Warm Up: None
Blue:
- Fire from friction + marshmallow roast (almost certainly!)
- Get the Unit 4 packet.
Warm Up: None
Blue:
- Today: Optional test retake
- Tomorrow: Wear warm clothes, and shoes for walking in the snow. Fire from friction + marshmallow roast (hopefully!)
Gold: You're done. See you on Thursday!
Warm Up: None
Gold:
- Optional test retake
Blue: Prepare for your optional test retake on Monday and friction fire on Tuesday.
Warm Up: None
Gold:
- Today: Fire from friction + marshmallow roast (hopefully!)
- Tomorrow: Optional test retake
Blue: Prepare for your optional test retake on Monday and friction fire on Tuesday.
Warm Up: None
Today I will just be going over the tests. To help you prepare for the retake, I will provide a video link to the solutions.If you have questions about the optional (extra credit) project, I can answer those.
Warm Up: None -- Blue and Remote Test Today
Pick up a bearing block and/or twine if you want themWarm Up: None -- Gold Test Today
Pick up a bearing block and twine if you want them
 Class
34:
Thursday
1/14/2021
Class
34:
Thursday
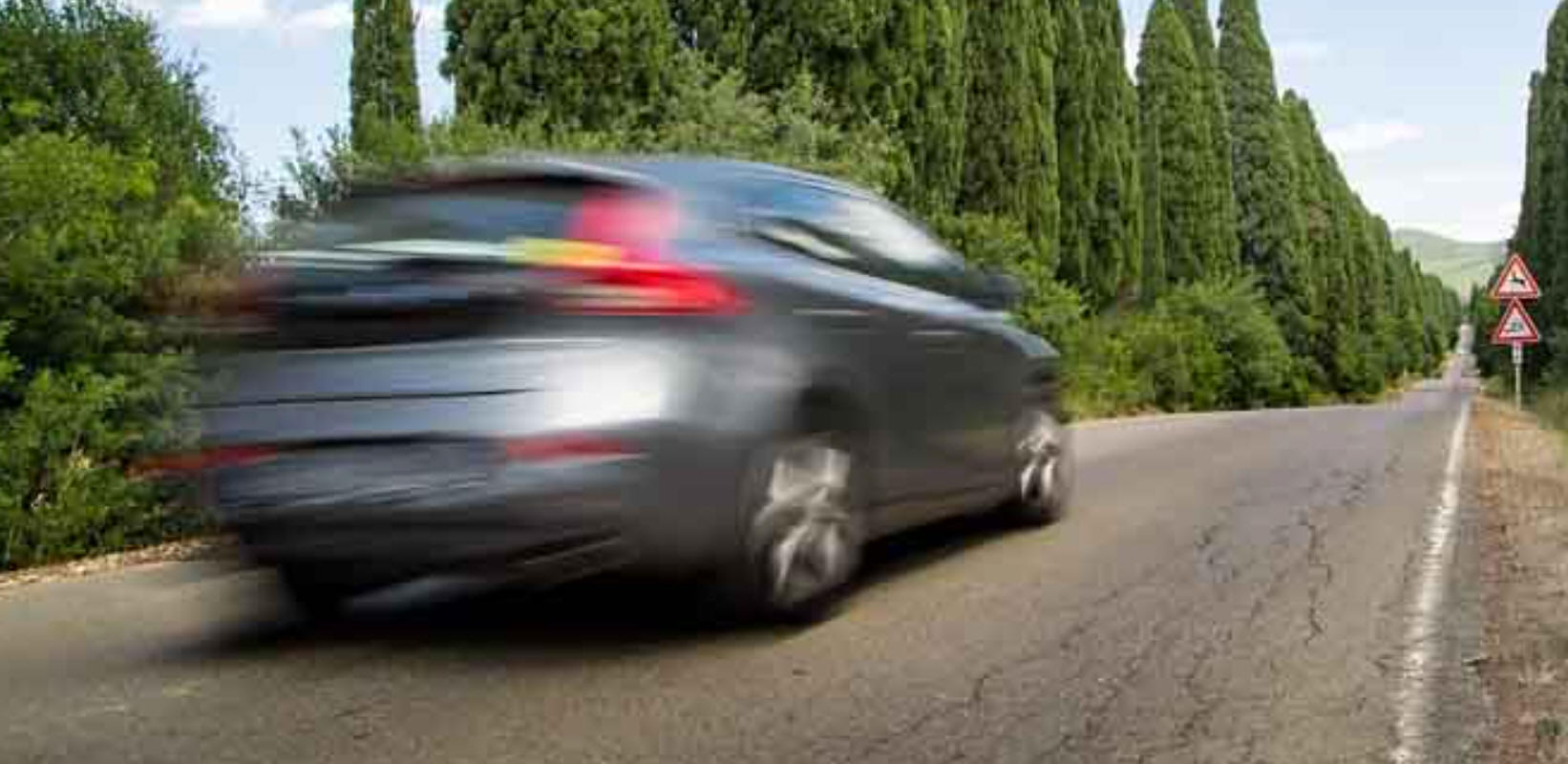
1/14/2021Warm Up: Draw a force diagram for each of the five numbered moments in the following scenario. Use arrows to represent the individual and net force vectors, and name all of the forces appropriately. Arrow lengths should be in proper proportion (approximately).
Starting from rest1, a car accelerates2 to its maximum velocity, maintains3 that velocity for a few seconds, and then brakes4 as quickly as possible, finally returning to rest5.
-
Google Meet:
-
Discuss the optional homework -- or anything else
-
Discuss an end of term project -- fire from friction + marshmallow roast?
-
-
Gold: Test tomorrow
-
Blue and Remote: Test on Tuesday
 Class
33:
Wednesday
1/13/2021
Class
33:
Wednesday
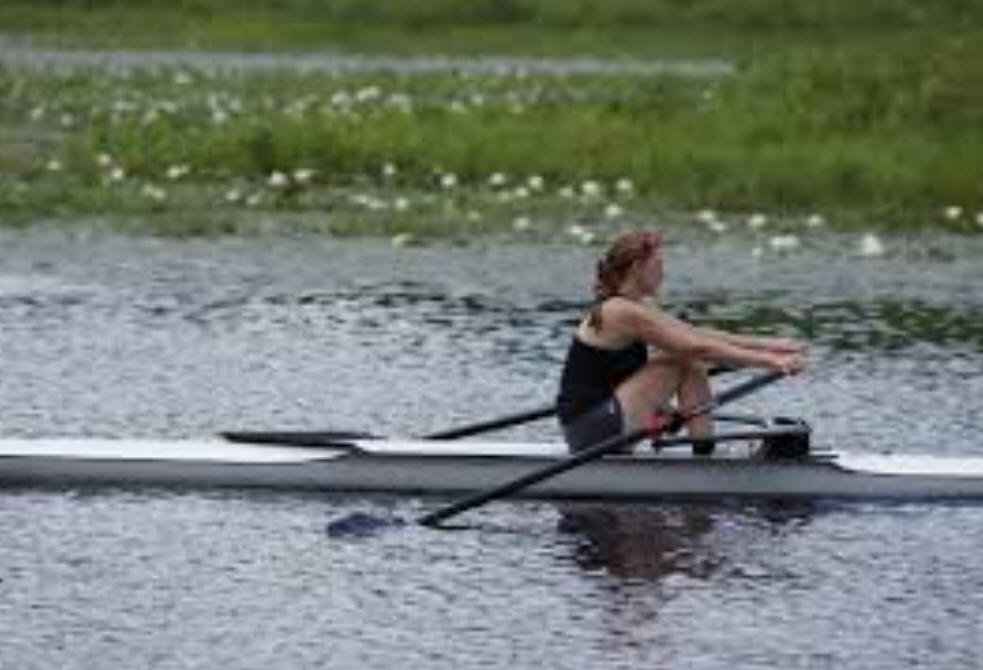
1/13/2021Warm Up: A 50kg rower accelerates to our left at a rate of -1m/s2. She does this by applying a 100N force to the oars. Draw all of the forces acting on the rower and calculate their magnitudes.
-
Google Meet:
-
Discuss the homework.
-
The Test:
-
Gold test this Friday. Blue and Remote tests next Tuesday.
-
Gold retakes next Friday (1/22). Blue retakes on Monday, 1/25.
-
-
Practice drawing and labeling forces.
-
Discuss the "extra days" between now and the end of the term.
-
-
All Students -- Optional (won't be recorded) Practice:
-
Packet p. 18-21 (More Newton's Laws in 1-D Practice) [This was another old test.]
