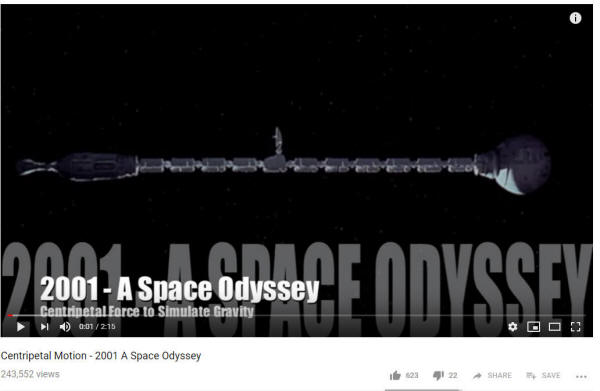
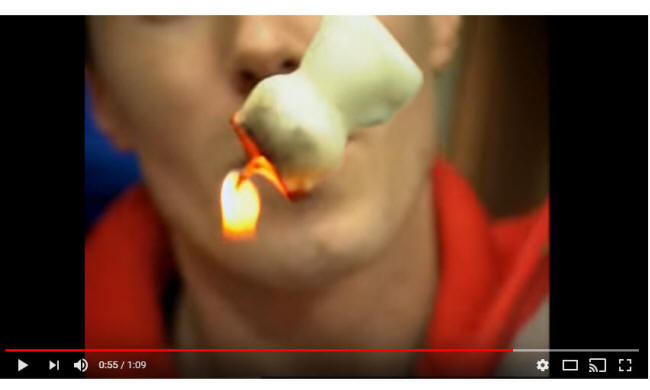
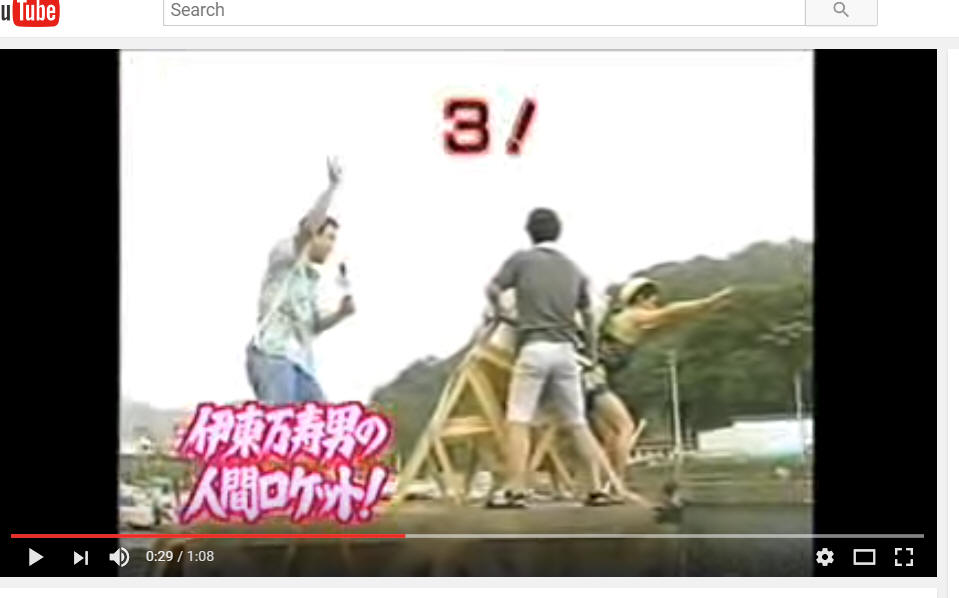
Class 37.5
Tuesday 1/3/23
Class 37.5
Tuesday 1/3/23
Warm Up: What will happen to kinetic energy, potential energy, thermal energy, and total energy of the skateboarder during a ride in the half pipe? A) with zero friction B) with a lot of friction
Today:
- Return tests -- Optional retake next Tuesday
- Midterm Exam:
- The midterm will cover Units 1-5 (through gravity and circlular motion).
- I have provided clean copies of the old tests in Google Classroom. I have also provided videos explaining all of the items on the tests.
- Here is a midterm review document from last year that you might find useful -- "Algorithms" for solving physics problems
- We will be doing some in-class review.
- The rest of the year:
- Finishing Mechanics
- Work and energy,
- Momentum and Impulse
- Rotational Motion
- Electricity
- Sound and Waves
- Optics
- Finishing Mechanics
- New Unit -- Work and Energy.
Unit 6 Handout (PDF)
- Notes -- work, power, and energy filled-in notes
Homework:
-
Work and Energy Practice Problems #1 &2 on p. 3-4 of the packet -- helpful video
Class 37 Thursday 12/22/22
Warm Up:
Today:
- Test -- Gravity, Circles, Kepler...
- If your rocket project corrections are done, turn them in.
Homework:
- None!
Warm Up:
1. Some cultures celebrate a character called Santa Claus, who delivers presents around the world in a sleigh. This event occurs over a time interval known as Christmas Eve. If Santa were to deliver a present to every child who believes in him, how fast would Santa need to accelerate between stops in order to deliver all of the presents on Christmas Eve? Santa Claus from an Engineer's Perspective
2. What happens at 4:26 this
afternoon?

Today:
- Return Retakes
- Check/review homework
- Test review
Homework:
- Study
 Class
36
Tuesday 12/20/22
Class
36
Tuesday 12/20/22
Warm Up:
1. What is a geosynchronous satellite?
2. What's the difference between a geosynchronous orbit and a geostationary orbit?
3. What is a space elevator?
Today:
- Return some graded stuff.
- Optional Test Retake -- Forces in 2-D
- Disassemble your group's rocket. Recycle large pieces of plastic (>2" diameter). Make a pile of clean plastic sheet.
Homework:
- Continued from yesterday... Practice test #1 (packet p. 9-12) Answers/Solutions Video Explanations

 Class
35.5
Monday 12/19/22
Class
35.5
Monday 12/19/22
Warm Up:
From 2016-2017 EPS 200...
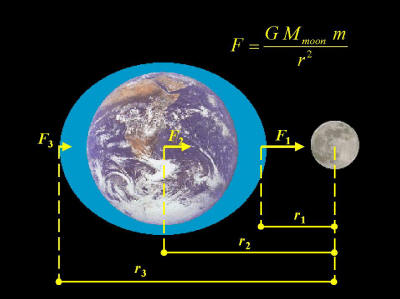
The Sun, Earth, and Moon are continually spaghettifying one another. On Earth, we see the effects of this spaghettification in the form of tides.
1. What causes spaghettification?
2. How much gravitational force do the Sun and Moon each exert on 1,000,000 pounds of water?
3. Even if there were no water on Earth, there would still be tides, just as there are tides on the Moon. Describe these tides.
4. Why do we always see the same side of the moon?
5. Is the Earth's 24 hour rotational period speeding up or slowing down over time? Answer
Today:
- Check/review homework
Homework:
- Due on Wednesday -- Practice test #1 (packet p. 9-12) Answers/Solutions Video Explanations
Class 35 Friday 12/16/22
Warm Up: ??
Today:
- Check/review homework (+/- Kepler's 2nd Law Activity)
- Work on problems section
Homework:
- Problems section of 2019-2020 test (p. 15-16) Answers/Solutions
Class 34.5 Thursday 12/15/22
Warm Up: Let's do the "Chapter 6 4-Minute Drill" at the end of the packet. But add one more... the velocity of an object in a circular orbit with orbital radius r and period T.
Today:
- Check/review homework (+/- Kepler's 2nd Law Activity)
- Work time
Homework:
- Due tomorrow: Multiple choice section of 2019-2020 test (p. 13-14) Answers/Solutions
- Due on Monday: Problems section of 2019-2020 test (p. 15-16)
Warm Up:
1. Is this an answerable question -- Approximately how fast is the jogger in this video moving?
2. If the jogger turned around and jogged the other way, would he feel any different?
3. What must move in order for the person to experience simulated gravity... the space station, the person, neither, or both? What does "move" mean in outer space?
Today:
- What's an AU?
- Return tests
- Review homework
- Kepler's 2nd Law -- orbit activity
Homework:
- Kepler's 3rd Law Problems: #9.5 on p. 4, and #14 on p. 6 Solutions **In the solutions, #9.5 is listed as #10 Note that 1AU is essentially the Earth's orbital radius around the Sun.
- Finish 2nd Law activity -- if necessary
Class 33.5 Tuesday 12/13/22
Warm Up: None
Today:
- 2nd half of small test (problems 3-4)
- Rocket Project Corrections Due Dates: I plan to enter scores over break, so if you want to have a different score entered, turn in your corrections by next Thursday. Otherwise, get them in on or before the end of the quarter (January 13th).
Homework:
- Due on Wednesday (tomorrow): #15 on p. 6. Solution . Also try #8 on p. 18 -- You only need two starting formulas, and one of them is the equation from yesterday's warm-up.
 Class
33
Monday 12/12/22
Class
33
Monday 12/12/22
Warm Up:
1. Starting from the assumption that this
orbit is a perfect circle, write an equation that relates the velocity
of the orbiting body to its orbital period (T) and orbital radius (r).
Orbital period (T) is the time required
 for
one full revolution.
for
one full revolution.
2. What is the object on the right?
**This is another formula that you will need on the next test, but that will not be provided on the formula sheet. There are two others.
Today:
- Note that I've populated the cells above for the rest of the year. There will probably be minor changes.
- Check/review homework
- Quick Notes -- Kepler's 3rd Law (and practice problem -- #9 on p. 4) Solution
- First half of small test (problems 1-2)
- Dates of next test and test retake?
- Rocket Project Corrections Due Dates: I plan to enter scores over break, so if you want to have a different score entered, turn in your corrections by next Thursday. Otherwise, get them in on or before the end of the quarter (January 13th).
Homework:
- 2nd Half of small test tomorrow -- problems 3-4
- Due on Wednesday: #15 on p. 6. Solution . Also try #8 on p. 18 -- You only need two starting formulas, and one of them is the equation from today's warm-up.
 Class 32.5
Friday 12/9/22
Class 32.5
Friday 12/9/22
Warm Up:
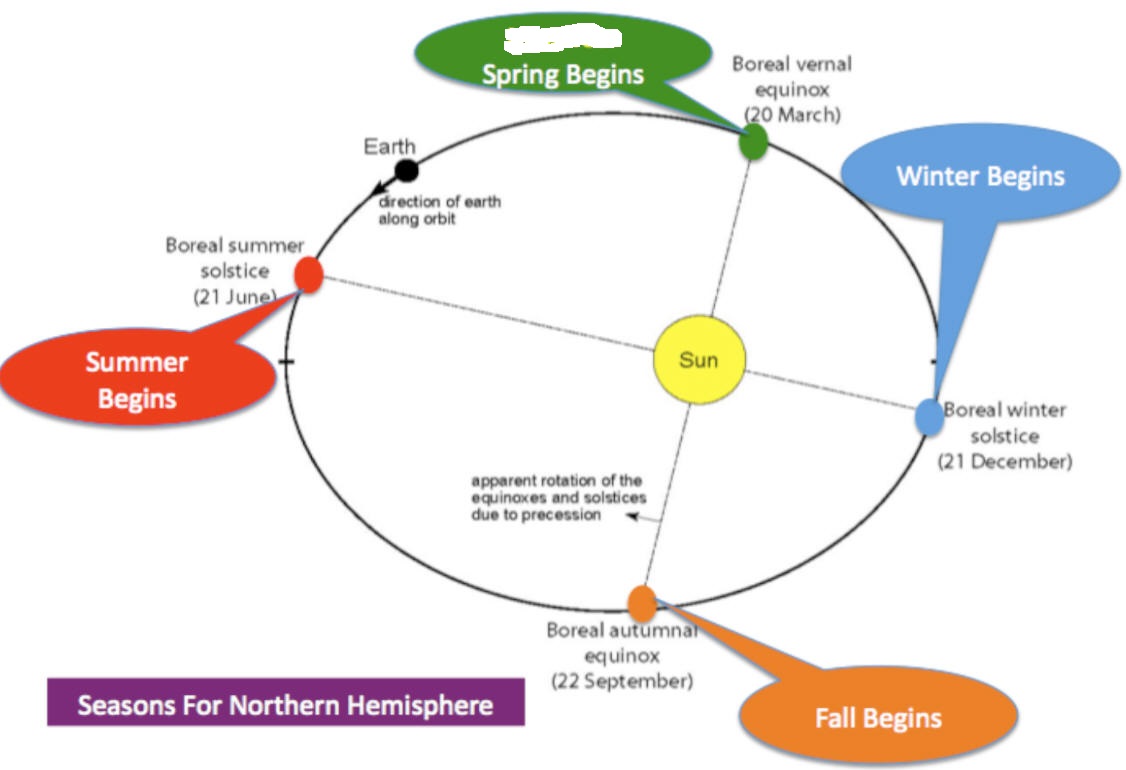
According to the diagram on the right...
1. At what approximate date is the Earth orbiting with the fastest speed? When is it orbiting the slowest?
2. Rank our seasons in order of length. Answer
3. Why are elliptical foci called foci? Is anything being focused, and, if so, what and how?
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Return Rocket Analyses and Discuss
- Begin Kepler's Laws -- 2nd Law and elliptical orbits activity (at least draw the ellipse)
Homework:
- Half of small test on Monday -- problems 1-2
- Problems:
Solutions
Video Solutions to
4, 8, 10, 12, 13.
