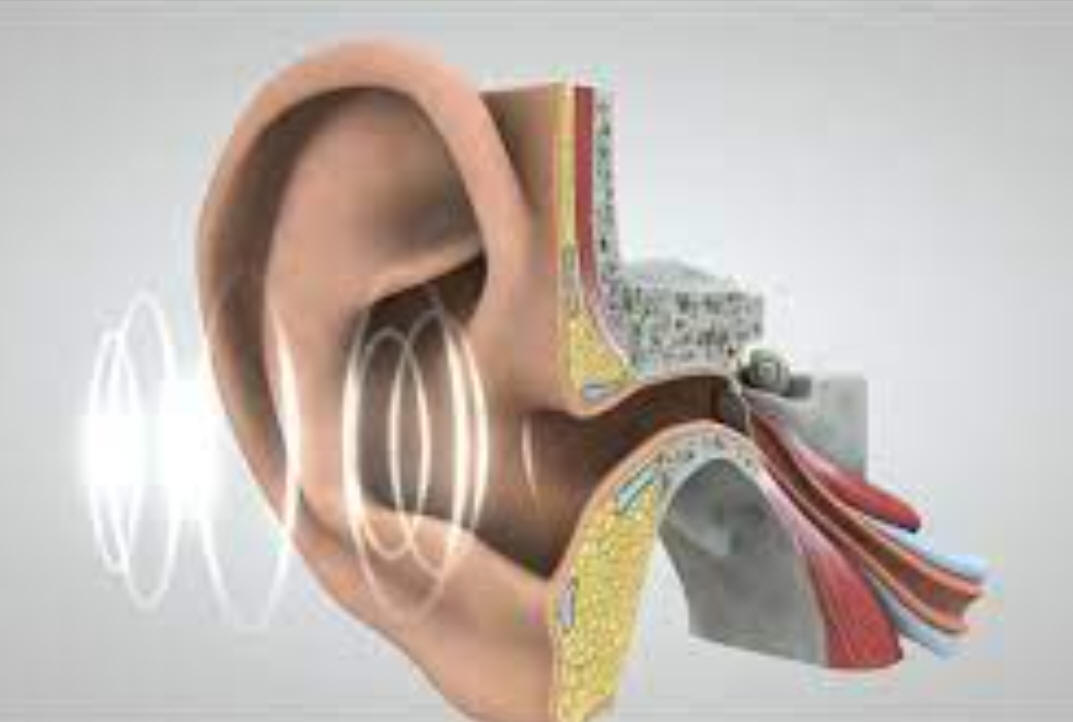
What is a wave? What is a sound? How do ears work?
Today:
- New Unit -- Sound and Waves VIDEO of notes
Homework: Complete practice questions on packet p. 7-8, except for number 9 and the wavelength on number 16. Notes and homework answers
 Class
27:
Friday,
5/5/23
Class
27:
Friday,
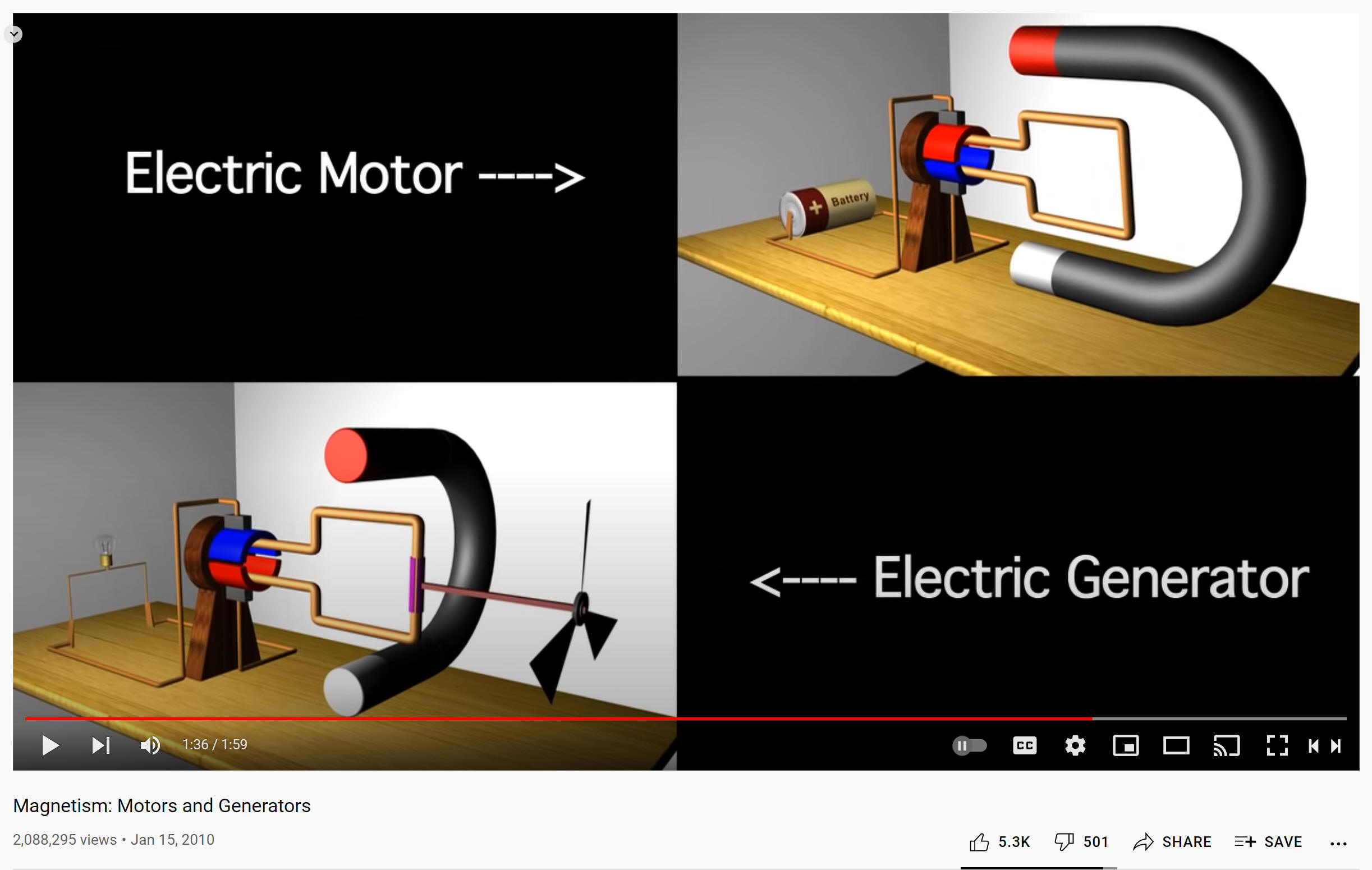
5/5/23Warm-up: How is an electric generator like an electric motor?