-
This assignment has a few mistakes that you may want to fix or be aware of:
-
The car's motion and initial acceleration in question #3 should be rightward (not leftward).
-
Problem #1 is not a great test question, but it still works.
-
Problem #5b should say "downward."
-
The coefficient of friction in problem #6 should be kinetic friction
-
-
Video Explanations: Part 1 (short answer), Part 1.5 (problem #1 -- a bad problem), Part 2 (problems 2-7)
-
-
 Class
32:
Tuesday
1/12/2021
Class
32:
Tuesday
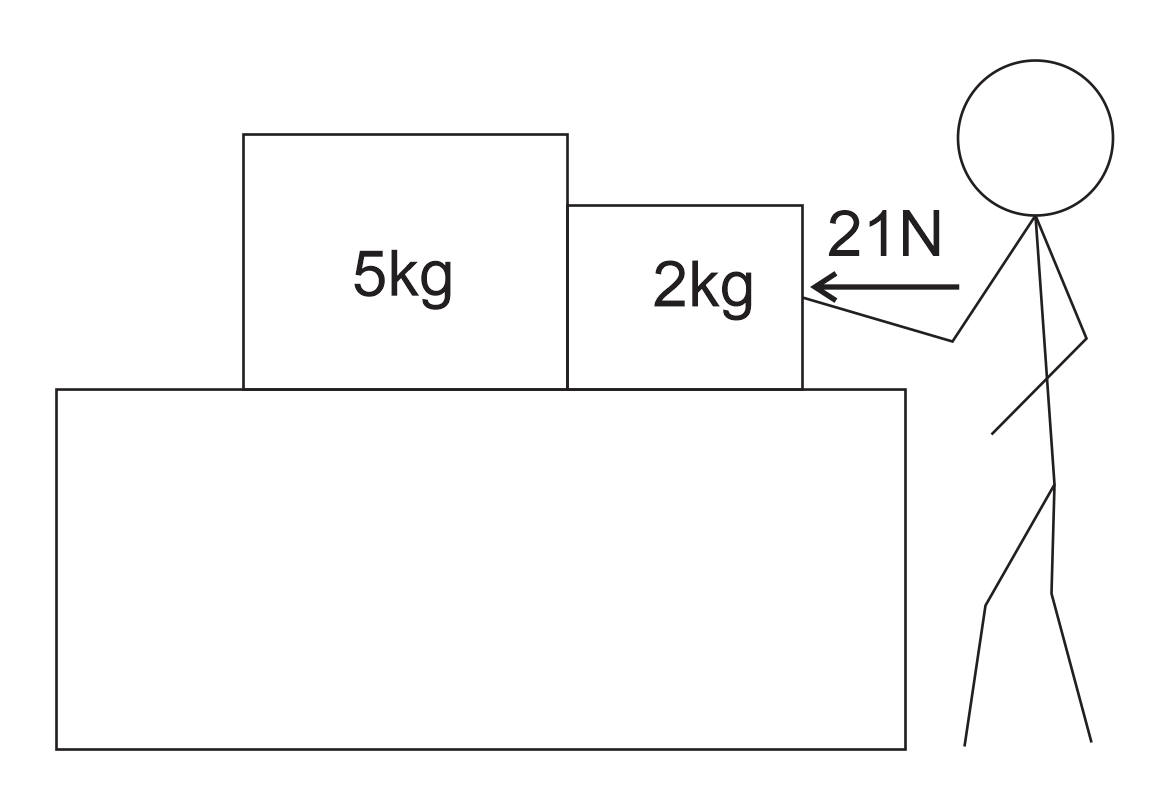
1/12/2021Warm Up: A person pushes a box with a force of 21N, as shown. This causes the two boxes to accelerate. If there is no friction between the boxes and their sliding surface...
1. What is the "contact force" between the two boxes?
2. What are all of the individual forces and net forces that are acting on each box?
3. Compare and contrast this "contact force problem" with a "tension problem."
-
Google Meet:
-
Discuss the homework.
-
-
All Students -- Practice:
-
Complete p. 17-22 of the packet (Last Year's Newton's Laws Test #3) pdf version answers.
-
In addition to graphing net force in #2 on page 23, it would be a good idea to create force diagrams for the ball at various moments during the event. Show individual forces and net force. Here's a video of me discussing short answer #2
-
 Class
31:
Monday
1/11/2021
Class
31:
Monday
1/11/2021Warm Up: Suppose a skydiver steps out of a stationary helicopter, falls until reaching terminal velocity, deploys a parachute, reaches a new terminal velocity, lands on the ground, and then stands still. [Skydiving physics video]
Draw one force diagram for the beginning of this trip (t = 0s), another force diagram representing t = 2s, and new force diagram for every instance when the net force switches between positive, negative, or zero. Use labeled arrows to identify the individual and net forces, and use arrow length to show relative magnitude.
How many diagrams should you draw?
-
Google Meet:
-
Discuss the homework.
-
If you want to complete the skydiving graph in the notes (similar to today's warm-up), watch this video, starting at about 33 minutes.
-
-
All Students -- Practice: Packet page 17 ("Newton's Laws in 1-D 20-21 Practice Problems")
 Class
30:
Friday
1/8/2021
Class
30:
Friday
1/8/2021Warm Up:
According to this article, emergency clinic records of 132 cats that jumped from windows of buildings showed a 90% survival rate. The average drop was 5.5 floors.
1. What's going on?
2. What's the rule for deciding whether to use "less" or "fewer?" Which applies here?
3. When does a falling cat experience zero net force?
4. When is a falling cat a "free-falling" cat?
5. Aside from the moment of impact, when does a falling cat experience maximum net force?
-
Google Meet:
-
Discuss the homework -- #5 & 6 from Multibody drill A
-
Notes: Drag and Terminal Velocity pdf version Filled-in notes and solutions -- If I have to cut this short, watch the video in the "notes" assignment in Google Classroom, and complete the skydiver graph. It starts at 32 minutes into the video.
-
-
All Students -- Practice:
-
Packet Page 16, #1-4 (Conceptual Practice with Drag) Answers
-
Packet Page 19, #4 (More newton's Laws in 1-D Practice) Answers If you want more help, watch the warm-up part of this video from Term 1 class #30.
-
-
Gold and Remote Students:
-
Test retake opportunity
-
Work time
-
 Class
29:
Thursday
1/7/2021
Class
29:
Thursday
1/7/2021Warm Up:
1. Which can you throw with more force, a Wiffle Ball® (0.045kg), a baseball (0.145kg), or a bowling ball (6.3kg)? Or is there no difference? Explain your thinking.
2. What limits the amount of force that you can apply when you throw a light object, like a Wiffle Ball, or a feather?
Interesting Link: article about the fastest pitch ever thrown
-
Meet:
-
Questions about the homework?
-
Analyze some systems in Notes: Tension and Systems pdf version Filled-in notes
-
-
Gold and Remote Students:
-
Test Retake Time
-
-
All Students -- Practice:
-
Multibody Drill A problems 5 and 6 in today's handout. pdf version
-
 Class
28:
Wednesday
1/6/2021
Class
28:
Wednesday
1/6/2021Warm Up:
If you need to stop a car quickly, why should you avoid locking the tires and skidding?
-
Meet:
-
Questions about the homework?
- Notes: Tension and Systems pdf version Filled-in notes
-
-
Blue Students:
-
Test Retake Time (gold retakes on Thursday and Friday)
-
-
All Students -- Practice:
-
Complete Multibody Drill A problems 1-4 in today's handout. pdf version
-
Old solutions -- missing some tensions Multibody Drill A Solutions -- Stapleton
-
New last night -- Video of Solutions
-
 Class
27:
Tuesday
1/5/2021
Class
27:
Tuesday
1/5/2021Warm Up: From the homework...
15. According to Newton’s third law, each team in a tug of war pulls with equal force on the other team. What, then, determines which team will win?
-
Meet:
-
Discuss #13 from the homework. The warm-up should have covered #15.
- Friction notes -- Notes: Newton's 3rd Law and Friction pdf version Video Link Filled-in version
- Do one or more of the homework problems, together.
-
-
Blue Students:
-
Test Retake Time (gold retakes on Thursday and Friday)
-
-
All Students -- Practice:
-
Complete problems #36-47 from Practice with forces in 1 dimension pdf version New Solutions to 36-38 New Solutions to 44 and 47 Answers/solutions
-
 Class
26:
Monday
1/4/2021
Class
26:
Monday
1/4/2021Warm Up:
One way to find the center of mass (a.k.a. balance point) of a stick is to support it with two hands and then slowly move those two hands together until they meet under the stick's center of mass. Why does this method work?