- Page 2, #2
- Page 5, #10
Warm Up:
1. Are astronauts and candles weightless when they are in the international space station? What word best sums up their motion?
2. Would candles "work" on a space station?
Today:
- Video of today's notes (circular motion and law of gravitation)
- Derivation of ac = v2/r
- Notes: Circular motion and Gravity -- p.1 & 3 of packet Unit 5 Packet (PDF) Solutions
Homework: Solutions Video Solutions to 4, 8, 10, 12, 13.
- p.2, #1 and #3
- p.3, # 8
- p.5, #12
 Class 31.5
Wednesday 12/7/22
Class 31.5
Wednesday 12/7/22
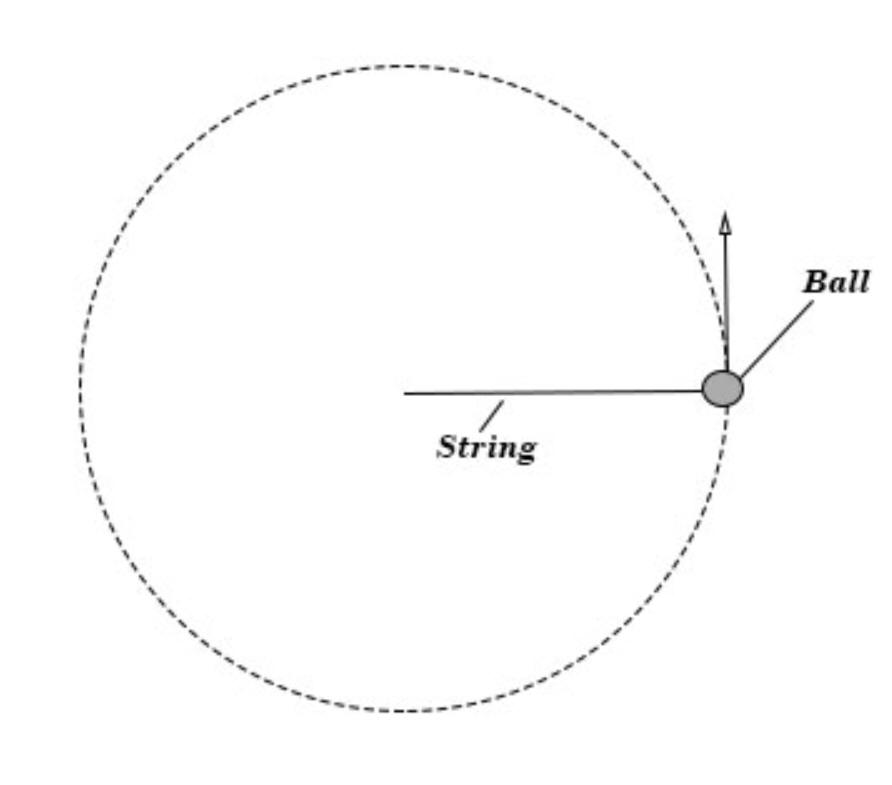
Warm Up: The ball is moving at a constant speed in a circular path. Describe its acceleration.
Today:
- Hand out Unit 5 Packet (PDF) Solutions?
- When should we have the test? We could break it up into 2 pages.
- Check/review homework
Homework:
-
Optional -- More Test practice -- packet pages 11-12. Solutions
 Class 31
Tuesday 12/6/22
Class 31
Tuesday 12/6/22
Warm Up: A waiter at Bramble is delivering a chunk of bone (marrow in the middle), basted in synovial fluid, to some dinner guests. Touching only the perfectly smooth and flat serving tray (also made of bone), the waiter must deliver the dinner bone to the guests and place it carefully on their table.
1. Assuming the guests' table is to our left in the picture, describe what the waiter would need to do in order to make this happen?
2. Can you sketch the forces on the bone using the head-to-tail method? [Let's just assume that the bone is frictionless.]
Today:
- Do problem #3 (VIDEO) on page 6 of the packet. Unit 4 Handout (Forces in 2D) PDF Solutions to 1-4 on p 5 and 6
-
Work time -- practice test (small test on Monday)
Homework: Complete the 2020-21 test retake, on pages 7-10 of the packet. Here's a spreadsheet with the answers. You can look at the formulas for hints to the solutions. Written solution to number 3.
 Class
30.5 Monday 12/5/22
Class
30.5 Monday 12/5/22
Warm Up:
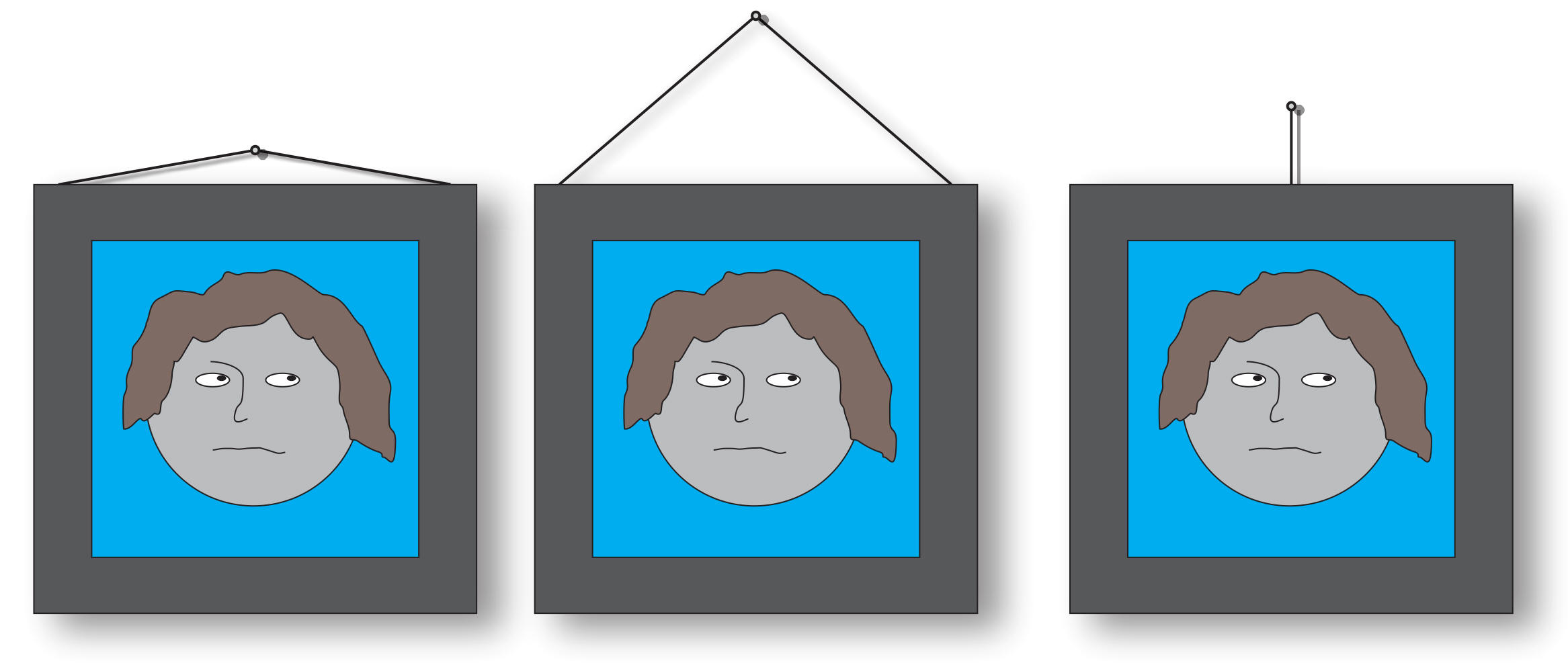
Cheryl wants to use some string and a nail to hang a treasured portrait of great-great-grandfather Ernesto as a young man. The portrait is rather heavy. Rank the three configurations on the right according to their risk of exceeding the breaking strength of the string.
Today:
- Return papers
- Check/review homework
- Do problem #1 on page 5 of the packet. Unit 4 Handout (Forces in 2D) PDF Video from 20-21
- Turn in rocket analysis, all parts, stapled together.
Homework:
Complete # 2 from page 5 of the packet. Solutions
Class 30 Friday 12/2/22
Warm Up: None
Today:
- Optional Test Retake
- Work time
Homework:
- Problems #2 and #3 (on packet p. 3&4) are due on Monday. Answers and Solutions
- Rocket Analysis (all parts) due on Monday
Class 29.5 Thursday 12/1/22
Warm Up: None
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Work time
Homework:
- Problems #2 and #3 (on packet p. 3&4) are due on Monday. Answers and Solutions
- Optional -- Test retake tomorrow
- Rocket Analysis (all parts) due on Monday
 Class
29 Wednesday 11/30/22
Class
29 Wednesday 11/30/22
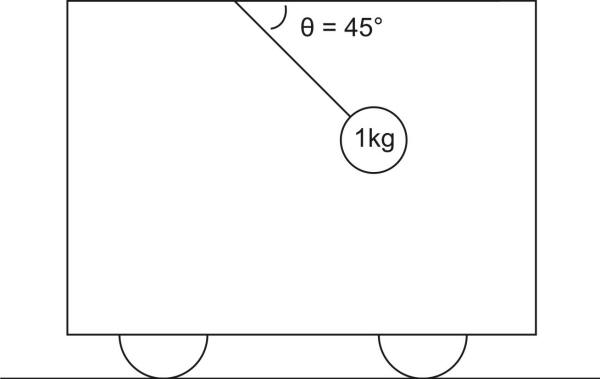
Warm Up:
A 1kg mass is suspended by an ordinary string from the ceiling of a fully-enclosed train car. The car is on a level surface, and the angle shown remains constant.
How many of these can we deduce from this information?
A) The mass' direction of movement
B) The mass' acceleration
C) The string tension
Today:
- Get the Unit 4 Handout (Forces in 2D) PDF
- Due date change, and a reminder -- the rocket analysis project is now due on Monday, but don't count on work time on Monday. Also, after your project materials are graded, you will have a chance to make revisions.
- Practice -- Analyzing a body on an incline (p.1) Video from 2020 Answers and Solutions
- Group Rocket Analysis Work Time
Homework:
- Page 2 of the Unit 4 Handout (Forces in 2D) PDF Answers and Solutions
- Optional -- Test retake on Friday
- All parts of the rocket analysis are due on Monday.
Class 28.5 Tuesday 11/29/22
Warm Up: None
Today:
- Reminder to work efficiently
- Group Rocket Analysis Work Time:
- Information Sources:
- Part 1: Finish #1-11 of the Rocket analysis. It would be a good idea to work on #11 individually, for homework, and then check in class to see if anyone got it right.
- Part 2:
Homework:
- Optional -- Test retake on Friday
- Both parts of the rocket analysis are due on Friday. After your project is returned, you will have one chance to make corrections. The project will be weighted as half of a normal test grade.
 Class
28 Monday 11/28/22
Class
28 Monday 11/28/22
Warm Up:
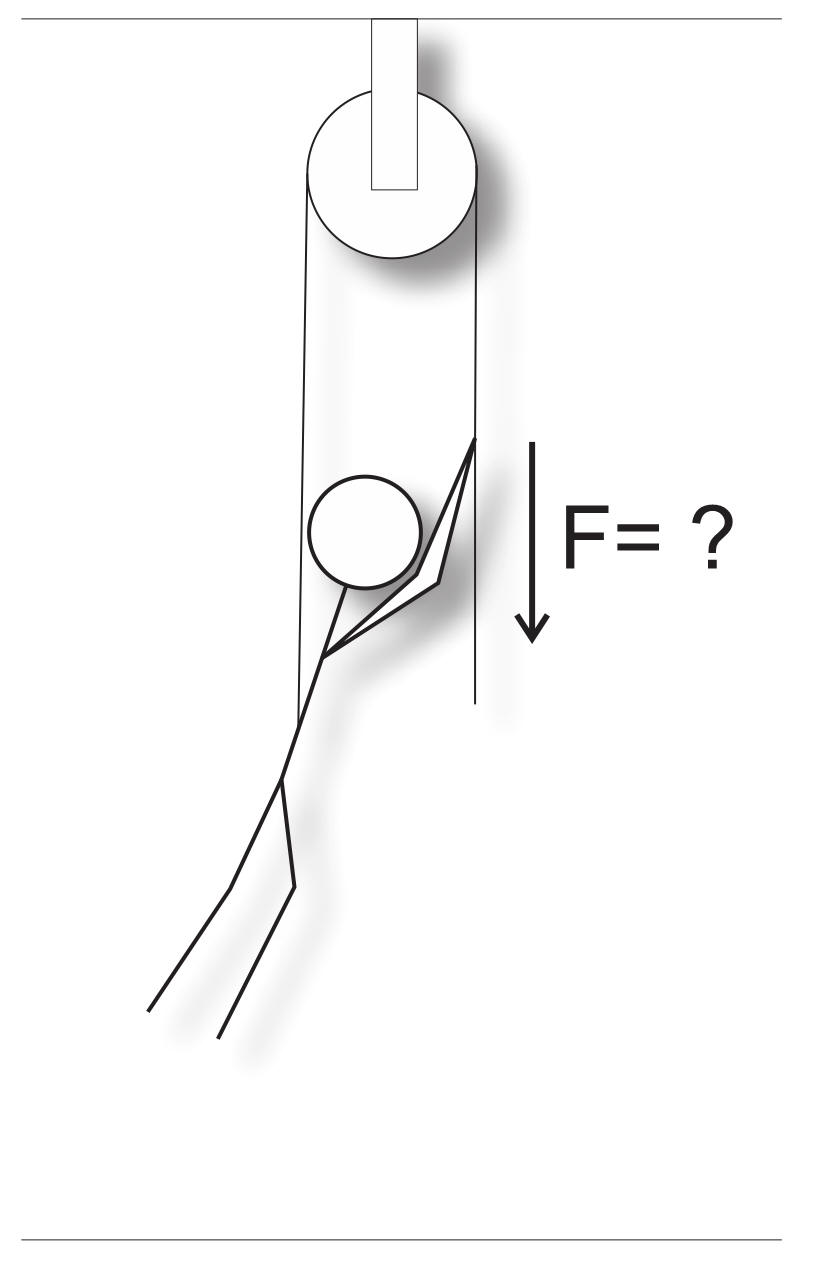
One end of a rope is attached to the Gladys' belt. Gladys is pulling directly downward on the other end. Assuming that the pulley and rope are massless and fictionless, how much downward force must Gladys apply in order to ascend? Gladys weighs 500N.