Today:
- Build your motor and make your motor video. In the video, show your motor working and explain how it works. In your video, you must answer the questions below. Everyone in your group (who wants credit) must answer at least one question during the video. If your explanations are correct, but your motor doesn't work, your score will be 80%. If it will only turn a little bit you can earn up to 90%. For 100%, your explanations must be correct, and your motor must continue to rotate when you are not holding it. You may come to FLEX to try to improve your score.
- As the coil rotates, sometimes current passes through the coil. What path does the current follow at these times? Trace the path of the current from the positive terminal of the power source to the negative terminal.
- Why does the motor move? What causes the force?
- This motor will only keep rotating if the current flow constantly turns on and off. This turning on an off can happen because you get lucky, and the electrical contacts bounce up and down. It can also happen because of the way you carefully sand the contacts on one side. What would this motor coil do if current were always (continuously) flowing through the coil?
- Disassemble your motor and return the materials.
- Correct your solenoid buzzer video and resubmit it in Google Classroom. Instead of using your real buzzer, you can print this picture of a solenoid buzzer and use it to make your video. Make it clear who is answering each question. I can't always identify voices.
Homework: None
 Class
26:
Wednesday,
5/3/23
Class
26:
Wednesday,
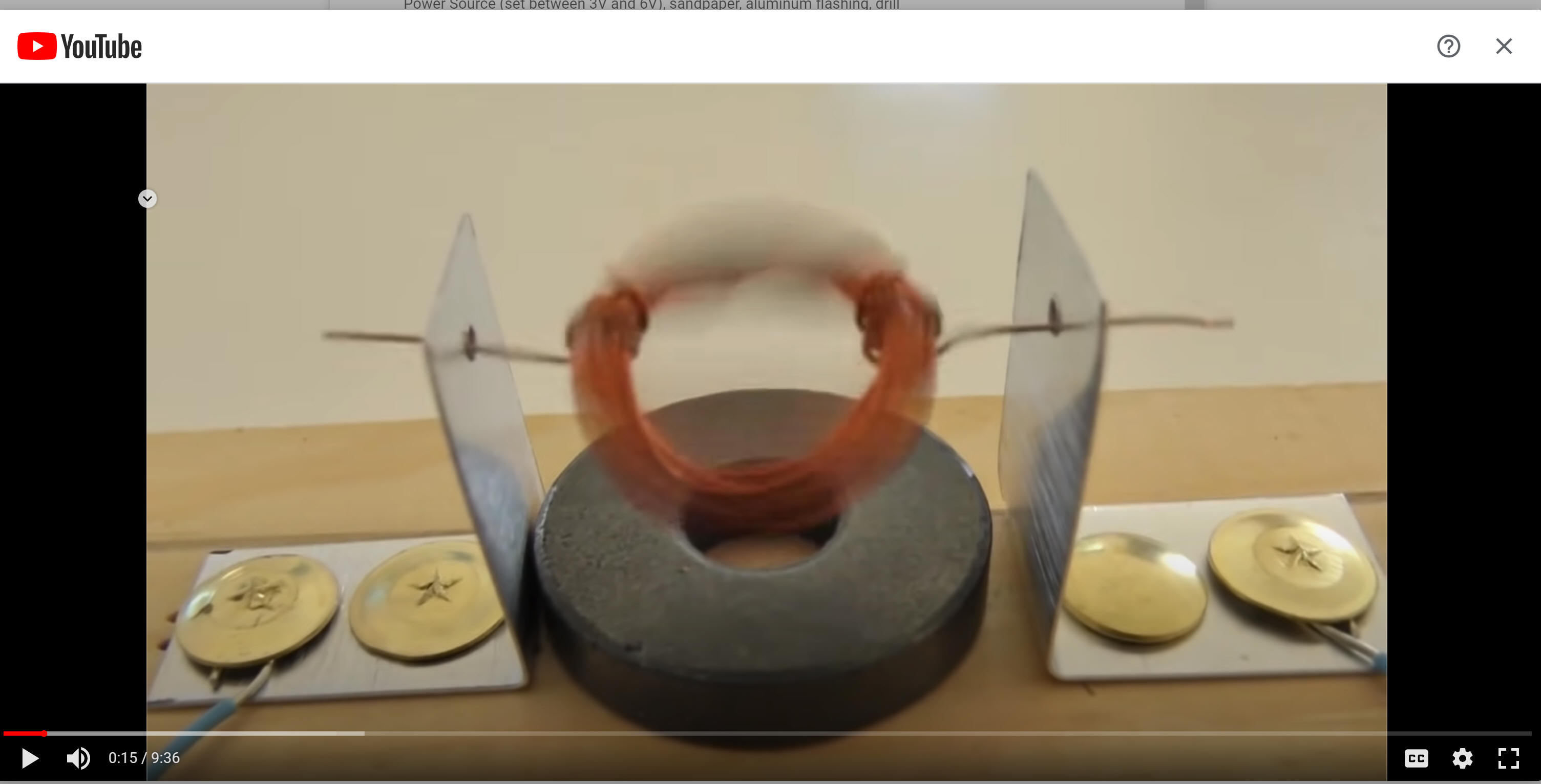
5/3/23Warm-up: How does this electric motor work? How can it be improved?
Today:
- 15 minutes to get your buzzer working.
- 20 minutes to make and submit a video. In the video, show your
buzzer working and explain how it works. In your video, you
must answer the questions below. Everyone in your group (who
wants credit) must answer at least one question during the video.
If your explanations are correct, but your buzzer won't buzz, your
score will be 80%. If it will buzz only while you hold it, you
can earn up to 90%. For 100%, your explanations must be
correct, and your buzzer must continue to buzz when you are not
holding it. You may come to FLEX to try to improve your score.