-
Meet:
-
Questions about the homework?
-
Notes on Newton's 3rd Law -- Notes: Newton's 3rd Law and Friction pdf version Video Link Filled-in version
-
-
Blue Students:
-
Test Retake Time (gold retakes on Thursday and Friday)
-
-
All Students -- Practice:
-
Answer the remaining two conceptual questions (#13 and #15) from Practice with forces in 1 dimension pdf version Answers/solutions
-
Warm Up: Santa Claus from an Engineer's Perspective
- Meet:
- Homework: Problems and Study
for Retake
- All students: Complete Problems #10-15 from Practice with forces in 1 dimension pdf version Answers/solutions I recommend trying the first problem on your own and then watching the video segment for that problem. Then try the second problem before watching that part of the video. Etc. Here's the video
- Blue Students: Retakes Monday and Tuesday after break (1/4, 1/5)
- Gold and Remote Students: Retakes Thursday and Friday after break (1/7, 1/8)
Warm Up: None
- No Meet
- Blue Test
-
Practice (Due before class tomorrow):
-
"Class #22 Practice" -- Conceptual #3-10 and Problems #1-9 from Practice with forces in 1 dimension Answers/solutions (not mine) Helpful formulas --
 Problem answers: 1. 75N, 2. 115kg, 4. 740N, 130N, 280N, 0N, 6.
-3600N 9. -780N
Problem answers: 1. 75N, 2. 115kg, 4. 740N, 130N, 280N, 0N, 6.
-3600N 9. -780N -
"Class #23/24 Practice" -- Complete Problems #10-15 from Practice with forces in 1 dimension pdf version I recommend trying the first problem on your own and then watching the video segment for that problem. Then try the second problem before watching that part of the video. Etc. Here's the video
-
Warm Up: None
- No Meet
- Gold Test
-
Practice (Due before class on Tuesday):
-
"Class #22 Practice" -- Conceptual #3-10 and Problems #1-9 from Practice with forces in 1 dimension Answers/solutions (not mine) Helpful formulas --
 Problem answers: 1. 75N, 2. 115kg, 4. 740N, 130N, 280N, 0N, 6.
-3600N 9. -780N
Problem answers: 1. 75N, 2. 115kg, 4. 740N, 130N, 280N, 0N, 6.
-3600N 9. -780N -
"Class #23/24 Practice" -- Complete Problems #10-15 from Practice with forces in 1 dimension pdf version I recommend trying the first problem on your own and then watching the video segment for that problem. Then try the second problem before watching that part of the video. Etc. Here's the video
-
 Class
22:
Thursday
12/17/2020
Class
22:
Thursday
12/17/2020Warm Up:
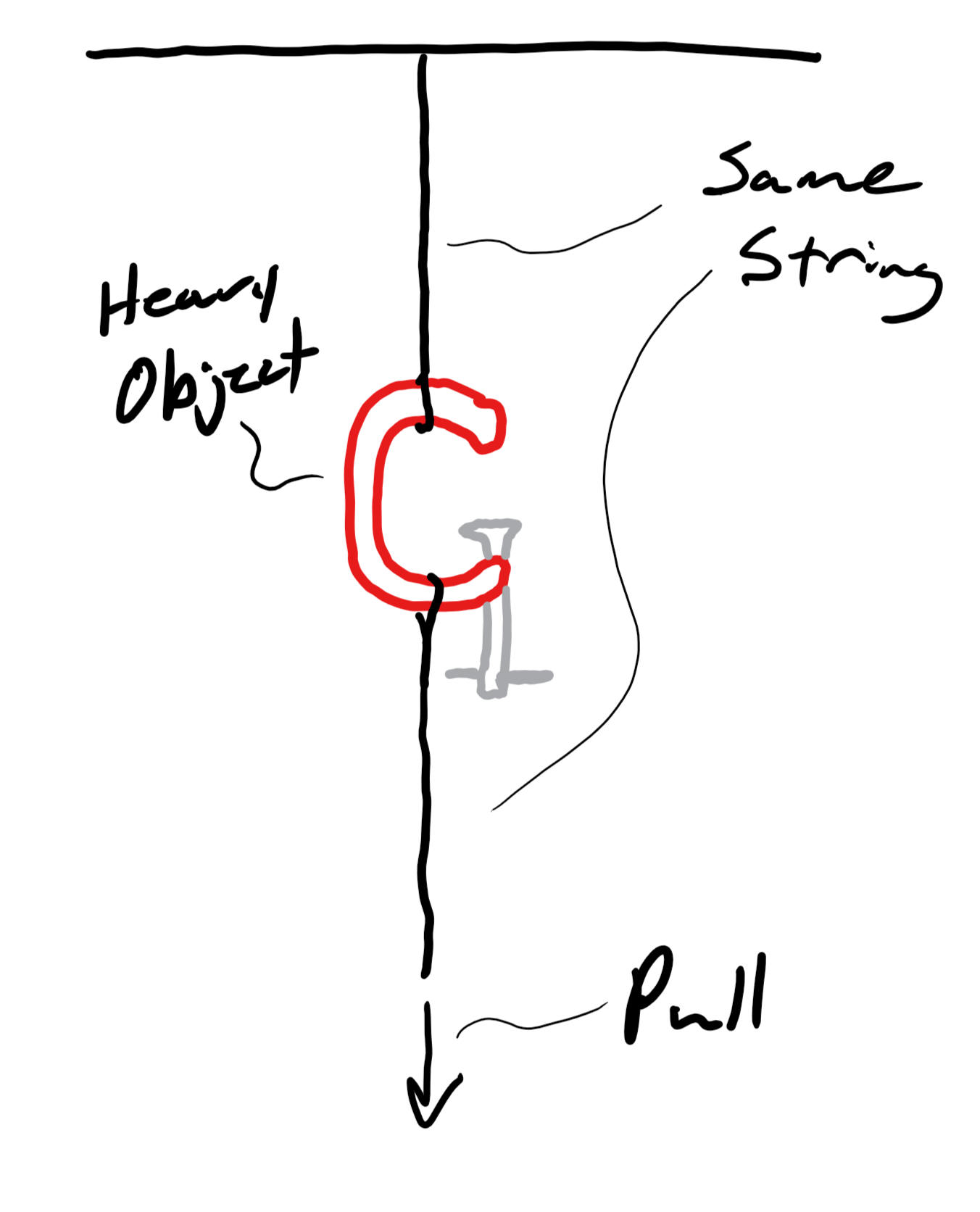
1. There is a heavy object suspended from the ceiling by a string. Another segment of the same string is hanging downward from the object. I am going to pull on the bottom string until one of the two strings breaks. Which string is going to break first? Why?
2. 1m/s = ____ mph. For next week's test, memorize this or be able to calculate it based on a known conversion.
- Meet
--
-
Begin New Unit: Newton's Laws
-
-
Upcoming Schedule:
-
Friday: Gold Test
-
Monday: Blue and Remote Test
-
Tuesday: Return Tests, go over homeworks
-
-
Practice (Due before class on Tuesday):
-
"Class #22 Practice" -- Conceptual #3-10 and Problems #1-9 from Practice with forces in 1 dimension Answers/solutions (not mine) Helpful formulas --
 Problem answers: 1. 75N, 2. 115kg, 4. 740N, 130N, 280N, 0N, 6.
-3600N 9. -780N
Problem answers: 1. 75N, 2. 115kg, 4. 740N, 130N, 280N, 0N, 6.
-3600N 9. -780N -
"Class #23/24 Practice" -- Complete Problems #10-15 from Practice with forces in 1 dimension pdf version I recommend trying the first problem on your own and then watching the video segment for that problem. Then try the second problem before watching that part of the video. Etc. Here's the video
-
Warm Up: Here are the problems we made up yesterday. Let's solve them..
1. A projectile in free-fall travels 5m horizontally and -20m vertically, in a time of 11s. What is its initial speed?
2. A second projectile has an inital y velocity of 2m/s. After 13 seconds of free-fall, it hits a horizontal surface. At the moment of impact, its x velocity is -8.5m/s. At what angle does the projectile hit the horizontal surface?
- Meet
- Review the homework.
- Unit 2 Test on Friday (Gold) and Monday (Blue and Remote) -- What's on the Unit 2 test
-
All Students -- Practice: None. No homework
Warm Up:
1. What is an "asymmetric" projectile problem?
2. How many fundamentally different types of asymmetric trajectories (for a physics problem) can you think of?
3. What are some variables that can be incorporated into a non-symmetric projectile problem?
4. Let's create a problem (or two). To give time for retakes, we can solve it (them) later.
- Meet
- Questions about the homework?