Today:
- Reminder to work efficiently
- Brief Overview
- Group Rocket Analysis Work Time:
- Information Sources:
- Part 1: Finish #1-11 of the Rocket analysis. It would be a good idea to work on #11 individually, for homework, and then check in class to see if anyone got it right.
- Part 2:
- Coming Up:
- Rocket analysis work time today and tomorrow
- Begin the new unit on Wednesday
- Rocket analysis is due on Friday
- Optional test retake on Friday
Homework:
- Optional -- Test retake on Friday
- Suggested -- #11 from part 1 of the rocket project
- Both parts of the rocket analysis are due on Friday. After your project is returned, you will have one chance to make corrections. The project will be weighted as half of a normal test grade.
 Class
27.5 Friday 11/18/22
Class
27.5 Friday 11/18/22
Warm Up:
What's wrong with this graph of some group's water rocket y position (height) vs. time? How could we fix it?
Today:
- Return Tests
- Review the scope of the Rocket Analysis (parts 1 and 2)
- Finish #1-11 of the Rocket analysis part 1.
- If you have time, begin part 2 of the water rocket forces project
Homework:
- None
Class 27 Thursday 11/17/22
Warm Up:
None -- test today
Today:
- Test
Homework:
- Identify your group's GoPro video and sensor data in their Google Drive folders. If there is no sensor data for your best flight, you can just use GoPro video only.
 Class
26.5 Wednesday 11/16/22
Class
26.5 Wednesday 11/16/22
Warm Up:
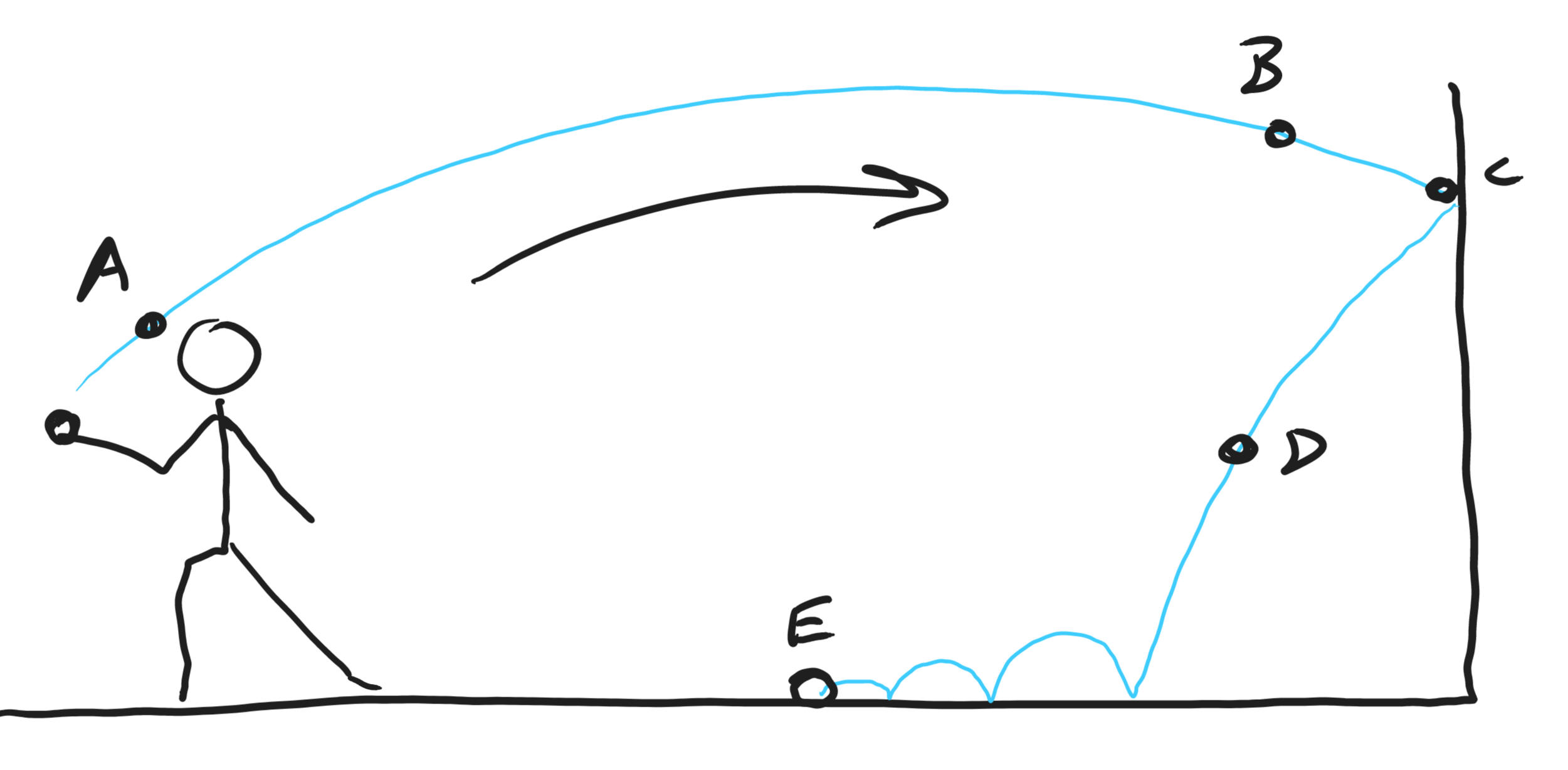
1. Draw a series diagrams showing and labeling all of the forces (and their relative magnitudes) acting on the ball in the diagram on the right, based on the following descriptions.
A. The ball has not yet been released. It is being accelerated by the thrower's hand.
B. Flying through the air, soon before hitting the wall
C. The ball has just touched the wall, and the wall is slowing it down, but it has not stopped completely, and it has not begun to bounce back.
D. Falling to the floor.
E. Sitting motionless after coming to rest
2. Did we really show all of the forces? If not, which ones did we miss?
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Test Format:
- [20 points] 4 Short answer questions
- Draw a diagram showing, calculating, and naming all of the forces acting on an object in some scenario.
- 3rd Law example of action/reaction
- Interaction of drag, weight, and normal force as an object falls
- Create a series of diagrams showing and naming forces (with arrows indicating their relative strengths) acting on an object, based on a description of its motion
- [28 points] 6 Problems (13 parts total)
- Weight
- Sliding object with/without friction -- horizontal motion
- Elevator Problems (vertical motion with tension)
- System of multiple masses with pulleys a tabletop, and friction (or maybe no friction)
- [20 points] 4 Short answer questions
- If you have extra time, see if you can complete #1-11 of the Rocket analysis part 1.
Homework:
- The actual homework -- Packet p. 26-27 (last pages of the 2019-2020 test) answers
- Test on Thursday
- Optional Extra Practice --
If you want more practice for the test, here is one of the tests from 2020-2021...
 Class
26 Tuesday 11/15/22
Class
26 Tuesday 11/15/22
Warm Up:
1. How does NASA simulate weightlessness?
2. You are trying to transfer some drippy sauce across a dinner table using only a drippy spoon. The sauce needs to go from the pot to your plate without dripping. Touching only the spoon, how can you make this happen?
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Final Rocket launch -- more data collection
- Record your water volume and dry mass.
- Save some space for the sensor, inside your nose cone, just under the spout.
- If you have extra time, see if you can complete #1-11 of the Rocket analysis part 1.
Homework:
- The actual homework -- Packet p. 26-27 (last pages of the 2019-2020 test) answers
- Test on Thursday
- Optional Extra Practice --
If you want more practice for the test, here is one of the tests from 2020-2021...

 Class
25.5 Monday 11/14/22
Class
25.5 Monday 11/14/22
Warm Up:
The graph on the right shows the current acceleration data for the PocketLab sensor sitting motionless on my desk. The positive Z axis (green) extends "perpendicularly" out of my desk surface. The positive X axis (orange) extends rightward from the sensor. The positive Y (purple) axis extends away from the camera, parallel to the desk surface.
Why are the X and Y axes showing a constant acceleration near 0m/s^2, while the Z axis shows a constant acceleration of around positive 1g?
Today:
- Check/Review Homework
- Prepare for tomorrow's launch. Measures that may possibly
help with nose cone separation...
- More mass at the tip of the rocket (as far foward as possible) -- adding a sensor will help a bit
- Nose cone perforations
- Reduced wind (forecast looks good), but if there is wind, angle rocket into it.
- Remove anything that might help the rocket stick together.
- If you have extra time, see if you can complete #1-11 of the Rocket analysis part 1.
Homework:
- The actual homework -- Packet p. 24-25 (continuation of the 2019-2020 test) answers
- Test on Thursday
- Optional Extra Practice --
If you want more practice for the test, here is one of the tests from 2020-2021...
Warm Up:
1. Some of the rockets did not come apart, so their chutes could not deploy. Speculate on why they didn't separate.
2. How many water bottles are used to launch this game show contestant? Is this for real? Could we launch a student this high?
Today:
- Work on Rocket analysis part 1 -- initial thrust phases and beginning of coasting phase
Homework:
- The actual homework -- Packet p. 22-23 (beginning of the 2019-2020 test) answers
- Optional Extra Practice --
If you want more practice for the test, here is one of the tests from 2020-2021...
Class 24.5 Thursday 11/10/22
Warm Up: None -- get your rocket ready for launching.
Today:
- Launch rockets -- launch person stands alone, same distance as camera from launcher
- Clean up. Time will be short. Please don't leave me with a mess.
Homework:
- None
Class 24 Wednesday 11/9/22
Warm Up: What's the best amount of water to put in a water rocket? [Find out, according to Clifford Heath.] How does the amount of water affect force and overall change in velocity?
1. What happens if you don't add any water?
2. What happens if you completely fill the rocket with water?
Today:
- Finish rockets
- Prepare for launch
- To get an idea of how much water to add, you might want to try Clifford Heath's simulation.
Homework:
- Decide how much water you're going to use in your rocket
- If you're not going to finish, sign up for my FLEX, and prepare before class tomorrow.
 Class
23.5 Tuesday 11/8/22
Class
23.5 Tuesday 11/8/22
Warm Up: How can you measure, mark, and cut a nice, big circle (about 65cm in diameter) out of plastic sheeting, in under 10 seconds?
Today:
- Speedwatch the parachute part of the Construction playlist
- Build rockets. Finish tomorrow and launch on Thursday.