- Show the solenoid. Explain what a solenoid is, and what it does.
- How does current travel when the solenoid is turned on (closed loop)? Trace the path of the current from the positive terminal of the power source to the negative terminal.
- Show how the solenoid gets turned off, and explain why.
- Show how the solenoid gets turned back on, and explain why this happens.
- Explain what causes the buzzing noise.
- Disassemble buzzers. Return wire for reuse next year.
- In groups of 3 or fewer, make a motor like the one in the warm-up video. Pay attention and take notes when I give directions and explain how the motor works. You will have to make a video explaining how it works!
Homework: None
 Class
25:
Monday,
5/1/23
Class
25:
Monday,
5/1/23Warm-up:
1. What is sound?
2. What's happening in the "Amazing Water and Sound Experiment?"
Today:
- Return tests
- Make a solenoid buzzer: Watch this
instructional video showing how to make a
Solenoid Buzzer.
Draw a sketch of a solenoid buzzer design that uses
only the materials below:
- wood, nails, hot glue/glue guns, drill/drill bits, sheet metal screws, enameled wire (10m of 28 gauge), sandpaper (and belt sander), saw (not really necessary), strips of springy magnetizable steel (approx 0.5" wide, 3" long), and a D.C. power source (set betwen 3V and 6V).
- With those materials, you will have to make a working solenoid buzzer, as shown in the video.
- Make a video. In the video, show your
buzzer working and explain how it works. Everyone in your
group (who wants credit) must explain part of this. Your video
must answer the following questions.
- Show the solenoid. Explain what a solenoid is, and what it does.
- How does current travel when the solenoid is turned on (closed loop)? Trace the path of the current from the positive terminal of the power source to the negative terminal.
- Show how the solenoid gets turned off, and explain why.
- Show how the solenoid gets turned back on, and explain why this happens.
- Explain what causes the buzzing noise.
Homework:
- None.
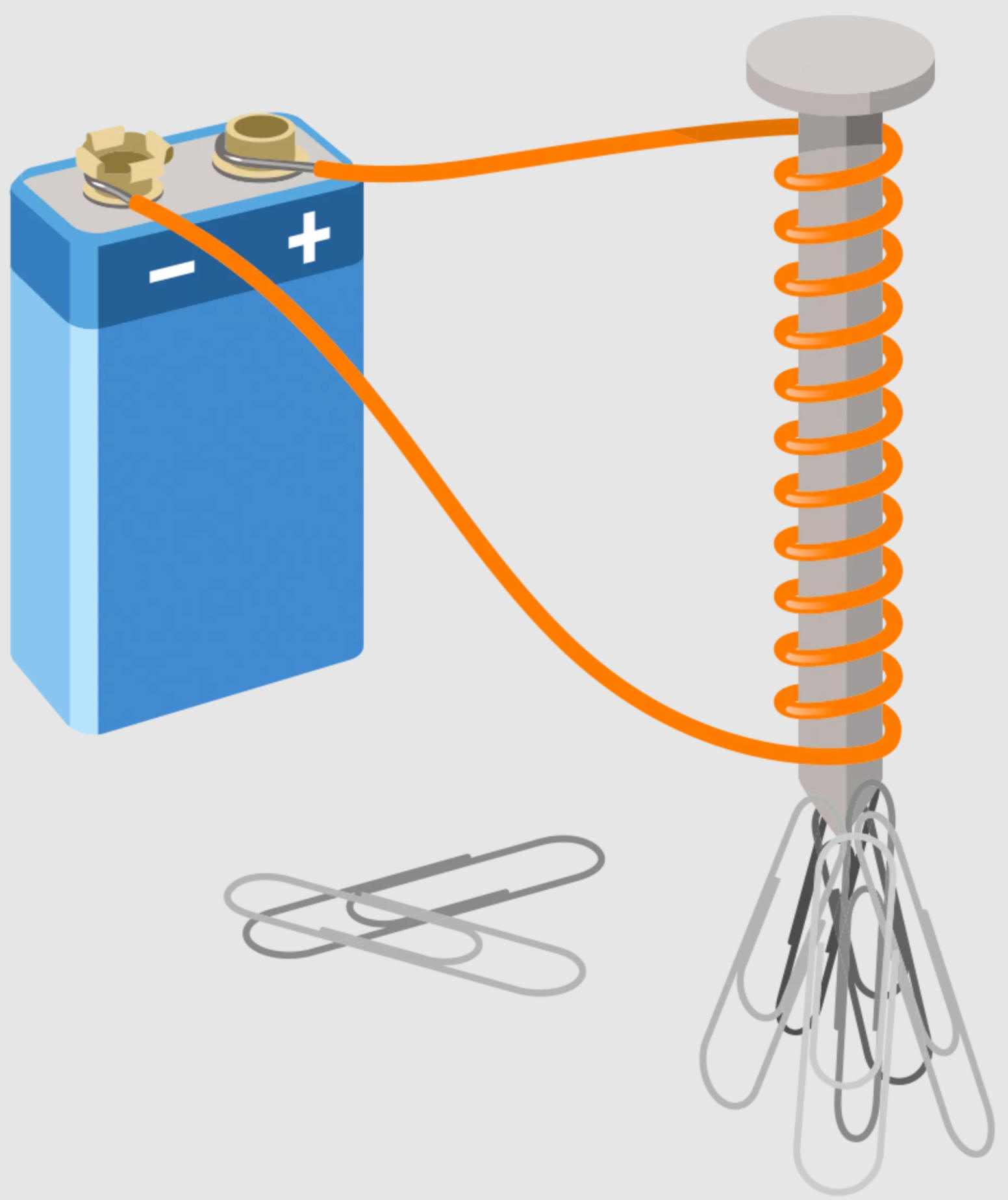 Class
24:
Thursday,
4/20/23
Class
24:
Thursday,
4/20/23Warm-up:
What is a solenoid? How does it work?
Today:
- Return quiz 2.
- Test!
- Today -- make and test the solenoid for this
project...
- Make a solenoid buzzer: Watch this
instructional video showing how to make a
Solenoid Buzzer.