- Here's an extra non-orthogonal river
problem, in case anyone is interested...
- A boat has a heading that is 25 degrees South of West, and its water speed is 14m/s. The boat is traveling in a river with a current that is flowing at a rate of 5m/s in a direction 65 degrees East of South. What is the boat's velocity, relative to the Earth? Video of my solution Answer: 11.5m/s, 44.5 degrees South of West
- All Students -- Practice:
- Complete the problems section (page 2) of Chapter 3 Practice Test #2 pdf version Solutions
- Ch3 PTest Conceptual Questions Video Ch3 PTest Probs 1-2 Video Ch3 PTest Probs 3-4 Video
- Blue:
- Retake opportunity
- Work time
 Class
19:
Monday
12/14/2020
Class
19:
Monday
12/14/2020Warm Up:
I usually solve simple (orthogonal) river problems by drawing a head-to tail diagram of the component vectors and the resultant vector. For complicated (non-orthogonal) problems, I make a table of x and y components.
Would a table work for simple problems, like number 1, below?
1. A river's current flows 5m/s southward. A boat on the river has a velocity of 7m/s westward. What is the boat's heading, and what is its speed relative to the water?
Here's a trickier one...
2. A second boat, on the same river, has an eastward velocity and a northeastward heading. Find it's speed relative to the water and its speed relative to the Earth.
- Meet:
- Questions about the homework? -- Mr. Pennington's Problems
- Remote students stay in the Meet for retakes
- All Students -- Practice:
- Complete the conceptual portion (page 1) of Chapter 3 Practice Test #2 pdf version Solutions
- Ch3 PTest Conceptual Questions Video Ch3 PTest Probs 1-2 Video Ch3 PTest Probs 3-4 Video
- Blue:
- Retake opportunity
- Work time
 Class
18:
Friday
12/11/2020
Class
18:
Friday
12/11/2020Warm Up:
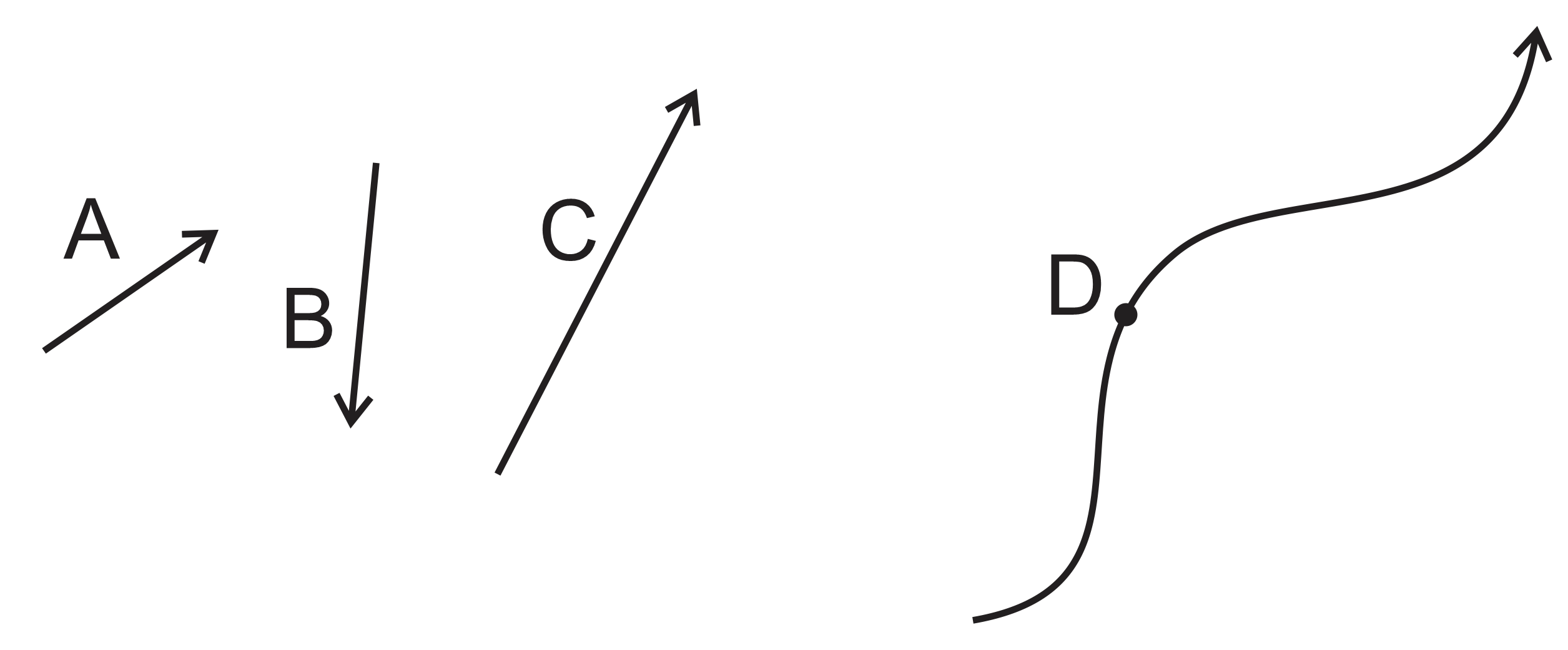
1. Two of the vectors A, B, and C add up to the third vector. Which is the resultant?
2. Point D lies on the curvy path followed by an object. How would we properly draw the object's V, Vx, and Vy at point D?
- Meet
--
- Discuss the homework.
- Finish the notes -- derivation of the Range Formula
- All Students -- Practice:
- Complete the problems choice section of Mr. Pennington's old Chapter 3 (2-D Kinematics) Test pdf version Solutions Video -- problems 1-3 Video -- problems 4-6
- Gold Only:
- Retake opportunity
- Work time
- Blue: Retakes on Monday and Tuesday
Warm Up: Use the Range Formula to solve the homework problem that I didn't assign.
- Meet
--
- Questions about the homework?
- Finish the projectile's notes -- derivation of the Range Formula
- Brief preview of Mr. Pennington's Ch 3. Test -- discuss what he means by "range."
- All Students -- Practice:
- Complete the multiple choice section of Mr. Pennington's old Chapter 3 (2-D Kinematics) Test pdf version Solutions Video explanations #1-5 Video Explanations #6-19 (and 3 revisited)
- Tomorrow's assignment will be to complete the rest of Mr. Pennington's test.
- Gold Only:
- Retake opportunity
- Work time
 Class
16:
Wednesday
12/9/2020
Class
16:
Wednesday
12/9/2020Warm Up: An airplane flying horizontally with a ground speed of 120 m/s releases a bomb from a height of 4,800 meters. If the bomb is not affected by air resistance, how far ahead of the target (in the x dimension) should the bomb be released? Assume that the bomb is in free-fall once it is released.
- Meet --
- Practice:
- Complete problems #1-4 from Currents and Projectiles -- Notes and Practice Problems Filled-in notes and solutionss Video of Notes from Classs
- If you need help, watch my video... Video help with #3 and #4
- Check your answers. They're provided in this link... Filled-in notes and solutions
- Prepare for the test retake
 Class
15:
Tuesday,
12/8/2020
Class
15:
Tuesday,
12/8/2020Warm Up: Another way to identify the resultant vector... The resultant vector in a "river problem" is the vector that is dependent on all of the other vectors. Any one of the other vectors, if altered, would change the resultant vector. This is not true of the component vectors.
Which of the following is dependent on all of the other vectors -- and is therefore the resultant vector?
--The captain of a blimp is following her compass, keeping the blimp on a Northward heading.
- -A mouse, running across the running surface of
a treadmill on the blimp, is traveling Eastward.
-A mouse, running across the running surface of
a treadmill on the blimp, is traveling Eastward.
--The wind surrounding the blimp is blowing to the Southwest.
--The running surface of the treadmill is traveling Westward.
- All Students -- Google Meet
-
- Return and briefly go over tests;
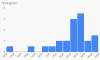
- Grade Distribution --
- Check for grading mistakes. Instead of going over all of the details of the test in class, I have made videos explaining each question or problem. Here are the links...
- Blue and remote retakes will be offered next Monday and Tuesday.
- Would the Gold people like to do their retakes this week (Thurs and Fri) or next week???
- Grade Distribution --
- Discuss recent river problem assignments and talk about your progress. Do you have questions?