Homework: None
Class 23 Monday 11/7/22
Warm Up:
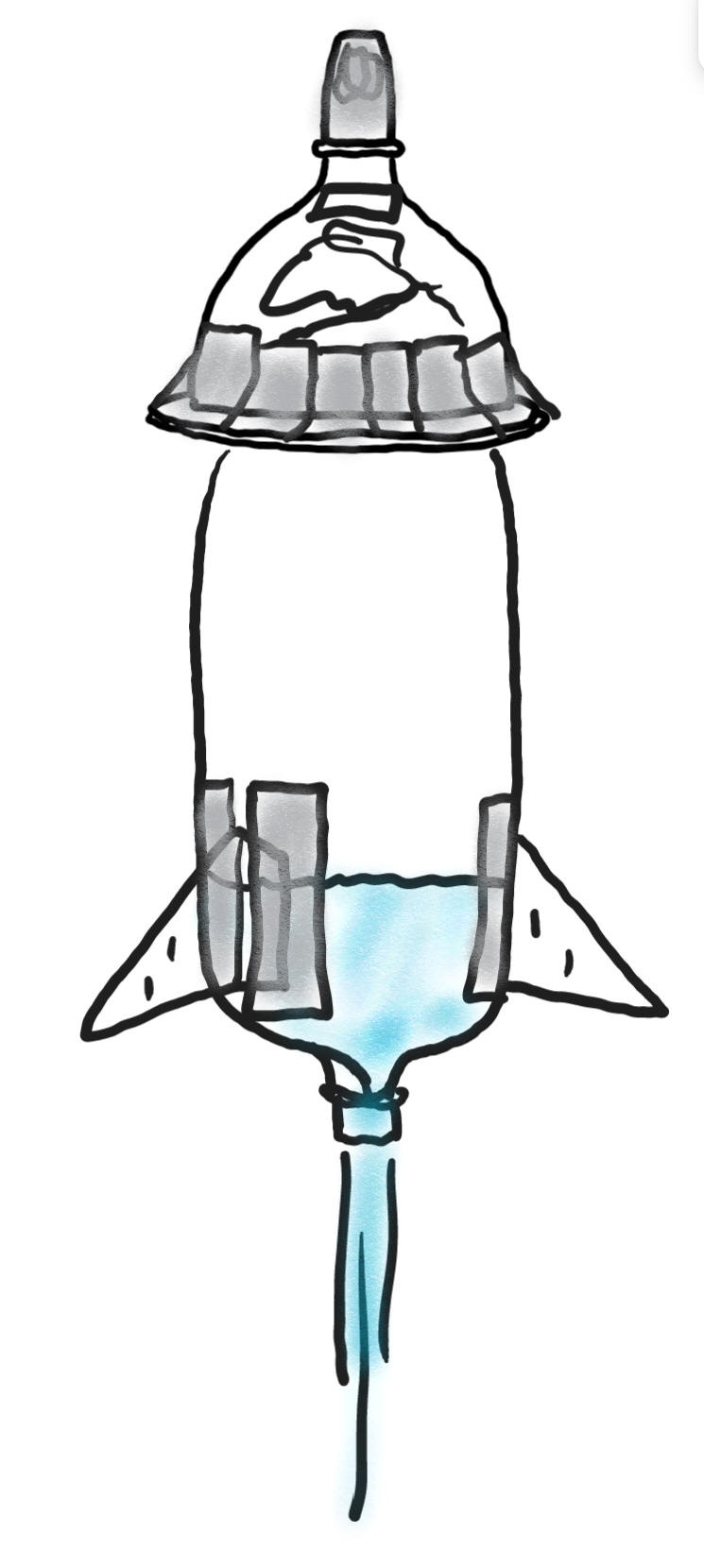
The diagram on the right shows a water rocket. Mass has been added to the tip of the rocket, and fins have been added to the back (bottom). There is a requisite 10cm long section dedicated to holding foam for protecting the probe.
1. What makes the rocket move upward?
2. Why do fins need to be added to the back of the rocket? How does this work?
3. Why does mass needed to be added to the front of the rocket? How does this work?
4. Aside from stability, what other reason is there for adding mass to the rocket?
5. What's the purpose for the flange at the bottom of the nose cone?
[Video link for absent students]
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Should we have the test next Tuesday
next Thursday?
- Rocket Project -- Check out last year's launches?
- Learning Goal: Analyze and understand the forces acting on a water rocket (with parachute) throughout its flight.
- Competition Goal: Build a rocket that flies the highest and lands with a terminal speed less than 4m/s
- Construction playlist
Homework: None
 Class
22.5 Friday 11/5/22
Class
22.5 Friday 11/5/22Warm Up:
On level ground, Tim begins sliding with a velocity of 6m/s. If Tim's slide lasts for 2 seconds, what is the coefficient of kinetic friction between Tim and the slide?
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Work time
Homework:
 Class
22 Thursday 11/3/22
Class
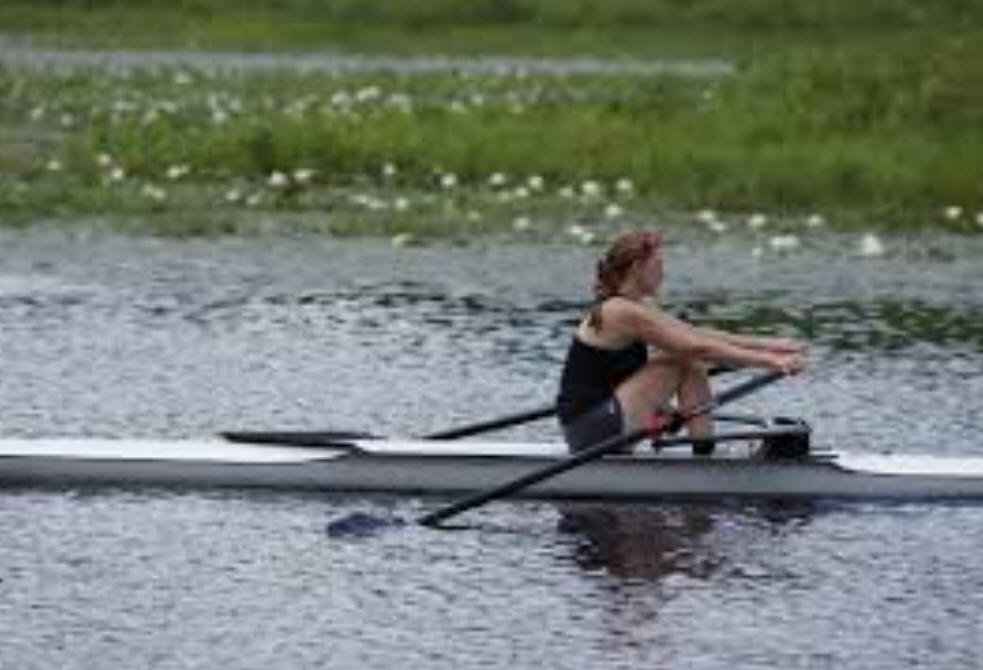
22 Thursday 11/3/22Warm Up:
The 50kg rower in the photo is accelerating at a rate of -1m/s2. She is pulling against the oars with a force of 100N. Calculate and show all of the forces acting on the rower.
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Work time
Homework:
- Packet P. 18-21 "More Newton's Laws in 1-D Practice" -- on problem #1 (p.19), change 600 pounds to 2,000N. **You can skip one page worth of problems/questions. Solutions -- In the solution to number 3, my note "reaches top speed" is a little too far leftward.
 Class
21.5 Wednesday 11/1/22
Class
21.5 Wednesday 11/1/22Warm Up:
1. Explain how a nordic skier can ski forward on level ground with parallel skis (classic style) and without using poles.
2. Downhill skis do not include these innovations, but, as people standing in lift lines often demonstrate, you can still shuffle forward on them (on level ground, without a skating motion or poles). In many situations, you can also shuffle backward, though it may be a little harder. Explain how this works.
Today:
- Check/review homework.
- Finish Notes -- p. 14 -- Acceleration and net force relating to a skydiver. Filled-in notes and solutions 2021 Notes Video -- Start at 15:48.
Homework:
- Packet P. 12 -- #3-5 (multibody problems)
-
Old solutions -- missing some tensions Multibody Drill A Solutions -- Stapleton
- #5 on Packet P. 16 (watermelon dropped from an airplane -- should be a helicopter) Solutions
 Class
21 Tuesday 11/1/22
Class
21 Tuesday 11/1/22Warm Up:
1. How fast does chalk fall? Is it faster than a cat?... My spreadsheet answer
2. Sometimes people celebrate special occasions by firing guns into the air. Is this safe?
 3. Why don't clouds fall out of the sky?
3. Why don't clouds fall out of the sky?
Calculated terminal velocities of various spheres.
Today:
- Check/review homework.
- B5/6 -- wrap up Newton Sled activity
- Notes -- p. 13-14 -- Drag and Terminal Velocity. Filled-in notes and solutions 2021 Notes Video -- Start at 15:48.
Homework:
- Packet P. 11 -- #1-2 (multibody problems)
-
Old solutions -- missing some tensions Multibody Drill A Solutions -- Stapleton
- #4 on Packet P. 15 Solutions
Warm Up: None
Today:
- Return retakes
- Finish Multibody notes -- VIDEO -- Multibody practice problem
- Check homework
- B5/6 -- wrap up Newton Sled activity
Homework:
- Multibody drill homework -- #6 on page 12 of the packet.
-
Old solutions -- missing some tensions Multibody Drill A Solutions -- Stapleton
Warm Up: None
Today:
- Test retake -- optional
- Work time
- B5/6 -- wrap up Newton Sled activity on Monday
Homework:
- Tomorrow -- optional test retake
- Due on Monday -- Packet p. 17, #1-7 solutions

 Class
19.5 Thursday 10/27/22
Class
19.5 Thursday 10/27/22Warm Up: I have a length of treated 4"x4" lumber, some large nails, a hammer, and a large rock. How will it feel if I put the rock on my head and then have someone pound nails into the wood on top of the rock?
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Notes: Tension and Systems pdf version Filled-in notes Class video from 2020 -- notes start around 18:50 and at about 35:00, the video reaches the place where we will stop today.
- B5/6 Newton Sled Activity PDF -- turn in and discuss answers
Homework:
- Tomorrow -- optional test retake
- Due on Monday -- Packet p. 17, #1-7 solutions
 Class
19 Wednesday 10/26/22
Class
19 Wednesday 10/26/22Warm Up: One way to find the center of mass (a.k.a. balance point) of a stick is to support it with two hands and then slowly move those two hands together until they meet under the stick's center of mass. Why does this method work?
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Notes: Friction (Packet page 8, and chapter 5.1 in the online textbook) Filled-in version
- Finish the Newton Sled Activity PDF -- turn in and discuss answers
Coming Up:
- Tomorrow -- multibody systems problems; two night's worth of homework assigned -- due on Monday
- Friday -- optional test retake; work time for everyone who is not retaking the test
Homework:
- Problems #10-12 on page 6 of the Unit 3 Packet Answers and Solutions
 Class
18.5 Tuesday 10/25/22
Class
18.5 Tuesday 10/25/22Warm Up: It is possible to remove a sheet paper from under a dry erase pen without touching or tipping the pen. How can one do this without tipping the pen? Why does the pen usually fall? What kind of pen would work better?
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Newton Sled Activity PDF
Homework:
- Problems #8-9 on page 5 of the Unit 3 Packet Answers and Solutions
 Class
18 Monday 10/24/22
Class
18 Monday 10/24/22 Warm Up: A typical Y-dimension acceleration problem...
1. A rappelling rock climber with a mass of 50kg is supported by a rope. If the climber is accelerating downward at a rate of 0.5m/s, what is the tension in the rope?
2. More generally, for the situation where a rope is applying an upward tension (T) to a mass (m) with acceleration a, write an equation relating m, T, and a.
Today:
- Return project grading sheets (and the remaining tests) -- Make sure that your group's projectile project graph has been submitted in Google Classroom.
- Check/review homework
- Finish the rest of the notes on p. 1,2, and 7 of the packet (1st and 3rd laws)
- Newton Sled Activity PDF
Homework:
- Conceptual #3-4 and Problems #4-7 on page 5 of the Unit 3 Packet Answers and Solutions
 Class
17.5 Friday 10/21/22
Class
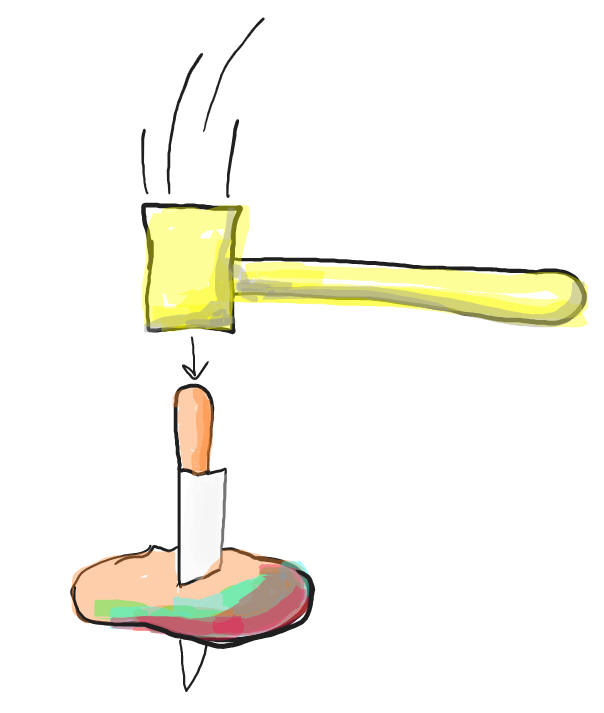
17.5 Friday 10/21/22 Warm Up: What will happen if I poke a knife through a potato, hold both objects in the air with the knife pointing downward, and then hammer the butt of the knife into the potato? Why? What if it's an apple, because I didn't have potatoes?
Today:
- Return tests
- Begin New Unit: Jump to Newton's 2nd Law, weight, and problem-solving notes p.1-3
Homework:
- Conceptual #1-2 and Problems #1-3 on pages 4-5 of the Unit 3 Packet Answers and Solutions
Warm Up: None
Today:
- Share the answer to number 4 on the test -- because I forgot to remind everyone
- Test -- change the point value for problems 3 and 4.