Draw a sketch of a solenoid buzzer design that uses
only the materials below:
- wood, nails, hot glue/glue guns, drill/drill bits, sheet metal screws, enameled wire (10m of 28 gauge), sandpaper (and belt sander), saw (not really necessary), strips of springy magnetizable steel (approx 0.5" wide, 3" long), and a D.C. power source (set betwen 3V and 6V).
- With those materials, you will have to make a working solenoid buzzer, as shown in the video.
- Make a solenoid buzzer: Watch this
instructional video showing how to make a
Solenoid Buzzer.
Draw a sketch of a solenoid buzzer design that uses
only the materials below:
Homework:
- None. Have a good break!
 Class
23:
Tuesday,
4/18/23
Class
23:
Tuesday,
4/18/23Warm-up:
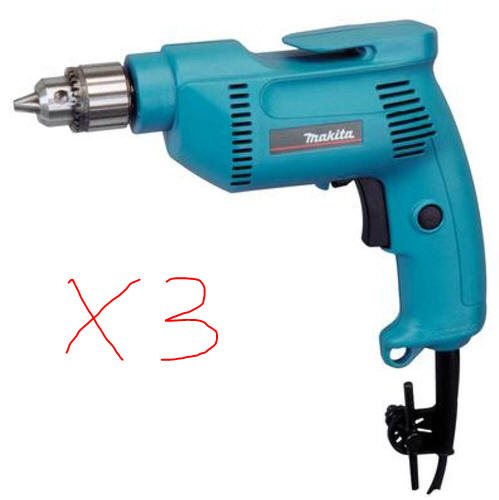
When electric current flows through an electric motor, a force is produced, causing motion.
An electric motor forced into motion generates electric current.
I have three identical corded drills and one driver bit. With no additional materials, how can we power two of the drills by plugging just one of them into the wall?
Today:
- Quiz 2 -- Review answers. Next class, if you like your grade for Quiz 2, you don't have to take that part of the test.
- Return quiz 1 and review -- VIDEO
- More circuit practice
- BN?
Homework:
- Test on Thursday, similar to the two quizzes and practice quizzes. Prepare!
 Class
22:
Friday,
4/14/23
Class
22:
Friday,
4/14/23Warm-up: What happens when you try to electrocute a pickle using a standard household 120V outlet? Will this work on other things?
Today:
- Return and look over Circuit Labs -- see if they follow the rules for series and parallel.
- Quiz
- Do the 2nd practice quiz from -- Practice Quizzes 1 and 2 (PDF) VIDEO
- More practice?
Homework:
- Quiz on Tuesday. Practice the practice quiz.
 Class
22:
Wednesday,
4/12/23
Class
22:
Wednesday,
4/12/23Warm-up: Which batteries and pumps on the right push out the most current? The least? How many amps of current flow from each battery?
Today:
- Check/review homework VIDEO