- Return and briefly go over tests;
- All Students -- Practice::
- Prepare for the test retake -- In general, each question or problem will have a comparable counterpart (testing the same concept(s)) on the retake. For example, the problems should be solvable with the same formulas, but you may be asked for different variables, and the scenarios will be new. The order will also vary. The extended problem may have parts that use require formulas than the original test..
Warm Up:
No warm-up. No Google Meet. Begin the test right away.
- Blue and Remote:
- Test today
- Remote students join Meet with cameras and mics on. You will either need to print the test or answer on your own paper.
- Homework for Everyone (unless you've already finished it): Complete #5-7 from Still More River Problems. Check your answers and watch the video if you need extra help.
Warm Up:
No warm-up. No Google Meet. Begin the test right away.
- Gold: Test today
- Gold Homework: Same as Blue homework from yesterday (see class #12 for more details)
- Complete "Still more River Problems" #3 and 4 in Combined handout with notes, vector addition practice, and river problems
- 2017 Solutions to Still more river problems -- with tables
- Homework help video
- Blue and Remote Homework:
- Study for Monday's test
- #5-7 from Still More River Problems, due before class on Tuesday.
 Class
12:
Thursday,
12/3/2020
Class
12:
Thursday,
12/3/2020Warm Up: Get your calculators out so that you can help me with this non-orthogonal river problem...
A golf cart on an aircraft carrier is traveling with a velocity of 4m/s in a direction 32 degrees west of North, relative to the Earth. If the aircraft carrier's velocity is 6m/s, in a direction 10 degrees east of North, what are the golf cart's heading and speedometer reading? Video of solution
- Google Meet:
- Discuss the homework
- Does anyone have questions about the test? Would any of the Blue cohort be interested in a question/answer session on Sunday at 5PM? I could record my answers for other students.
- Steps to solve Non-orthogonal (or orthogonal, if you want) river problems...
- Identify the vectors, including the given vectors
and the "unknown" vector (the one you're trying to find).
- Identify the resultant vector (the actual velocity of "the object," relative to the Earth) .
- The other vectors are the component vectors that "add up" to give the resultant.
- Resolve all given vectors into their X and Y components.
- Make a three column table for adding the X and Y components of all of the vectors in the problem (including the unkown). List the component vectors on the top rows and the resultant on the bottom row.
- Solve for the X and Y components of the "unknown" vector (the one you're trying to find).
- On a grid, draw the X and Y components of the unknown vector, head to tail. Then draw the unknown vector itself.
- Use the pythagorean theorem to find the magnitude of the unkown vector.
- Use an inverse trig function, and your diagram, to find the direction of the unknown vector.
- Identify the vectors, including the given vectors
and the "unknown" vector (the one you're trying to find).
- Gold Only: Questions about tomorrow's test?
- Blue and Remote Homework:
- Video from Term 1: Non-orthogonal River problems. You don't have to watch this, but it's here if you want it. I probably covered everything in the video.
- Complete "Still more River Problems" #3 and 4 in Combined handout with notes, vector addition practice, and river problems
- Gold Homework:
- Study for tomorrow's test
 Class
11:
Wednesday,
12/2/2020
Class
11:
Wednesday,
12/2/2020Warm Up:
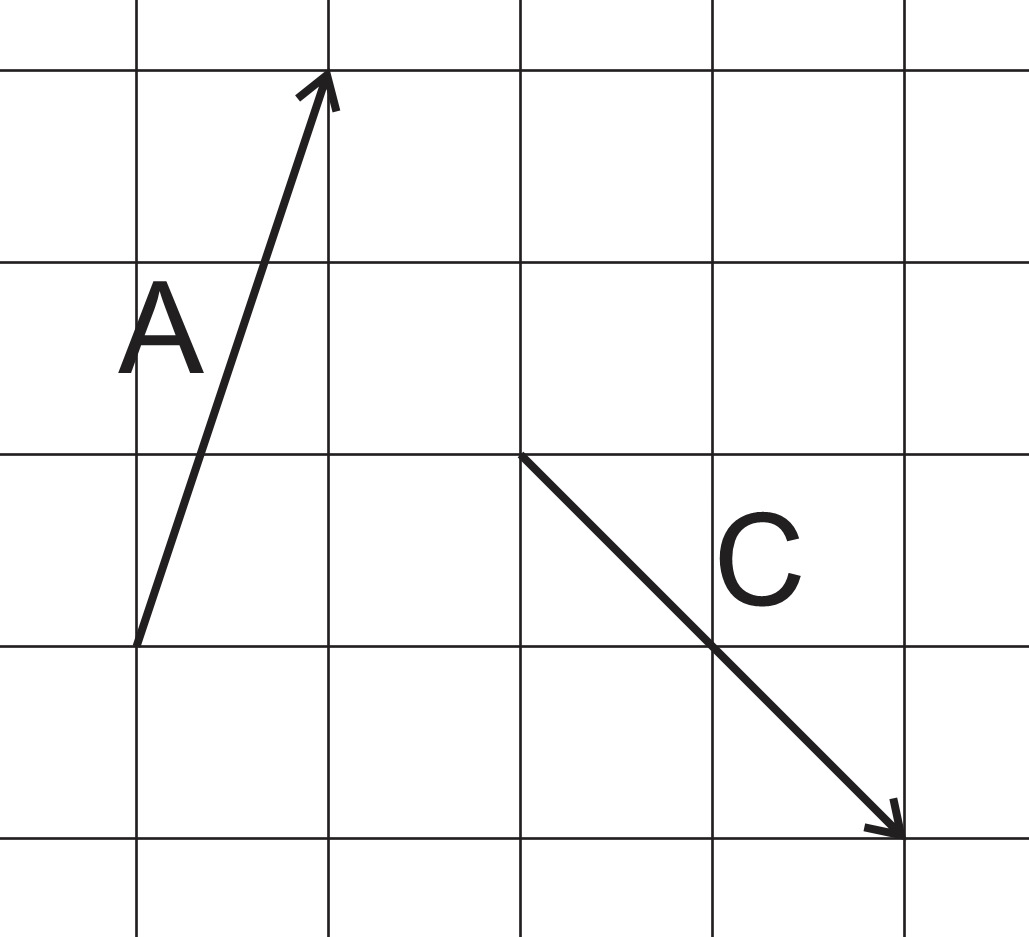
Vector A plus vector B gives the resultant vector C (vector sum). Find the magnitude and direction of vector B.
1) Estimate the answer graphically
2) Find the answer "analytically" (by reducing these vectors to their x and y components).
- Google Meet:
- Discuss the homework
- Introduction to "River Problems"
- "River Problems" Video (from 1st term)
- Homework:
- Complete the Classic River Problem and #2 of "Still More River Problems" -- These are "orthogonal" river problems -- the easier kind
- Solutions: Classic River Problem 2017 Solutions to Still more river problems -- with tables
 ClassClass
10:
Tuesday,
12/1/2020
ClassClass
10:
Tuesday,
12/1/2020Warm Up: Trig Review
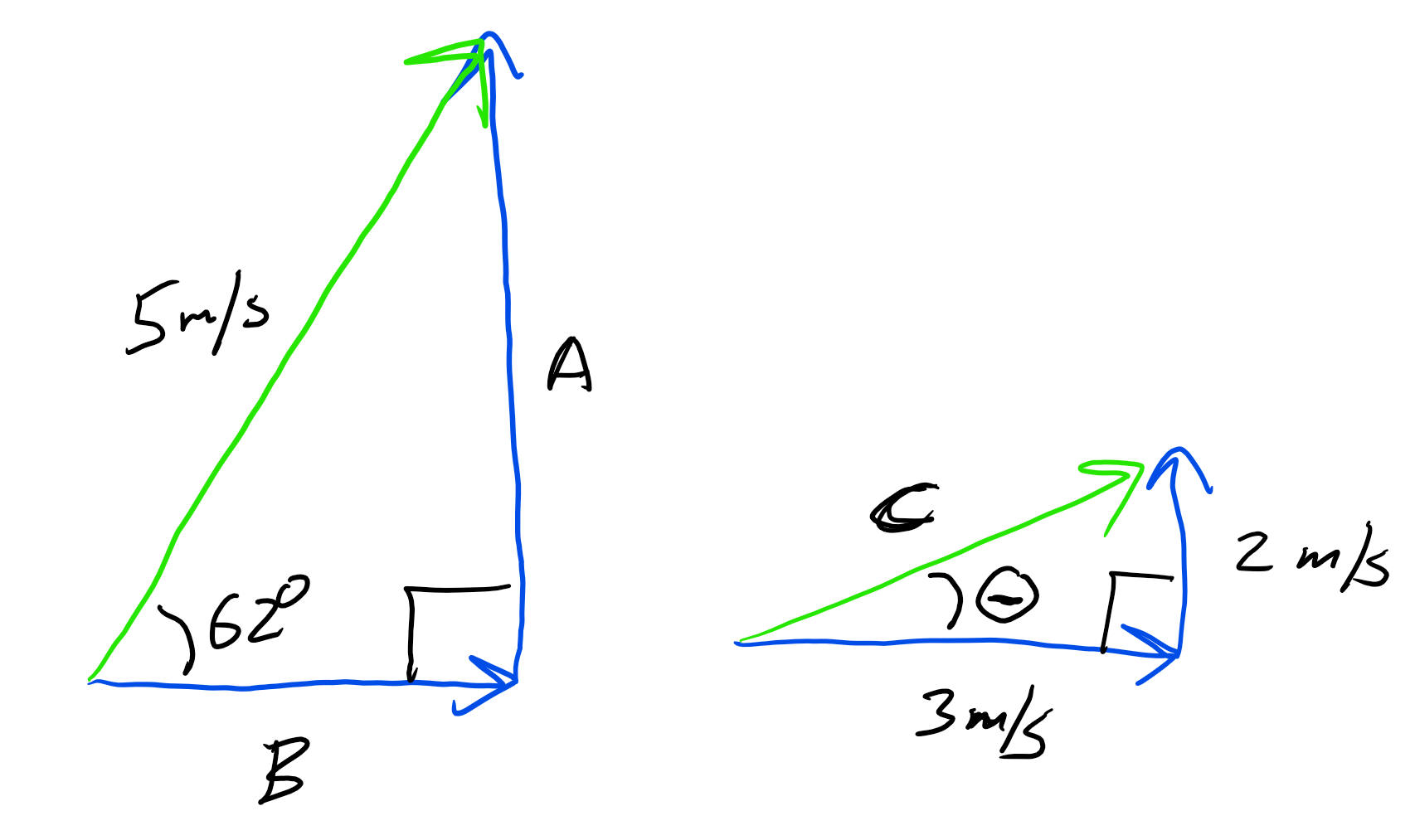
The figures on the right show two right triangles. What are the magnitudes of...