Homework:
- None
 Class
16.5 Wednesday 10/19/22
Class
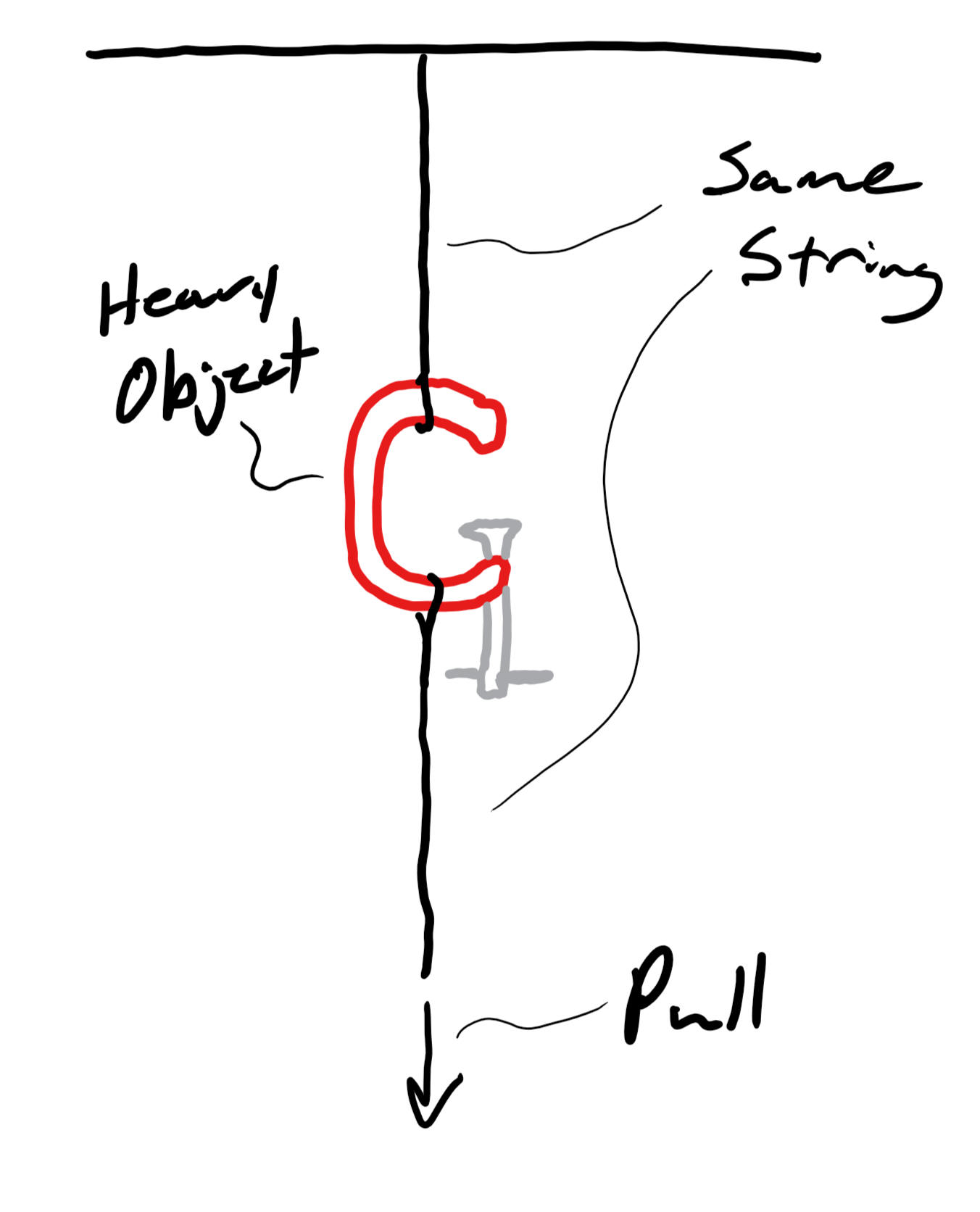
16.5 Wednesday 10/19/22 Warm Up: There is a heavy object suspended from the ceiling by a string. Another segment of the same string is hanging downward from the object. I am going to pull on the bottom string until one of the two strings breaks. Which string is going to break first? Why?
Today:
- Present the donuts. Contest results. I don't have the projects graded. Hopefully I can get them back to you tomorrow.
- Check/review the homework
- Test format:
- 10-15 short answer/multiple choice
- 2 River problems with multiple parts (one orthogonal, one non-orthogonal)
- 3 Projectile motion problems, each with multiple parts
- Next Unit -- Forces (Newton's Laws)
Homework:
- Study
Warm Up: No warm-up today
Today:
- Grab a copy of the homework problem -- it's the non-orthogonal river problem format that you can expect on the test.
- Get your contest problems scanned
- Compete
- Turn in your contest problems with your graph stapled to the back
Homework:
- One more non-orthogonal river problem Solution
- Test on Thursday
Warm Up: What do you need to do to get ready for tomorrow's contest?
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Hand-out contest problems
Upcoming Classes:
- Tomorrow -- Trajectory contest day. Trajectory project stuff is due -- graphs and answers. Homework -- some more non-orthogonal river problem practice
- Wednesday -- check/review homework; Q&A about the test
- Thursday -- Unit 2 Test (kinematics in 2-D, River Problems, Projectile Problems)
Homework:
- As a group -- Complete one set of contest problems. Tomorrow, by the end of the contest, submit your written contest solutions and a printed launcher calibration graph (showing initial velocity vs. launcher setting)
 Class
15 Friday 10/14/22
Class
15 Friday 10/14/22Warm Up:
A boat is following a heading of 56 degrees N of E, and its speed in still water is 1.3 m/s. Find the velocity of the river's current if the boat's actual velocity (relative to the Earth) is 3.2m/s in a direction 17 degrees W of N.
Solution...
 Video explanation
Video explanation
Today:
- Check/review homework (that was due yesterday)
- Last big chunk of contest work time
Upcoming Classes:
- Monday -- check/review homework; Hand out the projectile contest problems
- Tuesday -- Trajectory contest day. Trajectory project stuff is due -- graphs and answers. Homework -- some more non-orthogonal river problem practice
- Next Wednesday -- check/review homework; Q&A about the test
- Next Thursday -- Unit 2 Test (kinematics in 2-D, River Problems, Projectile Problems)
Homework:
- Page 16 Due on Friday; Page 17 Due on Monday -- Practice test #2 (Unit 2 Packet pages 16-17).
Warm Up:
see yesterday?
Today:
- Check/review homework (that was due yesterday)
- Trajectory Contest work time
Upcoming Classes:
- Tomorrow-- check/review homework; trajectory contest prep time.
- Monday -- check/review homework; Hand out the projectile contest problems
- Tuesday -- Trajectory contest day. Trajectory project stuff is due -- graphs and answers. Homework -- some more non-orthogonal river problem practice
- Next Wednesday -- check/review homework; test review
- Next Thursday -- Unit 2 Test
Homework:
- Page 16 Due on Friday; Page 17 Due on Monday -- Practice test #2 (Unit 2 Packet pages 16-17).
 Class
14 Wednesday 10/12/22
Class
14 Wednesday 10/12/22 Warm Up:
Final launcher considerations...
1. How are you going to aim your launcher in the horizontal plane?
2. How are you going to aim your launcher in the vertical plane?
3. How are you going to decide on your projectile's initial height? [Remember that you will be given a vertical "launch window," and it is up to you to determine the exact launch height.]
4. How are you going to hold your launcher steady, at the height and angle of your choice?
5. What are you going to do if you take a test shot and it turns out that your distance is off by a large amount?
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Trajectory Contest work time
Upcoming Classes:
- Tomorrow -- Warm-up; Contest preparation
- Friday -- check/review homework; trajectory contest prep time.
- Monday -- check/review homework; Hand out the projectile contest problems
- Tuesday -- Trajectory contest day. Trajectory project stuff is due -- graphs and answers. Homework -- some more non-orthogonal river problem practice
- Next Wednesday -- check/review homework; test review
- Next Thursday -- Unit 2 Test
Homework:
- Page 16 Due on Friday; Page 17 Due on Monday -- Practice test #2 (Unit 2 Packet pages 16-17).
 Class
13.5 Tuesday 10/11/22
Class
13.5 Tuesday 10/11/22Warm Up:
A green hunter and a blue hunter point their guns directly at a monkey. Then they fire simultaneously. Just as the two hunters fire their guns, the monkey slips and freefalls from the treetop.
Whose bullet (if either) hits the monkey?
Today:
- Hand-in launcher solutions and check some.
- Try a test shot. If you can't make it work, recalibrate your launcher and/or find a way to improve your precision.
Homework:
- Mr. Pennington's problems #4-6, on p. 14 of the Unit 2 Packet Solutions
- Review the trajectory project grading process at the end of the handout (Trajectory Contest Project handout (PDF))
- Optional -- show clearly that the blue hunter's bullet will hit the monkey given any tree height, hunter position, initial bullet velocity, initial launch angle, and x displacement. A satisfactory explanation can be substituted for any numbered projectile problem on the next test. **You must do all of the work on your own. This is due by class time on Friday.
 Class
13 Thursday 10/6/22
Class
13 Thursday 10/6/22 Warm Up:
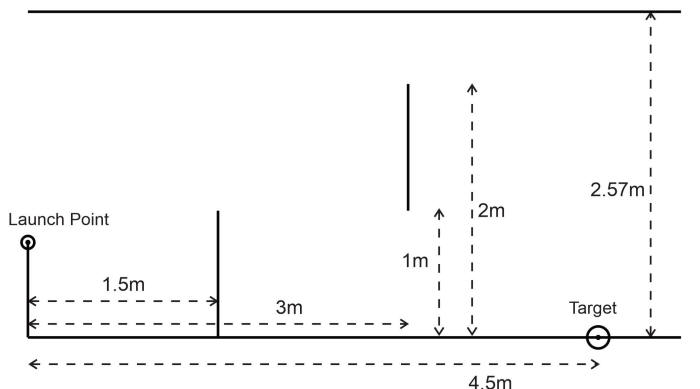
1. Use your spreadsheet to determine a correct combination of initial velocity and angle in order to hit the target.
2. Use your launcher calibration graph (or table)( to determine the correct launcher setting.
**Assume that the surface provided for launching is 0.62m high, so the launcher muzzle can be at any height between 0.645m and 1m.
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Finish your spreadsheet and share it with your group.
- Launcher practice. Set up practice shots. Test your calibration graph and methods. Refine your graph if necessary.
Homework:
- Use your spreadsheet to solve the launcher practice problems on page 15. Use guess-and-check method to find a correct combination of initial velocity and angle. Then use the calibration graph to find the correct launcher setting (for the fictitious practice problem launcher).
 Class
12.5 Tuesday, 10/4/22
Class
12.5 Tuesday, 10/4/22 Warm Up:
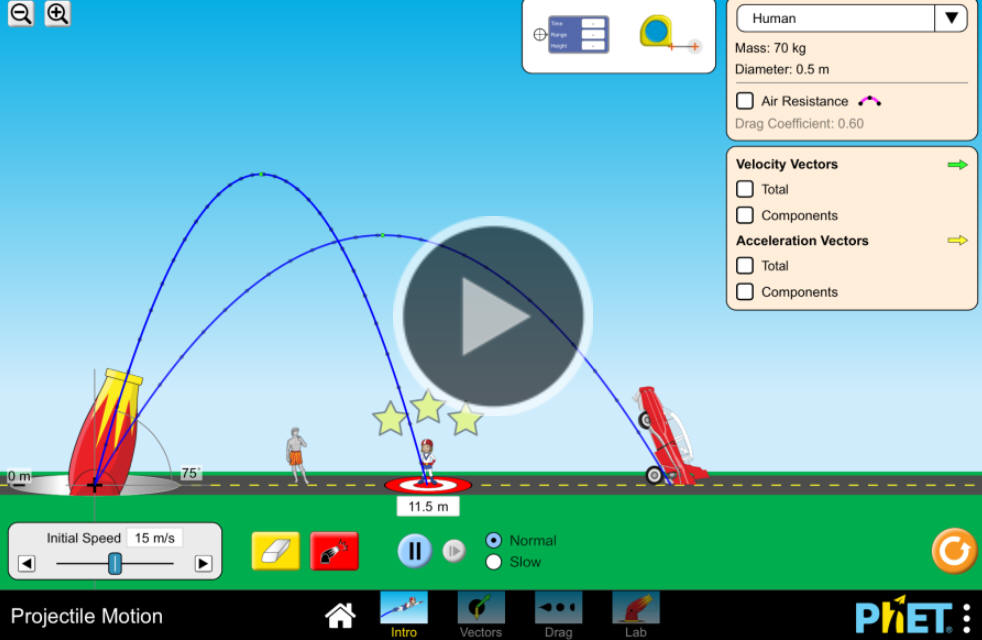
Let's try out the PhET Projectile Motion Simulation and see what it has to offer. What do the various buttons do?