- Do the 1st practice quiz from -- Practice Quizzes 1 and 2 (PDF) VIDEO of the first part of the practice quiz unfortunately, I forgot to start the video again for the second part.
- More practice?
Homework:
- Quiz on Friday. Practice the practice quiz and last class' homework.
 Class
21:
Monday,
4/10/23
Class
21:
Monday,
4/10/23Warm-up: Can we create a circuit with an electronic dog collar as the battery and people as the resistors?
Today:
- Check/review homework from class #19.
- Return circuit labs and discuss.
- Notes -- Current and Circuits, part 2 (PDF) VIDEO1 VIDEO 2
- More practice?
Homework:
- Finish the fill-in-the-blank circuit problems on the back of today's handout.
 Class
20:
Thursday,
4/6/23
Class
20:
Thursday,
4/6/23Warm-up:
1. How can you start a fire with a 9 Volt Battery and some steel?
2. Ohm's Law says V = IR. Guess what each of the letters means. Solve for I. Solve for R.
3. P = VI. Guess what each of the letters means. Solve for V. Solve for R.
Today:
- If you haven't already done it, turn in your handout from last week.
- Lets talk about lightning rods again. I was mislead! Openstax physics link. NOAA website
- Circuit Lab PDF Version
Homework:
- None
 Class
19:
Tuesday,
4/4/23
Class
19:
Tuesday,
4/4/23Warm-up:
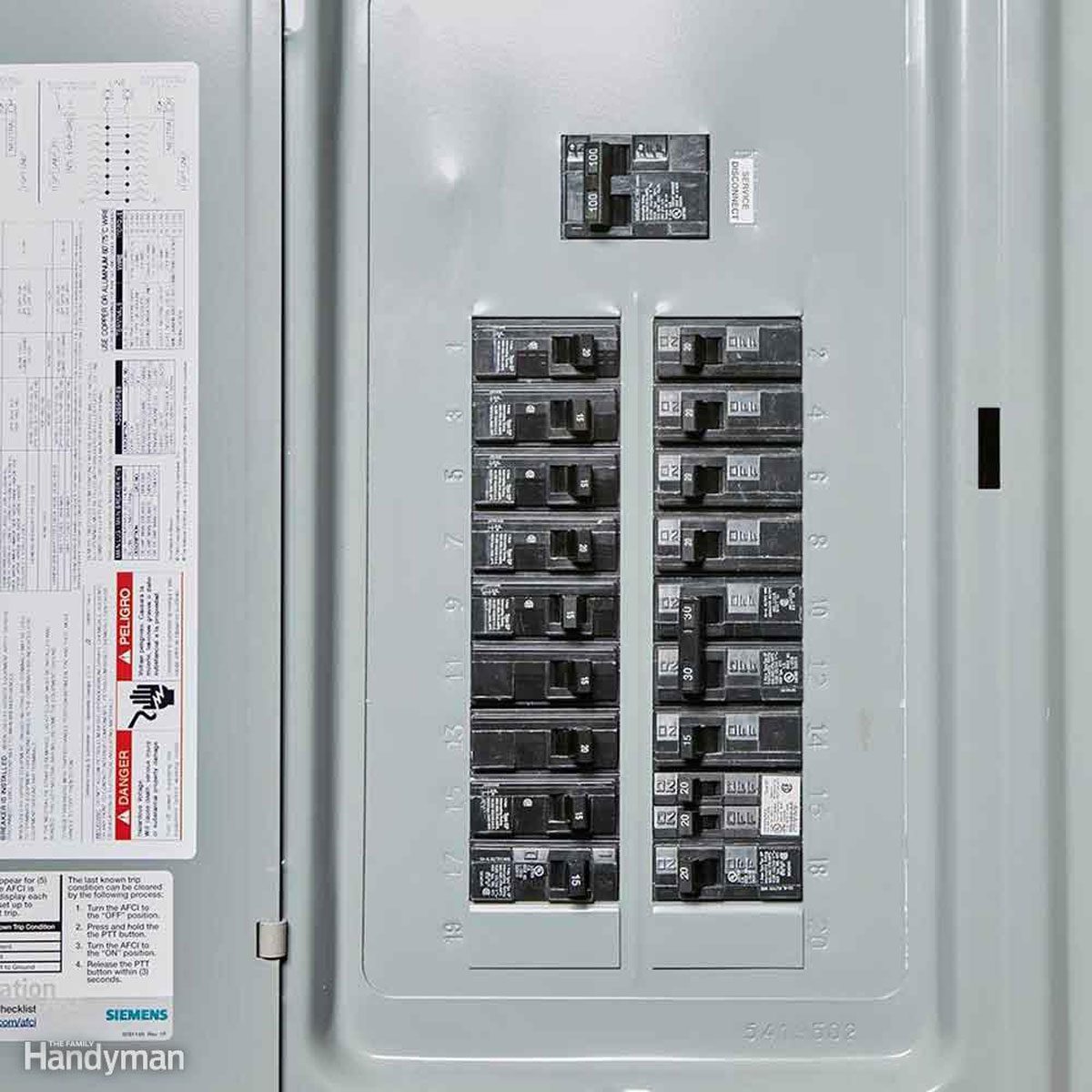
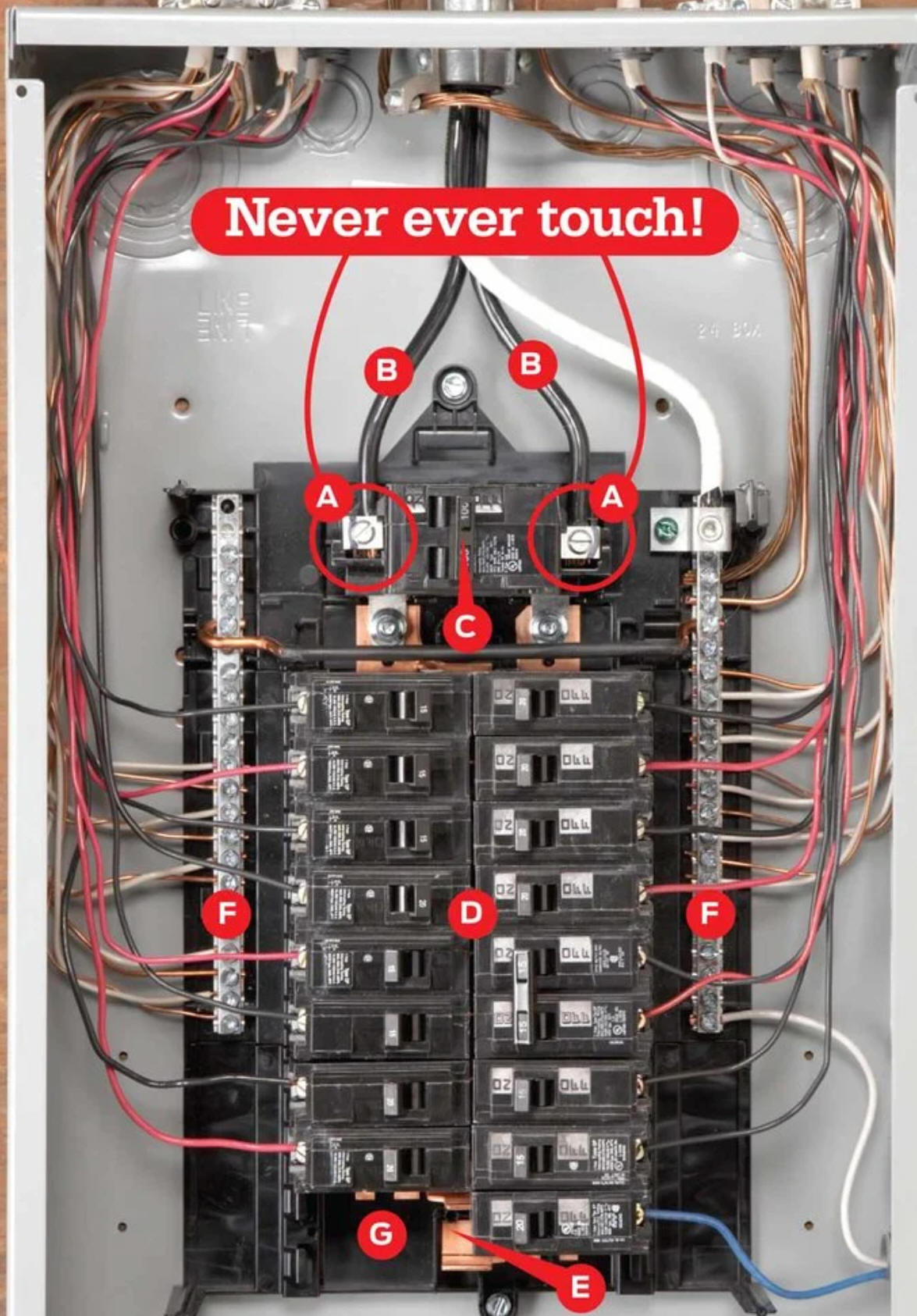
The pictures on the right show breaker panels.
1. What is the purpose of a breaker?
2. How does an electrician decide how many breakers are needed?
3. Why are there different kinds of breakers?
- Return tests and review (VIDEO). Come to FLEX by Friday if you want to retake part or all of the test. I have retakes ready to go.
- Turn in the video series handouts. How far did you get?
- Feedback on the substitutes.
- Circuit Notes and pHet activity PDF Version Filled-in Notes Video from class
Homework:
- Finish the Phet activity -- if you didn't finish it in class
 Class
18:
Friday,
3/31/23
Class
18:
Friday,
3/31/23Today:
- Continue the video series: Shedding Light on Electricity
- Answer the questions while you watch each segment.