1. Arrow A? 2. Arrow B? 3. Arrow C? 4. Angle theta?
- Google Meet:
- Discuss the homework
- Test format: 45 points total
- 16 multiple choice / short answer -- 1 point each
- 1 unit conversion -- 2 points
- 4 Problems -- 4 points each
- Extended Problem -- 5 parts, worth 2 points each
- Bonus (optional) -- one point if correct
- 1.5 points for opting out of the formula sheet.
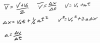 Here's a
Quizlet that you can use to memorize the formulas
Here's a
Quizlet that you can use to memorize the formulas
- Test Schedule: (No warm-ups on
these days. Just a short bit of teaching and a short
assignment.)
- Gold Test -- Friday
- Blue and Remote Test -- Monday
- Begin new unit (Kinematics in
2-dimensions)
- Unit 2 Packet (Word version; pdf version)
-
Notes:
- Mr. Pennington's 2-D Kinematics Notes
- Head-to-tail Vector addition (last year's warm-up) -- the relationship between the components and resultant. Adding vs. resolving.

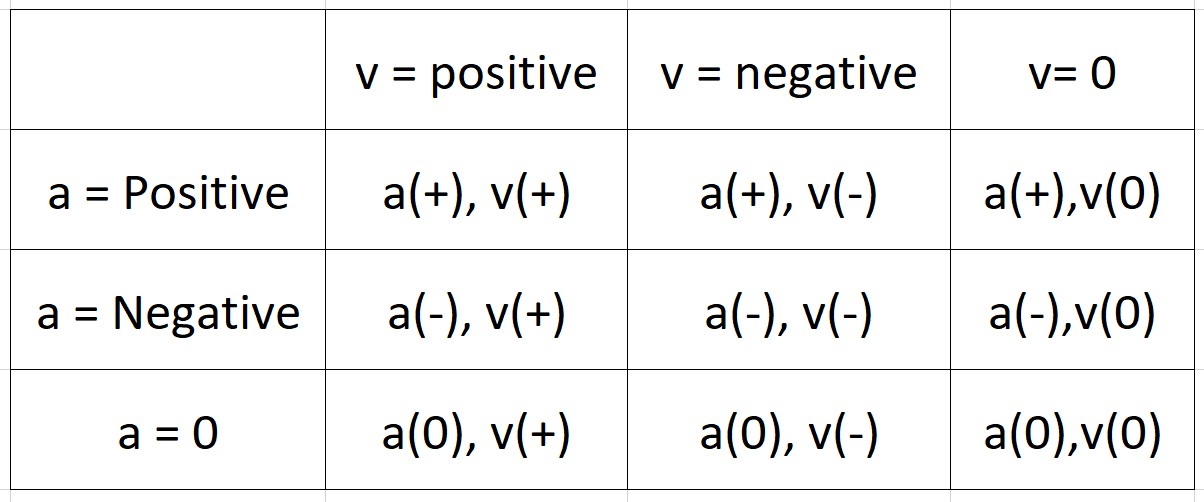 Class
9:
Monday,
11/30/2020
Class
9:
Monday,
11/30/2020Warm Up: Mr. Chase suggested a way to separate motion into 9 categories, based on an object's velocity and acceleration. This categorization is based on the fact that Velocity can be +, -, or 0, and acceleration can also be +, -, or 0.
Considering the motion of a swinging pendulum in the x dimension...
1. Identify where in the video each of those 8 types of motion occurs.
2. Which type of motion is not demonstrated?
- Google Meet:
- Discuss the homework.
- Homework:
- #57 and #60 from "More Kinematics Problems". These are like short extended problems that don't tell you what to do first. In that way they're harder than what you will see on the test. But they're good practice for developing your understanding. Do the others if you want more practice. Solutions Video explaining my solutions
- Review for the test. Look over all of our notes and assignments. Email Mr. Stapleton if you have specific topics that you would like him to prepare to discuss/reteach tomorrow.
- More Optional
Practice -- this was requested by a few students during term 1:
- More
practice creating graphs for events
- Blank PDF Handout -- "Extra Graphing Practice"
- Solutions(**On my graph of position vs time for the soccer ball kick, my graph should really have started and ended at the same position.)
- Video of me working through these and creating solutions
- More practice with simple (one formula required) kinematics problems. Make your own copy and expand column D to see the answers.
- More
practice creating graphs for events
- In-Person Only:
- Mr. Stapleton slideshow ?
 Class
8
Friday,
11/20/2020
Class
8
Friday,
11/20/2020Warm Up:
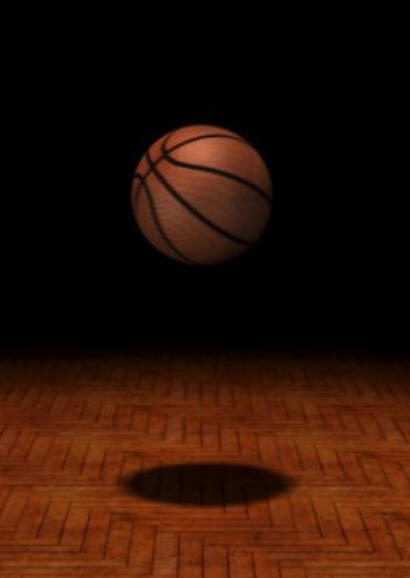
Sketch motion graphs for a basketball that is dropped (starting from rest) onto a gym floor and allowed to bounce back up to the point where its velocity is zero. Create graphs for position, velocity, and acceleration vs. time.
*For the acceleration graph, try to at least get the sign correct.
- Google Meet:
- Discuss the homework. Questions?
- Look ahead at the next few classes.
- Practice:
- P. 21-24 of the packet --1-D
Kinematics Practice Test #2
- Solutions except for conceptual #5 and problem #5 solutions to #5 and #5
- Video Help part 1 (it's unfortunately sideways, but it's short)
- Video Help part 2 (starts with #4, I think)
- P. 21-24 of the packet --1-D
Kinematics Practice Test #2
Warm Up: I never completed Example 2, from the Class 5 notes. Let's do it now...
Helpful hints: 1) Draw a diagram, 2) Identify "separate events" (intervals with different accelerations and/or starting points and endpoints) 3) List commonly-used variables,

- Google Meet
--
- Discuss the first test -- would you like it to be spread out over 2 days so that we can remain mostly synchronous? Or would you rather go asynchronous for a few days, and use a whole block for the whole test?