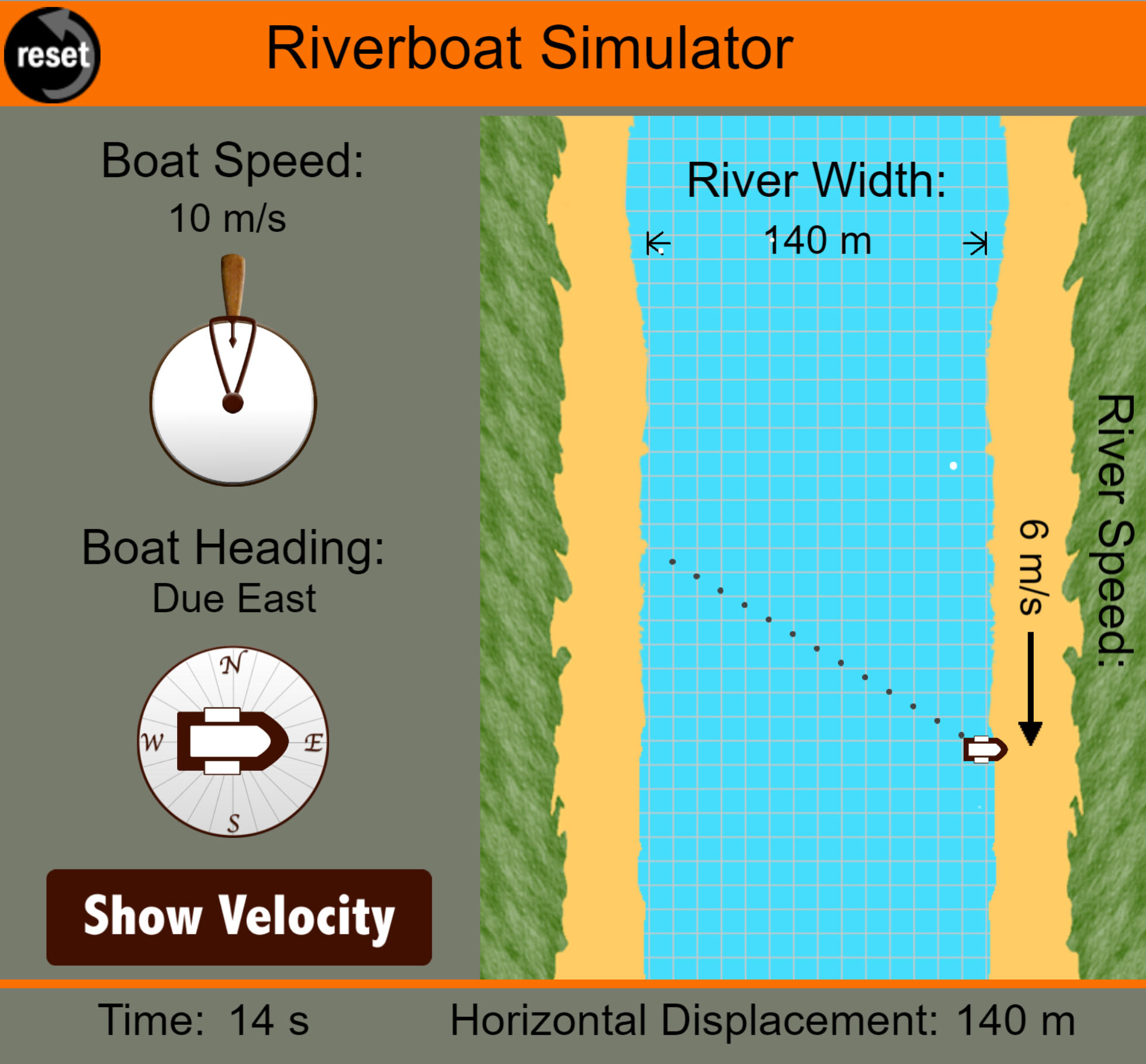 The riverboat simulator is also
a little bit interesting, but I would change the
wording a bit. Can you guess what I would change?
The riverboat simulator is also
a little bit interesting, but I would change the
wording a bit. Can you guess what I would change?
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Finish data collection (table of launcher settings and whatever other data you need for calculating initial velocities).
Homework:
- Mr. Pennington's problems #1-3, on p. 14 of the Unit 2 Packet Solutions
- If your project group doesn't have spreadsheet that is working
like this,
 fix it. Here are some helpful videos...
fix it. Here are some helpful videos...
 Class
12 Tuesday, 10/4/22
Class
12 Tuesday, 10/4/22 Warm Up:
1. Based on the diagram to the right, provide definitions for precision and accuracy. Which is easier to fix?
2. Can you suggest some ways to improve the precision of a projectile launcher like the ones you are using in this project?
3. How could you improve Accuracy?
4. What are some likely sources of error in attempts to hit the target?
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Make a copy of your spreadsheet, and submit that in the Google Classroom assignment.
- Get the Trajectory Contest Project handout (PDF)
- Choose partners. Then work on the data collection described in the trajectory contest handout. Try to finish your launcher calibration graph by the end of class tomorrow.
Homework:
- Add to spreadsheet -- include a "series" of data points for 2
obstacles, the ceiling, launcher muzzle position, and target
location. Like this...
 These are some videos that I made last year. Hopefully they
are helpful.
These are some videos that I made last year. Hopefully they
are helpful.
- Mr. Pennington's multiple choice questions #9-19, on p. 11-12 of the Unit 2 Packet Solutions
 Class
11.5 Monday, 10/3/22
Class
11.5 Monday, 10/3/22 Warm Up: Suppose you want to create a spreadsheet formula that tells you the initial velocity of a projectile following a symmetric flight path. Suppose cell B2 provides the projectile's range and Cell B3 provides the projectile's initial launch angle.
Write the formula as you would enter it into a spreadsheet.
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Add to spreadsheet (see assignment below)
Homework:
- Enter formulas into the velocity calculators (cells B4 and E4)
on the "launcher calibration" page of the trajectory
spreadsheet. The assymetric calculator is not required, but
you get extra credit if you can do it on your own (on your honor).
Then prepare a table to create a graph of initial velocity vs
launcher setting. Then make up some fake data as a placeholder
to check and see if your graph works. It should all look like
this screenshot (except for the assymentric calculator).

- Mr. Pennington's multiple choice questions #1-8 only, on p. 10-11 of the Unit 2 Packet Solutions
 Class
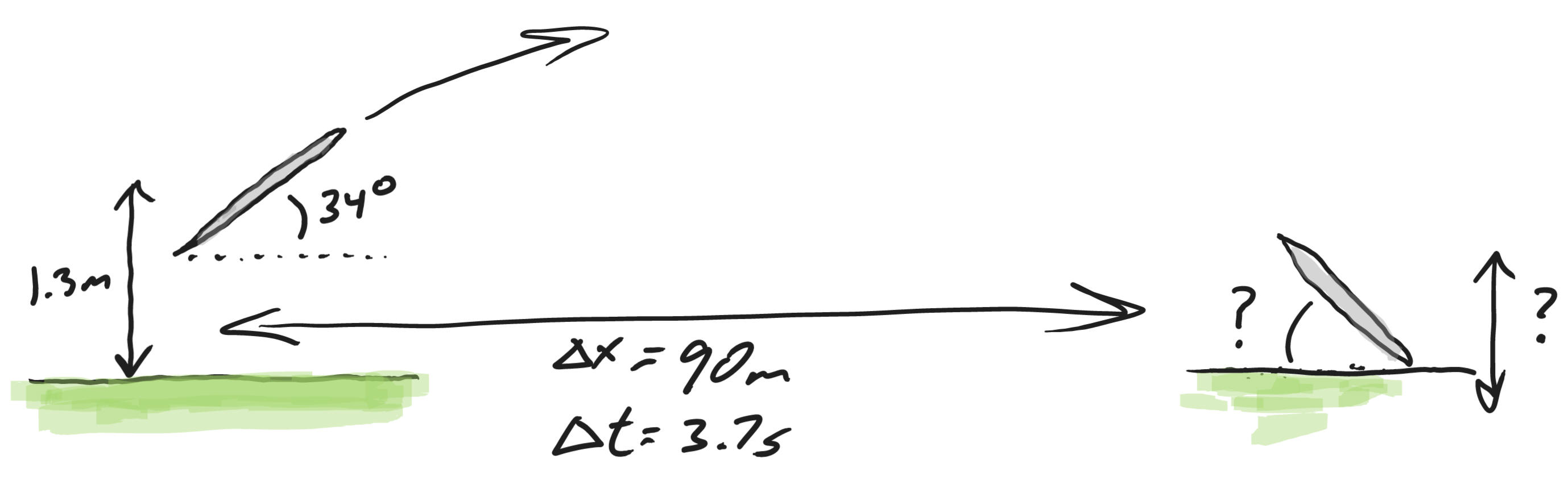
11 Friday, 9/30/22
Class
11 Friday, 9/30/22 Warm Up: An olympic athlete throws a javelin at an angle of 34 degrees, with respect to the ground. The release point of the javelin is 1.3m above the ground. The javelin travels a horizontal distance of 90 meters and lands after a flight lasting 3.7 seconds.
1. At what angle is the javelin sticking out of the ground at its point of impact?
2. It turns out that the field is not level. How much higher or lower is the field at the point of impact, compared to the field at the point of release?
Today:
- Return spool car graphing assignment
- Check/review homework
- Video of warm-up -- demonstrating strategy of separating motion variables into three dimensions (e.g. Vx, Vy, and V)
- Introduction to the Projectile Contest
- An example problem: how can we hit this target from
the release point (muzzle position) shown? What
combination of launch angle and initial velocity will work?

- Here is my launcher spreadsheet.
- Here is a
launcher template that you can use, and here is a screenshot
that you can use to check your calculations. Enter the
same numbers in the yellow cells, and see if you get the same
output.
 Here's a second screenshot with different yellow numbers, that
you can use as a 2nd check...
Here's a second screenshot with different yellow numbers, that
you can use as a 2nd check...
- An example problem: how can we hit this target from
the release point (muzzle position) shown? What
combination of launch angle and initial velocity will work?
Homework:
- Projectile Practice Problem #3 on page 9 of the Unit 2 Packet Solution Video with 3 column strategy
- Complete Projectile Contest: Assignment #1, in Google Classroom.
 Class
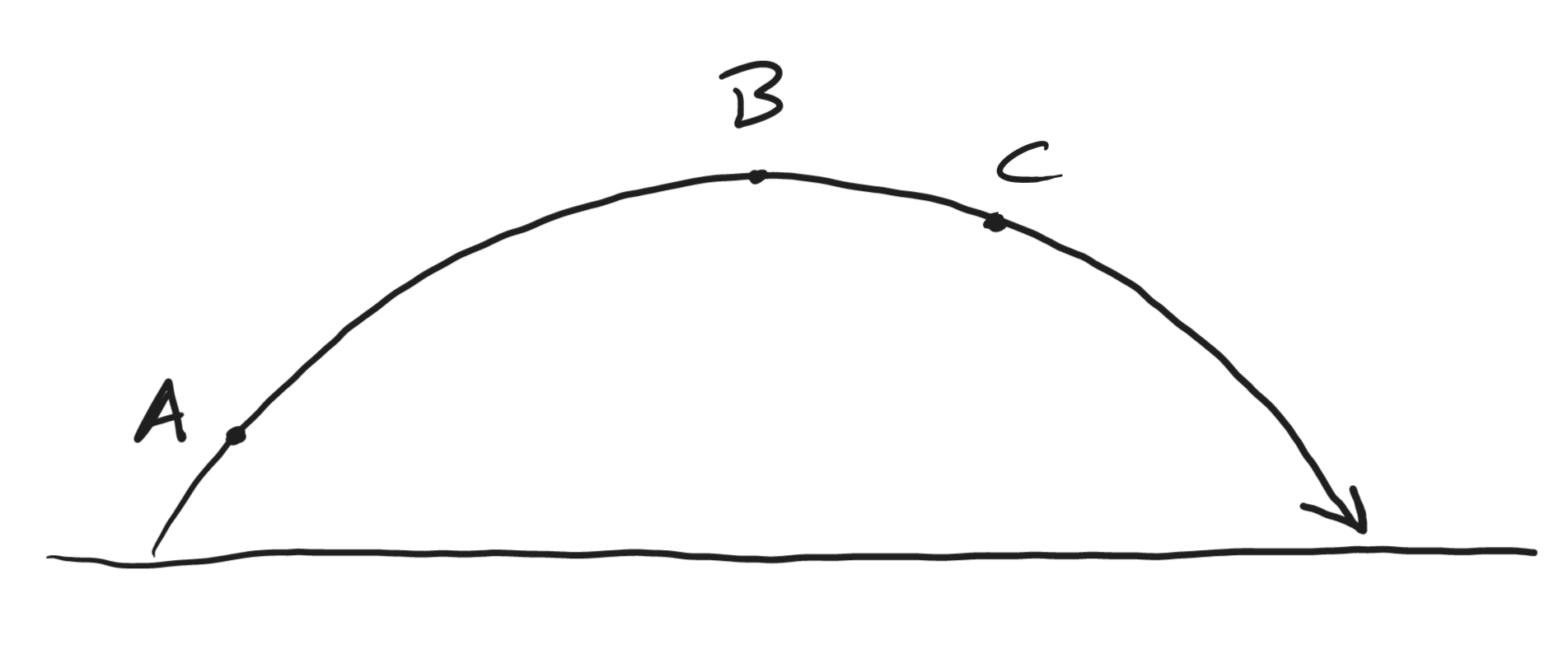
10.5 Thursday, 9/29/22
Class
10.5 Thursday, 9/29/22 Warm Up: The diagram on the right shows the symmetric trajectory of a free-falling projectile. Sketch the diagram.
1. What does free-falling mean?
2. Show/label the projectile's overall velocity vector (v), x velocity vector (vx), and y velocity vector (vy) at points A, B (apogee), and C.