-
Video Sign-in Information:
- Username: ehscte
- Password: hornets
- Episode 3: Electric Current
- Episode 4: Voltage, Current, and Resistance
- Episode 5: Electrical Safety
- If you need to print more QUESTIONS, use this link.
Homework:
- None
 Class
17:
Wednesday,
3/29/23
Class
17:
Wednesday,
3/29/23Today:
- Continue the video series: Shedding Light on Electricity
- Answer the questions while you watch each segment.
-
Video Sign-in Information:
- Username: ehscte
- Password: hornets
- Episode 2: Electric Circuits,
-
Episode 3: Electric Current,

- Episode 4: Voltage, Current, and Resistance
- If you need to print more QUESTIONS, use this link.
Homework:
- None
 Class
16:
Monday,
3/27/23
Class
16:
Monday,
3/27/23Today:
- Begin the video series: Shedding Light on Electricity. Answer the questions while you watch each segment.
- Video Sign-in Information:
- Username: ehscte
- Password: hornets
-
Episode 1: Sources of Electricity
- Watch the Video, and while you watch...
- Answer the questions
-
 Begin
Episode 2: Electric Circuits, and answer the questions while you
watch.
Begin
Episode 2: Electric Circuits, and answer the questions while you
watch. - If you need to print more QUESTIONS, use this link.
Homework:
- None
 Class 15:
Wednesday,
3/22/23
Class 15:
Wednesday,
3/22/23Warm Up: How does an electric fence work?
Today:
- Return quiz 3.
- Discuss the test review and get scores for Quiz 2.
- Test!
- Next week -- Mr. Stapleton is gone; video series on electricity, electric current, circuits, and more.
Homework:
- None
Warm Up: None
Today:
- Return quiz #2
- Take Quiz #3
- Complete the Electrostatics Test Review (PDF)
- Watch the video and check your answers. If you don't understand something, ask your classmates for help.
Homework:
- Study!
 Class
13:
Friday,
3/17/23
Class
13:
Friday,
3/17/23Warm Up: Why is the guy in the video wearing a metal suit?
Today:
- Another gas station fire
- Quiz
- Check/review homework VIDEO, Part 1
-
Two last things:
- How to defeat a Van de Graff generator (or keep your barn from burning down) -- and why it works.
- One way to stay safe in a lightning storm -- and why it works.
- Charge some conductors.
- I will be gone on Monday. On monday, you will take the last quiz, complete the test review, and check your test review answers. The test will be on Wednesday.
Homework:
-
Quiz on Monday over Electrostatics notes part 3 and these two
additional concepts: (VIDEO,
Part 1.
VIDEO
part 2)
- The electric field inside a conductor is zero (there is no electric field inside a conductor). This is why the inside of a car is a safe place to be during a lightning storm.
- Smooth surfaces store build up charge, and pointy surfaces leak charges. This is why barns have pointy lightning rods (to leak built up charge into the atmosphere). This is also why Van de Graaff generators are smooth and round.
 Class
13:
Thursday,
3/16/23
Class
13:
Thursday,
3/16/23Warm Up: What do you think will happen if we make John Travoltage rub his foot on the floor and then hold his hand by the doorknob? Why?
Today:
- Return quizzes
- Check/review homework VIDEO
- Charge some conductors.
- Electrostatics Notes, part 3 PDF VIDEO
Homework:
- Complete the practice on the back of Electrostatics Notes, part 3 PDF
- Study for quiz tomorrow, over electrostatics notes part 2 and practice quiz 2)
 Class
12:
Tuesday,
3/14/23
Class
12:
Tuesday,
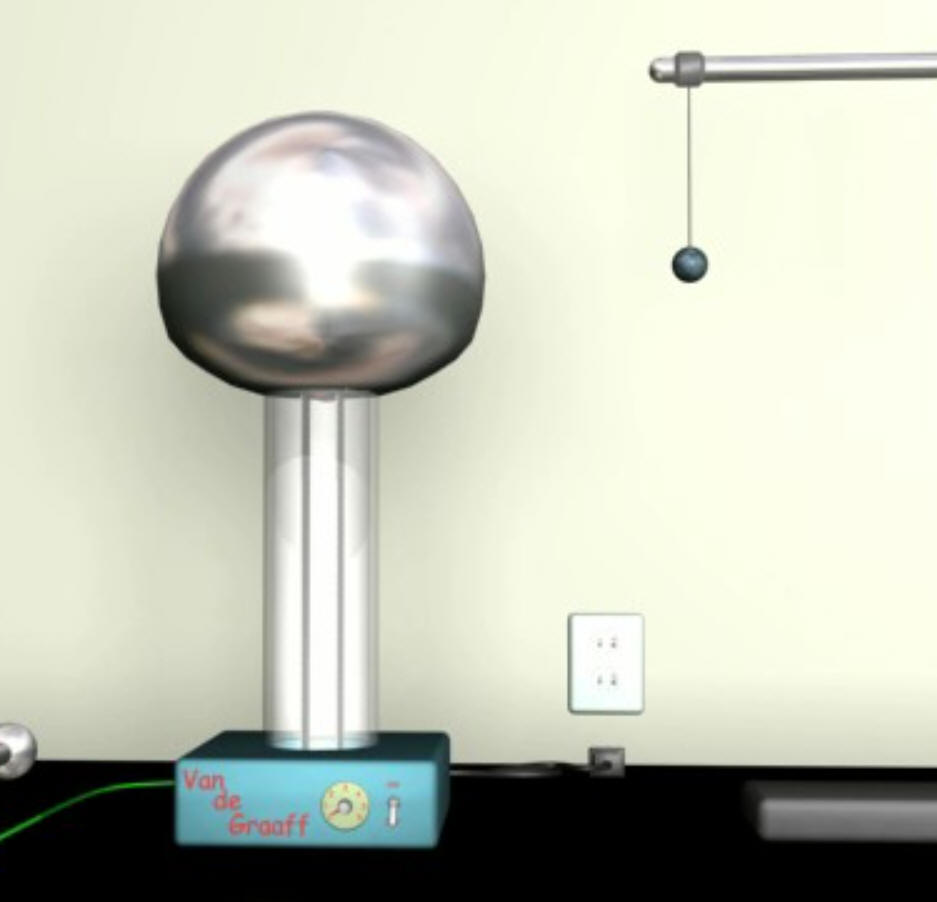
3/14/23Warm Up:
There is a "pith ball" hanging next to the Van de Graaff generator. The pith ball is foam that is covered with a conductive, metallic paint. What do you think will happen when the Vand de Graaff generator is turned on? Why?