- Questions about the homework? -- Mr. Pennington's test problems
- Discuss Extended problems -- give some tips -- draw a diagram and label some stuff
- All Students -- Practice:
 Class
6 Wednesday,
11/18/2020
Class
6 Wednesday,
11/18/2020Warm Up:
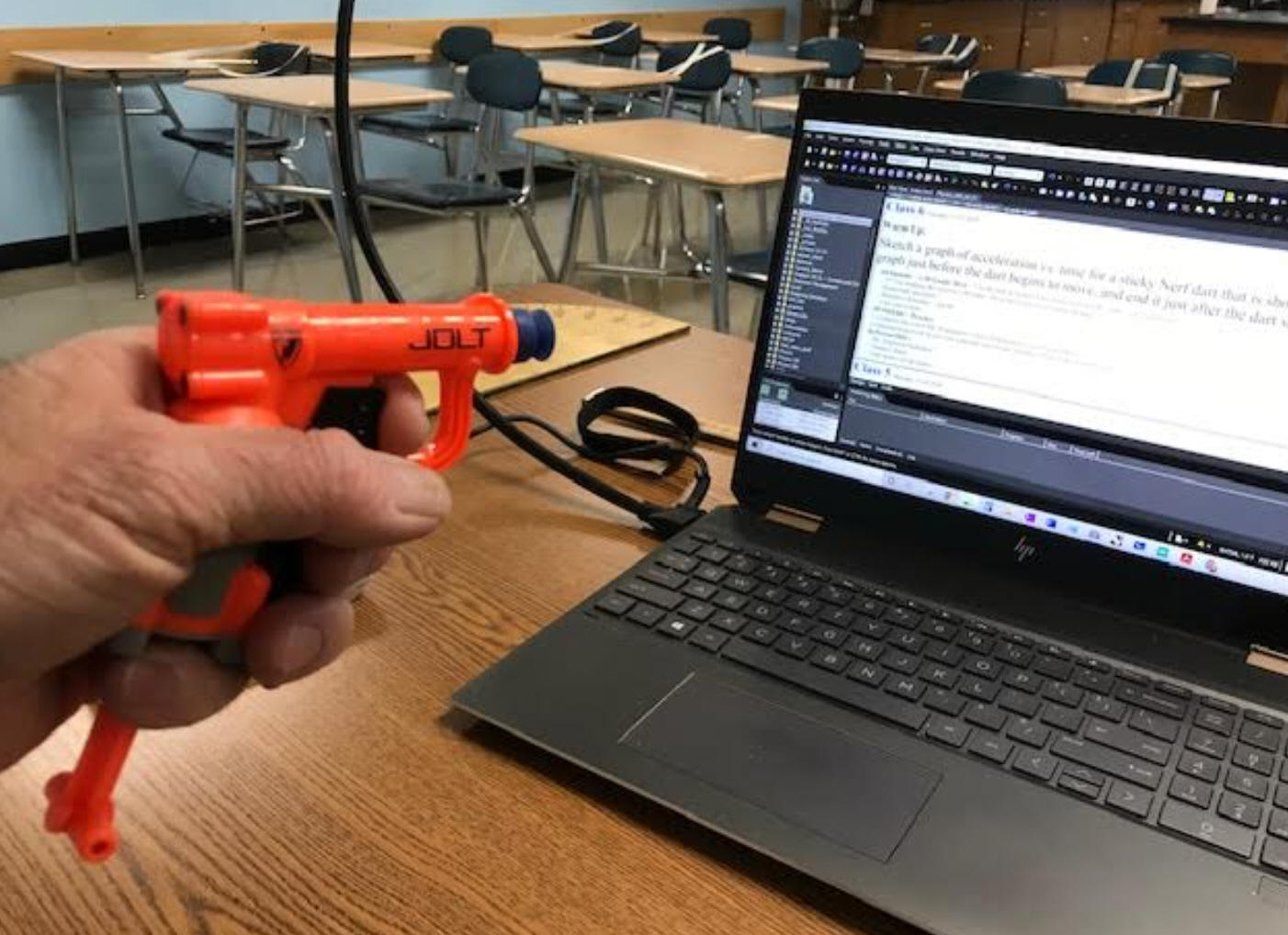
Sketch a graph of acceleration vs. time for a suction cup Nerf dart that is shot at a wall. Start your graph just before the dart begins to move, and end it just after the dart stops.
Today:
- Google Meet
- A note about "due date" in Google Classroom.
- Discuss the homework
- Optional: Memorize kinematics formulas for extra points on the test. You can use this Quizlet.
- Video this, because I didn't do it on this day during Term 1 -- Unit conversions (by multiplying by 1) -- example -- convert 4mph to m/s. Use dimensional analysis
- Practice:
- Complete the rest of Mr. Pennington's Old 1-D Kinematics Test Answer Key. video help
- Optional homework in case you want unit conversions practice -- Unit Conversions Practice
 Class
5 Tuesday,
11/17/2020
Class
5 Tuesday,
11/17/2020Warm Up: In the physics world, an object is in "free-fall" as long as gravity is the only force acting on that object. The object may free-fall upward or downward. Near the Earth's surface, the acceleration of free-falling objects due to gravity is approximately -9.8m/s2.
Consider this scenario... At t = 0s, a ball is free-falling directly upward with a speed of 20m/s. Sketch graphs of the ball's position, velocity, and acceleration (vs. time) over the next 4 seconds. [For simplicity, use g =10m/s2 instead of g = 9.8m/s2]
Today:
- Google Meet starts around 1:25 -- Use the link in Google Classroom (or watch the video -- class playlist).
- Practice: Complete the Multiple Choice Section Only of Mr. Pennington's Old 1-D Kinematics Test Answer Key. If you have questions, watch this Video for Help
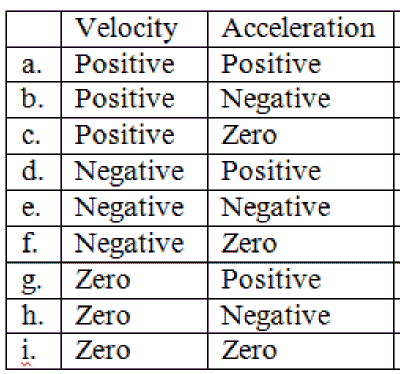 Class
4
Monday, 11/16/2020
Class
4
Monday, 11/16/2020Warm Up:
1. For letter a, on the right describe what an object could be doing in order to have both positive velocity and positive acceleration.
2. Do the same for the rest of the letters.
3. Can you state a general rule (or some rules) for determining whether the object is speeding up or slowing down in this exercise? (i.e. speed increasing vs. speed decreasing)
Today:
- Google Meet
- Note -- Google Meets will start around 1:25 from now on.
- Review/Discuss the homework
- Preview the practice test
- Notes: Intro to Kinematics Formulas Answer Key -- Kinematics Formulas and Practice Problems
- Practice:
- Finish the problems in Notes: Intro to Kinematics Formulas Answer Key -- Kinematics Formulas and Practice Problems
- In case you're insterested here's a derivation of the basic displacement formula for constant acceleration
- Mark this assignment complete in Google Classroom!
Warm Up:
A ball is thrown at the floor from a height of 4m.
It hits the floor and bounces back up to a height of 6m, where it
is caught. Assuming that the
entire round trip takes 2 seconds…
1. What is the total distance traveled by the ball on its round trip?
2.
3.
What is the ball's average velocity for this round trip?
4. What is the ball's average speed for this round trip?
Google Meet -- Use the link in Google Classroom (or watch the recording later on the class YouTube channel). Just in case I mess up today's video, here's a video of the same notes from 2017.
- Review/Discuss the homework
- Complete Acceleration Notes -- Answer Key
Homework:
- Complete Graph Comparisons [p.7 & 8 of the Unit 1 Handout] Graph Comparisons solutions Extra Video Help
- Mark this assignment complete in Google Classroom!
.JPG) Class
2:
Thursday,
11/12/2020
Class
2:
Thursday,
11/12/2020Warm Up:
1. For each letter, describe what is happening to the person's speed and direction during the 10 seconds represented on the graph.
2. Does anyone have a theory regarding why the moon is brightest on each end of the blur (in the photo from last class)? Or did you click the link?
Today:
Google Meet -- Use the link in Google Classroom
- Warm-up
- Discuss "video on" vs "video off."
- Discuss homework. Ask questions if you have questions!