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Finish the Notes: Packet p. 6-7 Currents and Projectiles -- Notes and Practice Problems Filled-in notes and solutions Video of Notes from a past year's Class
Homework:
- Projectile Practice Problems 2 - 4 on -- p. 8-9 of the Unit 2 Packet Solutions
Warm Up: None -- test retake day
Today:
- Test retake -- optional
Homework:
- See yesterday
 Class
9.5 Tuesday, 9/27/22
Class
9.5 Tuesday, 9/27/22Warm Up:
Suppose you shoot a projectile, horizontally, from the edge of a school tabletop that is 0.95m above the floor. If the projectile hits the floor at a distance of 14 floor tiles from the table...
a. What is the projectile's v0?
b. How would you find the projectiles' final speed?
c. How would you find the angle at which the projectile hits the floor?
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Notes: Packet p. 6-7 Currents and Projectiles -- Notes and Practice Problems Filled-in notes and solutions Video of Notes from a past year's Class
- Turn in spool car graphs (position, velocity, and acceleration)
Homework:
- River problems 6 and 7, on page 5 of the Unit 2 Packet. Solutions for 2 & 3 Solutions for 5-7
- Projectile Practice Problem # 1 on p. 8-9 of the Unit 2 Packet Solutions
 Class
9 Monday, 9/26/22
Class
9 Monday, 9/26/22 Warm Up: Someone is crossing a river in a boat, navigating by compass in complete darkness. The river flows 30 degrees south of west at a rate of 5m/s. The boat's velocity is 20 degrees west of south, at a rate of 20m/s. How do we calculate the boat's speedometer reading and heading?
Today:
- The optional test retake will be Wednesday, not tomorrow. I had forgotten that tomorrow is a split block day.
- Check/review homework -- solution
- Do a practice orthogonal problem together -- #4 on p 5. VIDEO from class
- Spool Car Video Analysis -- finish your graphs of position, velocity, and acceleration vs time. Turn them in before the end of class. My example -- thanks to SF for an excellent idea regarding acceleration graphing in sheets
Homework:
- River problems 2, 3, and 5 on page 5 of the Unit 2 Packet. On #3, change the current speed to 2.5m/s. Solutions for 2 & 3 Solutions for 5-7
Warm Up:
Sketch a head-to-tail diagram for each of the following. Two "component" vectors should add up to the "resultant." The trickiest part is identifying the resultant.
2. A river's 3mph current flows in a direction 15
degrees West of North. A swimmer, whose speed in s till
water is 2m/s, swims across the river with a heading 35 degrees South of
West. What is the swimmer's velocity, relative to the Earth?
till
water is 2m/s, swims across the river with a heading 35 degrees South of
West. What is the swimmer's velocity, relative to the Earth?
3. A superhero steward on an airplane is traveling in a direction 10 degrees East of South, and their speed is 580mph. The plane's velocity is 460mph in a direction 5 degrees West of South. What is the steward's heading and their "speed on a still plane?"
Sketches and answers: --- I got rid of number 1. Just ignore solution #1.
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Spool Car Video Analysis -- create graphs of position, velocity, and acceleration vs time. Due at the end of class on Monday. You may not have much class time to work on them on Monday.
Homework:
- Complete the "classic river problem" on p. 4 of the packet. I'm not provided solutions on this one.
- Optional test retake next Tuesday.
 Class
8 Thursday, 9/22/22
Class
8 Thursday, 9/22/22 Warm Up: A delivery airplane flying horizontally with a ground speed of 120 m/s releases packages from a height of 4,800 meters. If the packages are not affected by air resistance, how far in advance of the target (in the x dimension) should the packages be released?
Today:
- Notice the test retake help video links in Classroom.
- Unit 2 Notes -- Pages 1-3 of the Unit 2 Packet
Filled-out version of the notes
VIDEO
from today's class.
- Trigonometry -- using trig functions (SohCahToa) and their inverse functions. Short video from last year.
- Intro to kinematics in 2 dimensions
- Orthogonal and non-orthogonal vector addition
- Helpful videos:
- Spool Car Video Analysis is on hold until next class.
Homework:
- Complete the vector addition practice #4-6 on p. 3 of the Unit 2 Packet. Here are my solutions. Homework help -- Vector addition
- Optional test retake next Tuesday.
Warm Up:
1. Suppose the two vectors on the right represent two forces acting on the clam. In what direction will the clam accelerate? How will that acceleration compare to the accelerations we would observe if each force were acting alone?
2. The diagram on the right shows a top view of a train car that is moving at a rate of 2m/s. You are in the car. In which direction and how fast should you walk in order to have the intended velocity shown on the right.
Today:
- Return tests
 Mean = 81.5%, Median = 85.1%
Mean = 81.5%, Median = 85.1% - Spool Car Video Analysis: In Google Sheets... VIDEO
- Paste your data
- Create a new column to calculate velocity
- Create scatterplot graphs of position vs. time and
velocity vs time.
- Move each graph to its own sheet.
- Label your x (time) and y (position or velocity) axes
- Set up useful major and minor gridlines.
- Create a third graph showing acceleration vs time. You can use any method you like to make this graph. It can be in your spreadsheet, or you can draw it by hand. Graph paper will be provided.
- Turn-in your spreadsheet in google classroom. If you have a physical acceleration graph, hand it in to morrow, in person.
Homework:
- Finish the video analysis. It will be due on Friday, and you will probably have a little class time to work on it tomorrow. This is not an optional assignment. If you don't do it, a zero will go in PowerSchool.
- Optional test retake next Tuesday.
Warm Up: None
Today:
- Test
Homework:
- None -- work on the bonus, if you add a signed statement that you did all of the work yourself.
 Class
6.5 Monday,
9/19/22
Class
6.5 Monday,
9/19/22Warm Up: Velocity and Acceleration Combinations Matching Quiz. Use this link to take the quiz.
Today:
- Questions relating to the test?
- Spool Car Analysis.
- Download your car video onto a laptop.
- In Logger Pro
- "insert" your video
- Right click to confirm that the frame rate is correct.
- Use the three dots to open tools
- Set the scale of the race course to 5m
- Collect data for the entire race -- you can skip some frames to space things out, but don't skip too many.
- Copy your time and X position data
- In Google Sheets
- Paste your data
- Give your spreadsheet a name that will help you find it later this week.
Wednesday and/or Thursday:
- In Google Sheets
- Paste your data
- Create a new column to calculate velocity
- On separate sheets, Make graphs of position vs. time and
velocity vs time.
- Position graph should have major gridlines at 1m and minor gridlines at 0.1m (vertical axis). Choose helpful gridline spacing for the time axis.
- Velocity graph -- choose helpful gridline spacings (minor and major)
- Print the two graphs on one sheet of paper (double sided)
- Use your graph of velocity vs. time to create a third graph showing acceleration vs time. You will need to draw this one by hand.
Homework:
- Test tomorrow. Optional retake next Tuesday.
 Class
6 Friday,
9/16/22
Class
6 Friday,
9/16/22 Warm Up: How does a spool car work? Why is the stick necessary?
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Spool Car Activity:
Configure a spool car until it is fast enough to break the
rubber band car world record for speed. Then use video
analysis of your car's 5m performance to create graphs of position,
velocity, and acceleration vs. time.
- To do today: VIDEO
- Get your car going as fast as possible.
- Get a video (in "most compatible" format -- I will explain) of your car starting from rest and traveling 12 meters.
- If there's time, begin extracting video data using Logger Pro.
- To do today: VIDEO
Homework:
- Test on Tuesday -- Be prepared to ask any questions that you may have on Monday.
More Unit 1 Practice (optional!)
-
New questions and problems
- Extra Unit 1 Test Practice -- Questions and problems
- Extra Unit 1 Test Practice -- Answer Key The answer to #5 on the first section was wrong. It should be correct now (if it's highlighted in yellow). Solution to Extended Kinematics Problem
-
Optional -- Here is some more
practice creating graphs for events. These are harder than
what you will encounter on the test.
- Blank PDF Handout -- "Extra Graphing Practice"
- Solutions(**On my graph of position vs time for the soccer ball kick, my graph should really have started and ended at the same position.)
- Video of me working through these and creating solutions
- Optional -- More practice with simple (one formula required) kinematics problems. Make your own copy and expand column D to see the answers.
Warm Up: Try problem #58 from p. 26 of the packet (also below). You will see this type of problem again. It doesn't ask for a measurement, but rather a multiplication factor (like 2x, 3x, 1/2x...).
1. What's a good strategy for this type of problem?
2. What's the answer to this one?
The
acceleration due to gravity on the Moon is
about one-sixth what it is on Earth. If an object is thrown vertically
upward on the Moon, how many times higher
will it go than it would on Earth, assuming the same initial velocity?
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Practice setting up and operating a spool car. The goal is to break the rubber band car world record. You will then be using video analysis of your car's 5m performance to create graphs of position, velocity, and acceleration vs. time.
Homework:
- "More kinematics problems" 57 and 60, on packet p. 27 and 28 of Unit 1 Packet (PDF) Answer Key
- Test on Tuesday -- understand and be able to do anything in the packet, but especially the types of concepts that are on on the final practice test (23-26)
 Class
5 Wednesday,
9/14/22 (B5/6 ends at 11:55)
Class
5 Wednesday,
9/14/22 (B5/6 ends at 11:55)Warm Up:
1. Suppose students enter our school at a rate of 54 pounds/sec (pounds of student). After they enter, they lie down, head-to-toe, forming a line whose length is the sum of their heights. Since an average 16 year old student's weight:height ratio is about 2.07 lb/in (and assuming these are all average students with that ratio), how many days will it take them to form a line 3 miles long?
2. How does dimensional analysis work? On what basic mathematical premise is it based?
3. This problem (#1) is fine for dimensional analysis practice, but it's not actually solvable given the information provided. Explain.
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Briefly discuss the Velocity and Acceleration Combinations Activity (Google Classroom assignment).
- Practice test work time. Use this practice test to pinpoint your weaknesses. Don't discuss a problem or look up its answer until after you've finished it.
Coming Up:
- Test on Tuesday, similar in format to today's practice test
- Tomorrow and Friday, attempt to break the rubber band car world record for average speed over 5 meters. Use video evidence to determine your car's elapsed time, average speed, average acceleration, and maximum speed.
- Tomorrow and Friday -- homework will be the problems on pages 27 and 28 of the packet
Homework:
- Finish the practice test -- p. 23-26 of the
Unit 1
Packet (PDF)
- Answer Key
- Video Help part 1 (it's unfortunately sideways, but it's short)
- Video Help part 2 (starts with #4, I think)
- Optional -- Kinematics formulas Quizlet -- to help you memorize the basic kinematics formulas
- Optional (won't go into PowerSchool), if you want to brush up on your dimensional analysis skills -- Unit Conversions Practice
 Class
4.5 Tuesday,
9/13/22
Class
4.5 Tuesday,
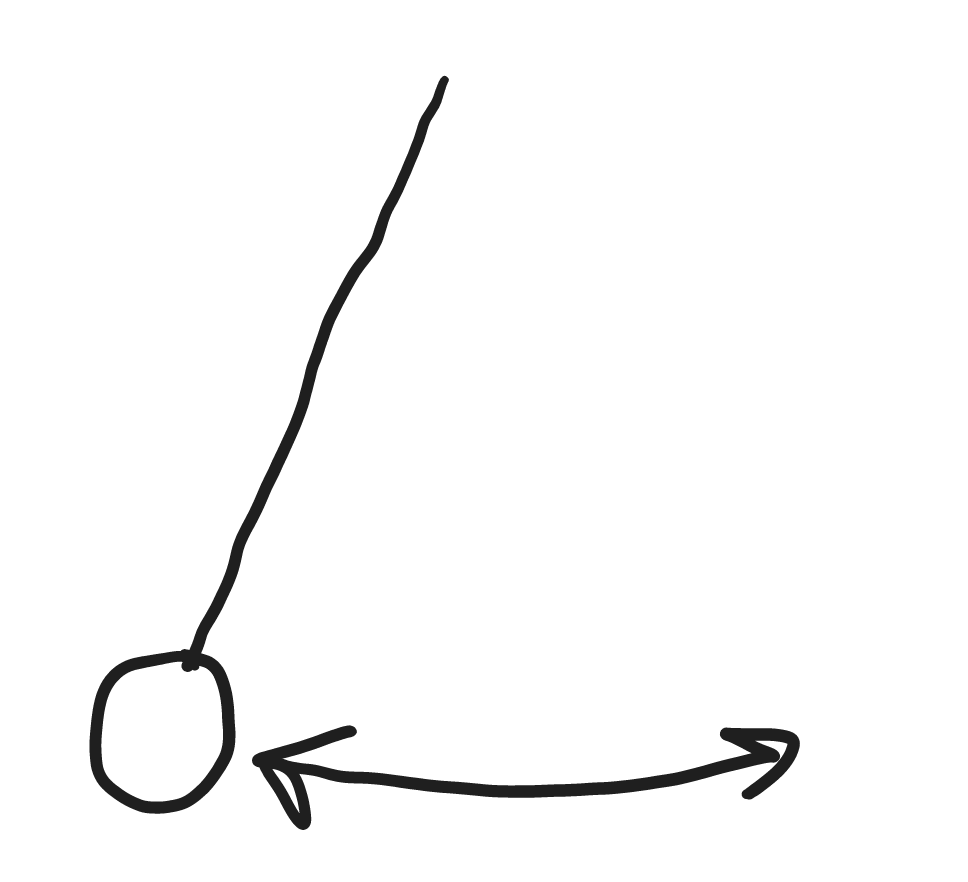
9/13/22Warm Up: What would a graph of X velocity vs time look like for a pendulum that is swinging back and forth (left to right and back). Assume that it starts from the far left of its swing.