Today:
- Quiz
- Electricity Notes, Part 2 (Conductors, Insulators, and Charging by Induction) (PDF) VIDEO from class
Homework:
Warm Up:
1. What events contributed to this gas station fire?
2. How could it have been prevented?
Today:
- Who is going to retake the test next week?
-
Finish the
Sticky Tape (Static Electricity) Activity
PDF Version
Results/Answers VIDEO
- Confirm answers with the electric field sensor
- What static charges are created when you remove some tape from a tape dispenser? What if you use duct tape, instead of clear tape?
- How can you create the most positive charge using clear tape?
- Take the electrostatics practice quiz #1 (pdf) Page 1 VIDEO Page 2 VIDEO
- Electricity Notes, Part 2 (Conductors, Insulators, and Charging by Induction) (PDF)
Homework:
- Quiz next class. Study your notes and the practice quiz.
 Class
10:
Wednesday,
3/8/23
Class
10:
Wednesday,
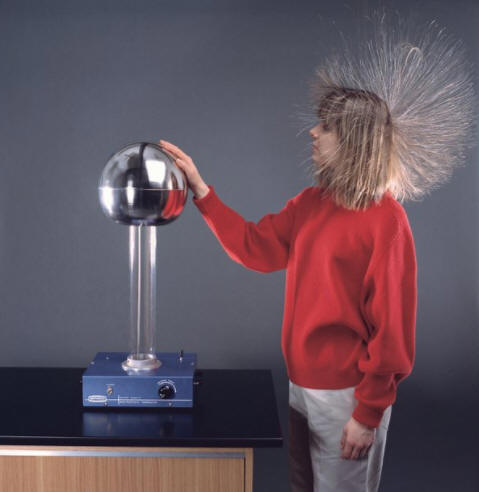
3/8/23Warm Up:
How does a Van de Graaff Generator Work?
Today:
- Return tests
- Finish Electrostatics Notes Part 1 (PDF) VIDEO
- Sticky Tape (Static Electricity) Activity PDF Version VIDEO introduction
Homework:
- None

 Class
9:
Tuesday,
2/21/23
Class
9:
Tuesday,
2/21/23Warm Up:
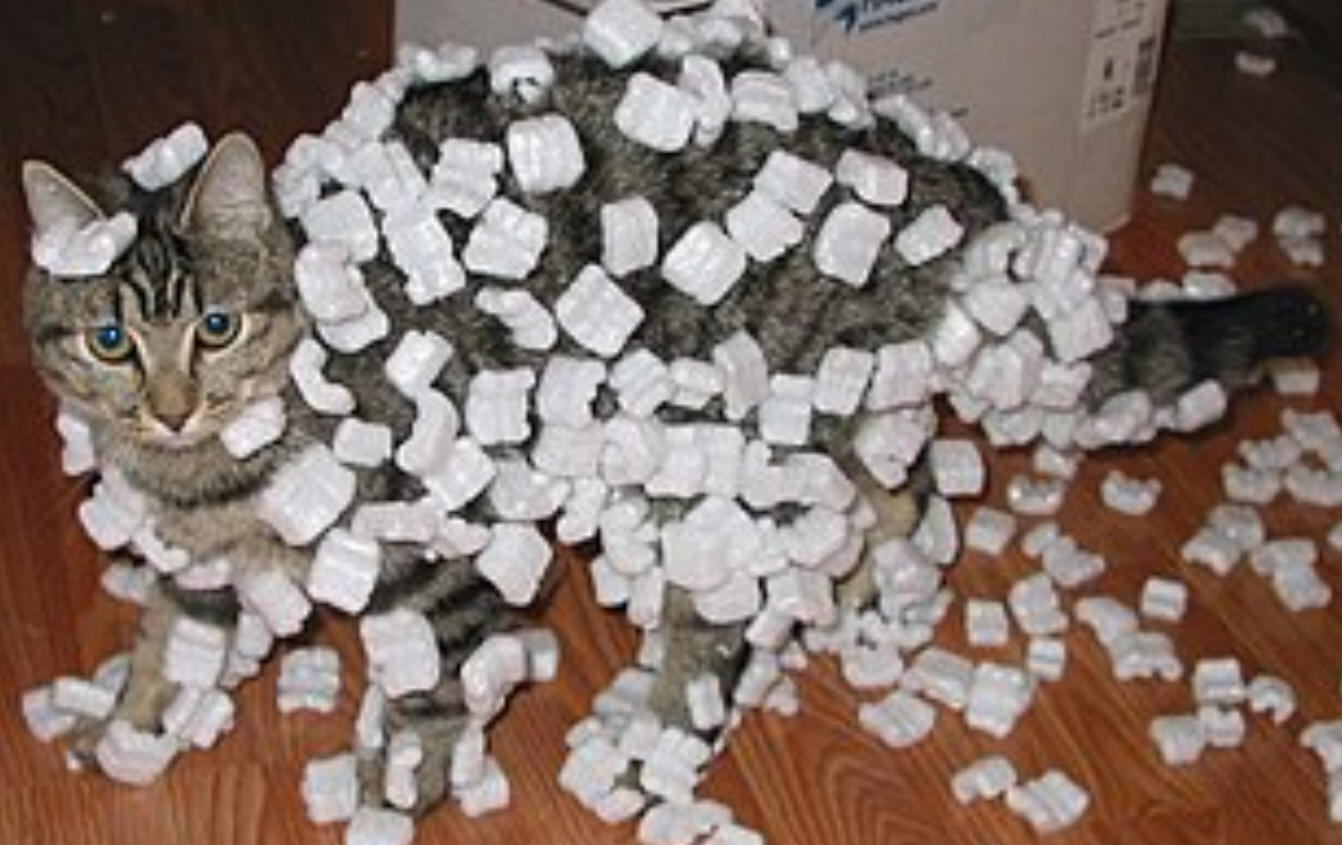
Which of the following can we say with certainty? Why?
A) The balloons have the same net charge
B) The cat and the foam "peanuts" have opposite net charges.
C) Both A and B are correct.
D) None of these answers is (are) correct.