- Notes: Work through 1-D Kinematics notes. Here is a filled-in version: 1-D Kinematics notes Answer Key
- More from the Physics 200 (Stapleton) Course Syllabus
Homework:
- Complete #5-8 [p.5 of the Unit 1 Handout] in 1-D Kinematics notes 1-D Kinematics notes Answer Key
- Mark this assignment complete in Google Classroom!
 Class
1: Wednesday,
11/11/2020
Class
1: Wednesday,
11/11/2020Physics 200: Mr. Stapleton
Warm Up:
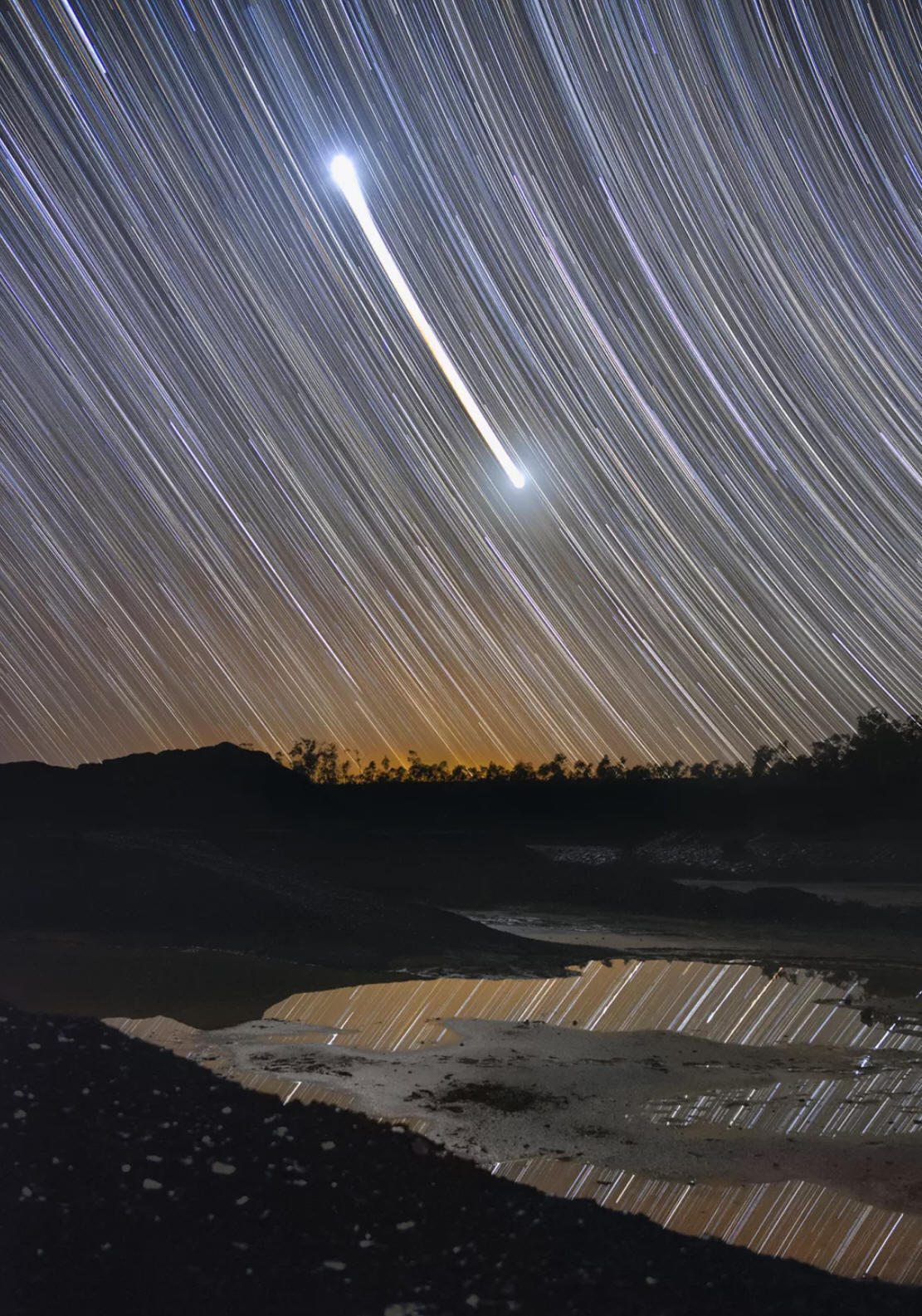
1. How were the photos on the right created?
2. Suppose you attach a flashlight to a bicycle tire, as shown in the diagram. Then you ride the bicycle in complete darkness while some one takes a long exposure photo. What pattern will the flashlight make in the photo? Why?
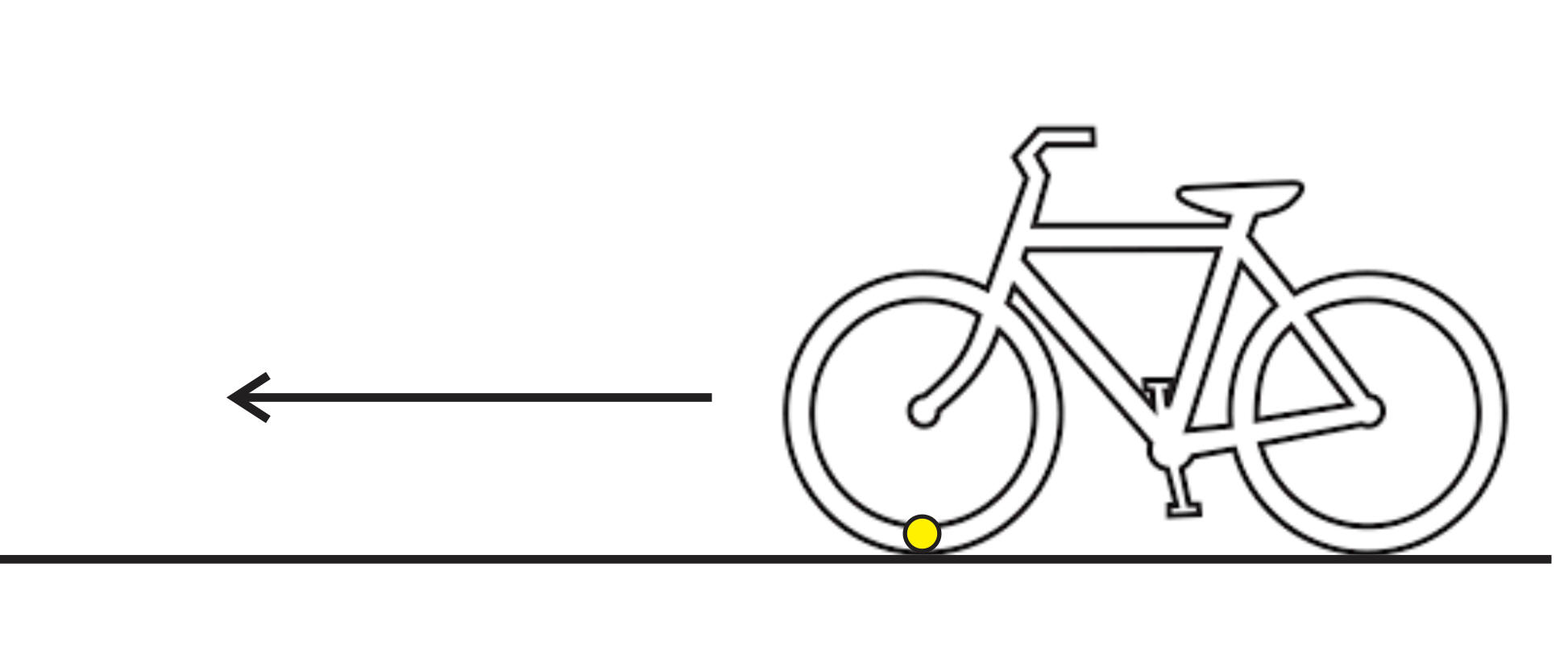
Today:
All Students -- 11:00 Google Meet -- Use the link in Google Classroom
- Warm-up
- Important things you need to know --
Highlights from the
Physics 200 (Stapleton) Course Syllabus
- Class logistics (how to find out
what you're supposed to do and when you're supposed to
do it)
- Google Classroom
- Class website
- Grading
- Google Classroom -- how to get credit for assignments
- Class logistics (how to find out
what you're supposed to do and when you're supposed to
do it)
- Motion matching interactive demo
- All Students -- Practice:
- Finish the motion matching questions at the end of 1-D Kinematics notes [p.6 of the Unit 1 Handout] Here is the answer key. 1-D Kinematics notes Answer Key And here is a video explaining the answers.
- Mark this assignment complete in Google Classroom!
- Handouts for Unit 1