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Make sure that someone (and only one person) in your group has turned in (in Google Classroom) the Velocity and Acceleration Combinations Activity (Google Classroom assignment).
Homework:
- Complete the extended problem on page 22. Answer Key Video Explanation
 Class
4 Monday,
9/12/22
Class
4 Monday,
9/12/22Warm Up: Suppose a dart is thrown rightward across a room, finally embedding in a dart board. Sketch a graph of the dart's x acceleration (horizontal acceleration only) from the time it begins to move to the time at which it stops.
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Finish the Notes: Free-fall and areas under curves (packet p 15-16) pdf Filled-In Version Video from 2020 -- start around 20:30
- Example extended problem. VIDEO
- Finish the Velocity and Acceleration Combinations Activity (Google Classroom assignment).
Homework:
- Complete the extended problem on page 21. Answer Key Video Explanation
 Class
3.5 Friday,
9/9/22
Class
3.5 Friday,
9/9/22Warm Up:
Consider the case of this ball. At t = 0s, the ball is free-falling directly upward at a height o 10m, with a speed of 20m/s. Sketch graphs of the ball's position, velocity, and acceleration (vs. time) over the next 4 seconds. [For simplicity, use g =10m/s2 instead of g = 9.8m/s2]
Today:
- Check/review homework
- In groups, work on the Velocity and Acceleration Combinations Activity (Google Classroom assignment).
Homework:
- Complete problems 3-7 (packet p. 20) from Mr. Pennington's Old 1-D Kinematics Test. Answer Key. If you have questions, watch this Video for Help with the Problems
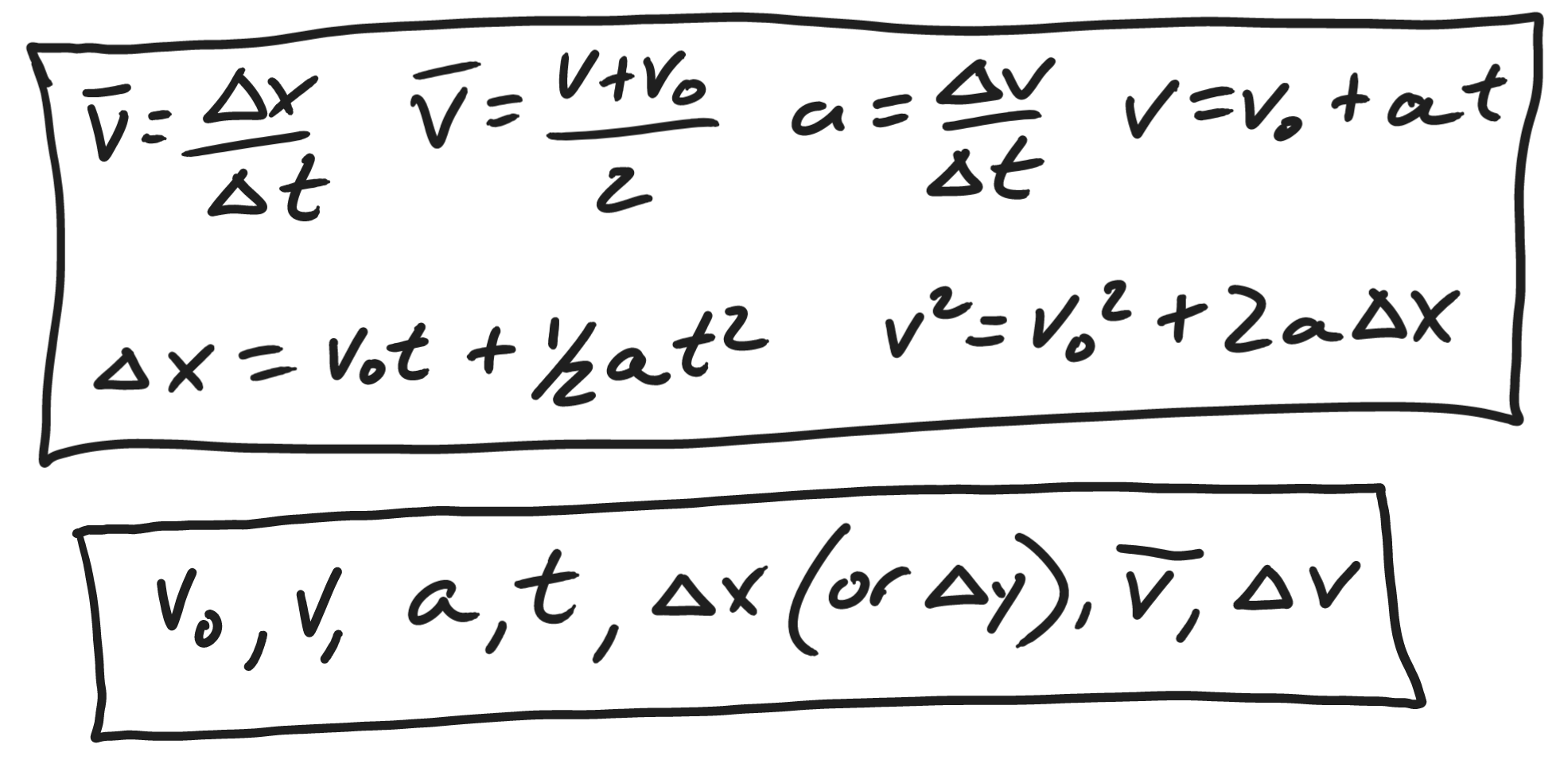 Class
3 Thursday,
9/8/22
Class
3 Thursday,
9/8/22Warm Up: The top box on the right shows the 6 formulas that you can use to solve any kinematics problem in this unit. The bottom box lists all of the variables that appear in the formulas. [Note that I have left out x and x0.]
1. Try to create an interesting physics problem, either by starting with a formula (or two) that will help solve the problem, or by selecting some variables as "givens."
2. Solve your problem.
Today:
- Check/review homework
- Notes: Free-fall and areas under curves (packet p 15-16) pdf Filled-In Version Video from 2020 -- start around 20:30
- In groups, work on the Velocity and Acceleration Combinations Activity (Google Classroom assignment).
Homework:
- Complete the rest of the multiple choice on Mr. Pennington's Old 1-D Kinematics Test (Packet pages 18-20). Answer Key. If you have questions, watch this Video for Help
Warm Up:
Match each position vs. time graph with the correct velocity and acceleration graph.Today:
- Check/review homework
Homework:
- Complete Multiple Choice 1-12 from Mr. Pennington's Old 1-D Kinematics Test (Packet pages 17-18). Answer Key. If you have questions, watch this Video for Help
 Warm Up:
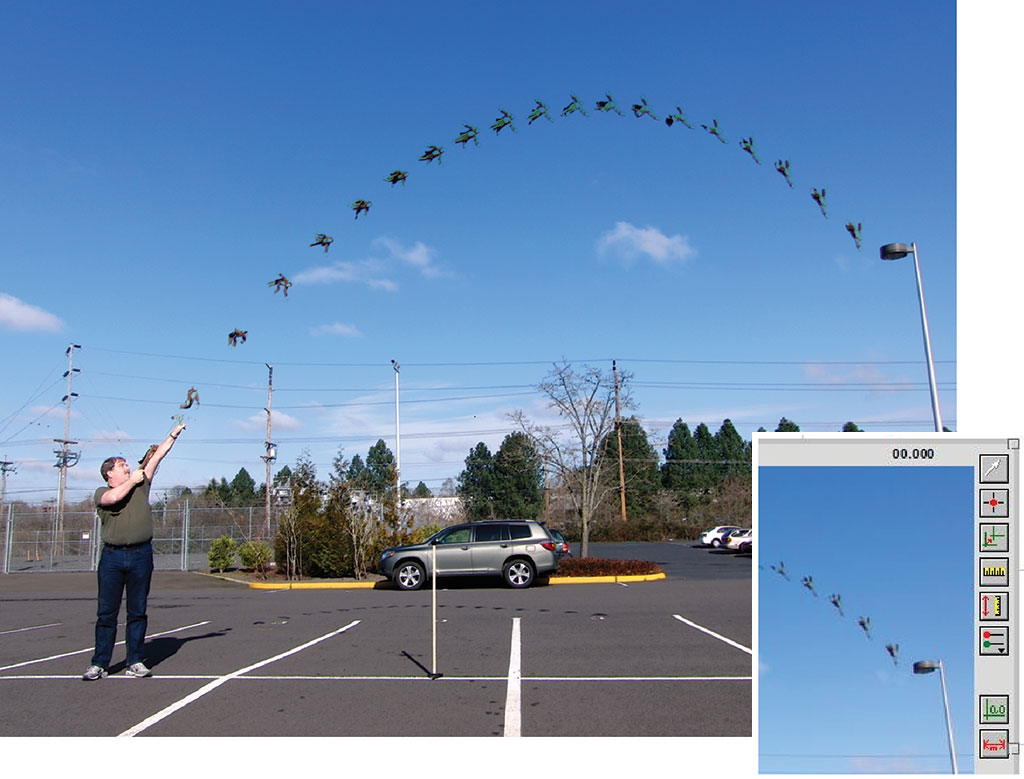
Warm Up:
1. Assuming that the man in the picture is 2m tall, and the frame rate of the camera was the usual 30 frames per second, what was the approximate maximum speed of the object?
2. Based on your answers, do you think the assumption of 30 frames per second was too low, too high, or about right?
Today:
- Check/review homework -- Graph Comparisons Graph Comparisons solutions
- Notes: Intro to Kinematics Formulas -- First, see that there's nothing mysterious about the formulas; Second, see that there's nothing mysterious about using them (guess and list method).
- If there's time...
- Info
- Slideshow -- stuff on my phone from the last year
- Student info sheet (PDF)
Homework:
- Finish the problems on p. 13 and 14 of the Unit 1 Packet. Answer Key -- Kinematics Formulas and Practice Problems
 Class
1.5 Friday,
9/2/22
Class
1.5 Friday,
9/2/22Warm Up:
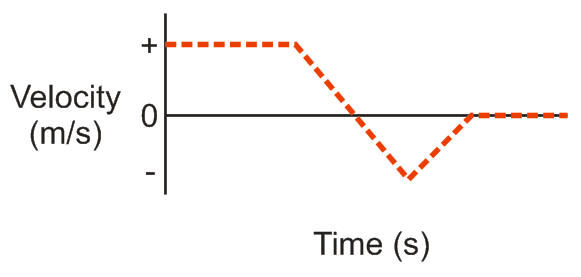
Use the velocity vs time graph on the right to sketch the shape of a corresponding position vs time graph. [Assume that motion away from the sensor is positive, and motion toward the sensor is negative.]
Today:
- Check/review the homework.
- Complete Acceleration Notes -- Answer Key Video from Last Year -- start at 12:50
- Graph comparisons work time
- Unit 1 packet Answer Key (PDF)
Optional Reading -- Online Textbook:
Homework:
- Complete graph comparisons on pages 9 and 10 of packet. Graph Comparisons solutions Video Solutions
 Class 1:
Thursday,
9/1/21
Class 1:
Thursday,
9/1/21Warm Up: Suppose you're involved in a 2 lap race. If you want your overall average speed to be twice as fast as your speed for the first lap, how much faster do you have to go during the 2nd lap? [To calculate average speed you can use rate = distance / time]
Today:
- Some of you... sign on to a laptop -- Username: guest-ehs Password: guestehs
- Course expectations -- see if we missed anything
- Motion Matching Activity
-- do the activity and answer the questions. Work in groups of
3 or 4.
- Directions: Matching Motion Graphs with motion detector (Web page)
- Questions are on packet page 6.
- Notes -- Kinematics in 1-D -- pages 1-4 of the packet. Video of the notes from last year. 1-D Kinematics notes Answer Key
- If there's time...
- My info
- Class goals
- Slideshow -- stuff on my phone from the last year
- Student info sheet (PDF)
- Online Textbook:
- My info
- **
Optional Online Textbook Reading:
Homework:
- Complete page 5 of the packet. Answer Key
Physics 200: Mr. Stapleton
Warm Up:
 Spin
one of the "sprotating cylinders" by pressing one end until it squirts
out from under your finger. Try pressing the other end.
Spin
one of the "sprotating cylinders" by pressing one end until it squirts
out from under your finger. Try pressing the other end.
When the cylinder is spinning, why do you only see the symbol that you press?
Today:
- Learn names/pronunciations -- fill out seating chart
- Get the Unit 1 Packet:
- Enter attendance
- Preview
- of the year (see last 2018-19 site).
- This unit -- skim through the packet
- B5/6 has D lunch (12:45)
- Today's block times are:
- B7 -- 12:25-12:58
- B8 -- 1:02-1:35
Links:
Online Textbook Reading:
Homework: None