Today:
- Return quiz 3
- Questions?
- Test (Energy)
- Continue Electrostatics Notes Part 1 (PDF) VIDEO
Homework:
- None!
 Class
8:
Wednesday,
2/15/23
Class
8:
Wednesday,
2/15/23Warm Up:
When you rub a balloon on your hair, why does the balloon then stick to the wall?
Today:
- Quiz -- Nonconservative work, and efficiency
- Energy Test review pdf --
Homework:
- Test next class. Study!
 Class 7:
Monday,
2/13/23
Class 7:
Monday,
2/13/23Warm Up:
If you rub a balloon on your head and then hold it next to your hair, your hair is attracted to the balloon, and both your hair and the balloon are attracted to other stuff. Why?
Today:
- Return quiz 2 VIDEO
- Small Quiz (Practice) -- Quiz 3 VIDEO
- Test Review -- Test on Friday.
- Start new unit -- Electricity!
Homework:
- Prepare for small quiz -- Quiz 3
 Class
6:
Thursday,
2/9/23
Class
6:
Thursday,
2/9/23Warm Up:
1. What's the purpose of pulley systems like these?
2. How do they work, in terms of work (W=Fd)?
Today:
- Quiz
- Finish THE REST OF practice quiz #2 (PDF). VIDEO Small quiz next class.
- More practice for the next quiz VIDEO
Homework:
- Prepare for small quiz (quiz 3) next class, similar to the 2nd part of quiz 2. See videos above.
 Class
5:
Tuesday,
2/7/23
Class
5:
Tuesday,
2/7/23Warm Up:
Let's calculate the efficiency of a typical arrow shot from a typical bow.
How can we do it? We can get our data from the internet.
Today:
-- Short break! --
- Finish practice quiz #2 (PDF). Quiz next class.
- More practice? More energy quiz practice
Homework:
- Quiz next class over practice quiz #2 (PDF). Practice!
 Class 4:
Wednesday,
2/1/23
Class 4:
Wednesday,
2/1/23Warm Up:
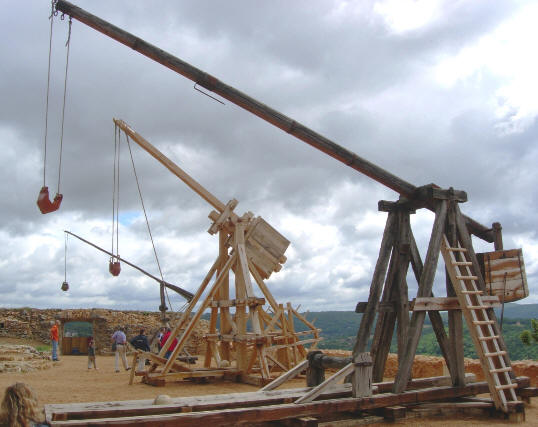
A trebuchet's projectile is launched as its counterweight falls, thereby turning PE into KE and accelerating the projectile.
1. Does the projectile do work on the counterweight or vice-versa? Or does each do work on the other? Explain.
2. At which end of the trebuchet arm does the work being done look like this -- Fd ?
Today:
- Quiz
- Finish -- Find the efficiency of a projectile launcher. (PDF)
- Work on practice quiz #2 (PDF)
Homework:
- Complete #1 -- the table, in practice quiz #2 (PDF)

Warm Up:
All of these "machines" work by changing the nature of work, but not the amount of work. W=Fd.
1. Identify all of the machines that the user's work so that it looks like... W=Fd. Explain why anyone would want to change work in this way.
2. Identify all of the machines that the user's work so that it looks like... W=Fd. Explain why anyone would want to change work in this way.
Today:
- Check/review the homework. VIDEO
- Look at the answers to the Lab from last class (Analyze a real system) (VIDEO how to do the calculations)
- Find the efficiency of a projectile launcher. (PDF)
Homework:
- Quiz next class -- prepare using the practice quiz. You can find a clean copy on page 2 of this handout.
 Class
2:
Thursday,
1/26/23
Class
2:
Thursday,
1/26/23Warm Up:
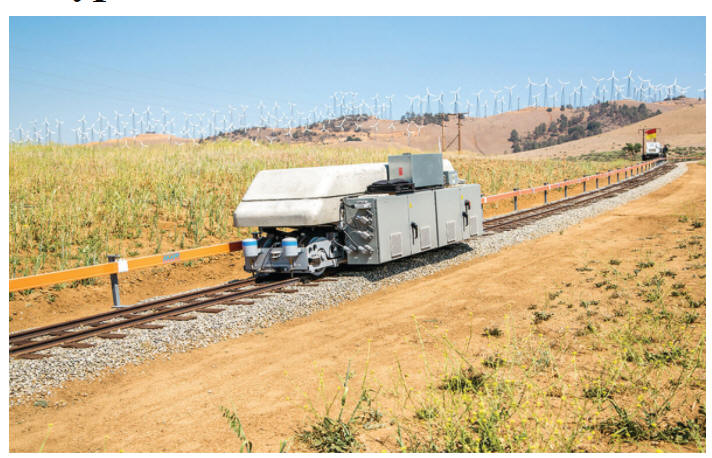
1. Can you guess what the "Sisyphus train" does? [Hint: it is an attempt to solve a big renewable energy problem.]
2. How did it get that nickname?
3. Starting from rest, a car travels 20m in 4 seconds. What are its...
1) Initial Speed? 2) Average Speed? 3) Final Speed?
Today:
-
- Check/review the homework. VIDEO
- Energy Notes Part 2 -- efficiency and practice (pdf) VIDEO
-
Analyze the energy in a pulley system -- including finding its
efficiency.
- Do a practice together
- Lab -- Analyze a real system
- Homework -- individual practice
Homework:
- Complete the practice quiz on the back of the notes (pdf)
 Class
1:
Tuesday,
1/24/23
Class
1:
Tuesday,
1/24/23Warm Up:
What is this simulation supposed to demonstrate?
Today:
- Look at midterm exams.
- New Unit: Energy
- Unit 4 -- Energy
- Handout -- Energy Notes, Part 1 (pdf) -- Filled-in version VIDEO
- Find the power output of real student (Conner volunteered). VIDEO
Homework:
- Complete #15 on today's handout. Follow the same process as #14.